Properties and characteristics
Aspen belongs to the extensive genus of poplars, the willow family. According to the structure of the trunk, this is a coreless, diffusely woody tree species. In Russia, this tree is found everywhere in the European and Asian parts of the country, from deciduous forests of mid-latitudes to tundra zones.
This tree grows up to 150 years, but the cause of its death is often not age, but rot that affects the core of the trunk, so trees between 30 and 50 years old are usually chosen for industrial felling. During this time, the tree reaches a height of 35-40 meters.
Aspen wood is dense, with poorly visible growth rings, and uniform in structure. The moisture content of the wood in the central part is lower than in the peripheral areas of the trunk. The color of the wood is white, grayish-white, sometimes greenish. In the cut, it is impossible to notice the rays emanating from the center. For some decorative work, such wood is valuable precisely because of its uniformity. After staining or painting, the structure of the wood remains uniform and does not reveal any structural elements.
The moisture content of a freshly cut tree is about 82%, while the maximum moisture content of this wood (when soaked) reaches 185%. With high atmospheric humidity, aspen quickly absorbs water, but also quickly loses it when drying, which is a positive quality.
In terms of resistance to biological factors, wood belongs to the lowest, fifth class (according to the ISO EN 350-3:1994 standard).
There are a total of five classes in the above standard. The first class of resistance includes, for example, Indian teak and Australian eucalyptus. Larch and oak are classified as class 2 in terms of wood stability. In Russia, the resistance of a tree to the effects of fungi and mold is determined in dimensionless conventional units. According to the Russian classification, resistance to fungi is 1.2 units for mature wood, and 1 for aspen sapwood.
Advantages of the material
Construction using wood has its advantages and disadvantages. The main advantages when choosing such material will be:
- Environmental friendliness. The most compelling argument in favor of wood is environmental friendliness. Some modern materials can emit fumes of heavy metals and other chemical elements, which will adversely affect the health of home residents.
- Maintainability. Parts made from wood will be fairly easy to repair if they break or wear out.
- Strength and resistance to many external factors, which makes the service life of wood products long. When properly processed, this material will serve without fail for many years.
- Ease of processing.
- Poor thermal conductivity.
- Good sound insulation properties.
This material is highly flammable
. Quite an extensive list. However, there are a small number of disadvantages:
- The properties of the material strongly depend on the conditions in which the tree grew. Because of this, it can be difficult to choose a quality copy.
- Changes in size due to exposure to humidity and dryness. But this shortcoming can be easily corrected by processing.
- Highly flammable.
The high cost associated with the difficulty of obtaining high-quality wood cannot be ignored.
Industrial felling of aspen
The international standard for industrial wood is called DIN 4076. Aspen wood belongs to group AS.
In Russia, industrial cutting of trees is carried out in wild forest plots, which are then restored naturally. In Western Europe, in recent decades, trees for industrial felling have increasingly been grown in nurseries. These are the so-called short-cycle forest nurseries. They grow primarily fast-growing tree species (poplar, aspen). This approach to environmental management makes it possible to preserve natural forests and grow wood of the required parameters.
Pine as a building material
Pine is a soft coniferous tree, from which it is very easy to make rounded timber . It is the most popular because this wood species is easy to work with even for novice builders. However, the wood has a small number of knots, which begin to resin at high temperatures.
When cut, the core has a pink tint, which darkens and becomes brown over time. It has wide sapwood and clearly visible growth rings.
The advantages of pine over other species are as follows:
- High strength.
- Ease of processing.
- Moisture permeability.
Disadvantages include resin release at high temperatures and "blue" discoloration. The latter phenomenon is associated with a change in color on the saw blade. This phenomenon does not affect the strength of the log in any way, and it can be dealt with by treating it with special antiseptic solutions.
Features of wood processing
If you look at an aspen trunk in a cross cut, you can see that the wood has a nuclear-free structure. In general, the wood is soft compared to other deciduous trees, its density is 400-500 kilograms per cubic meter (with a humidity not exceeding 15%).
Aspen timber, like other lumber, is capable of absorbing large amounts of water, both in the atmospheric air and under water, which is a negative characteristic of this wood. Aspen wood dries slowly, over several months; when dried, it practically does not crack and does not change its original shape (does not warp). Dried wood splits easily in the longitudinal direction. In the outer part of the trunk, the wood has a high density, so wear rates during operation of aspen products are high.
The humidity in the central part of the tree trunk is much lower than in the peripheral areas. Lumber manufacturers take this feature into account when organizing the drying of timber and round timber.
This wood can be easily processed with mechanical and sharp hand tools, it is easy to saw and cut, it is easy to peel, split and mill. It is easier to process wet, not completely dry wood. When polishing wood, it is not easy to achieve a good smooth surface, although it is uniform and there are no obvious annual rings or knots in the wood. Aspen takes well to impregnation and staining. Dried wood is not difficult to glue; it can be used to make furniture, the parts of which are connected using screws or nails.
Varnishes for lining
Varnishes are divided according to the substance that makes up the base:
- Acrylic;
- Polyurethane;
- Acrylic-polyurethane;
- Alkyd;
- Water-based.
Acrylic varnishes are universal. Will not allow dirt to concentrate on the surface. Dries quickly. Negative property - they begin to emit a specific odor when heated.
Varnishes containing polyurethane are suitable for treating indoor and outdoor surfaces. There are translucent compositions and darker ones - tinting. Lacquered panels will not turn yellow.
A combination varnish containing both acrylic and polyurethane gives some shine to the coated products. Protects against fungal colonies and mold.
Alkyd compounds will protect the wood from moisture. The negative property is the long drying time and unpleasant odor, so the room will have to be ventilated for several hours. Complete drying is guaranteed after two days.
Water-based varnishes are almost completely odorless, dry very quickly, and most importantly, there is no harm to health. In addition, water-based varnishes do not support combustion and do not emit harmful substances when heated.
If desired, you can use compounds and waxes - you can buy them or prepare them yourself.
When purchasing any varnishes and paints for residential premises, you should carefully read the instructions on the can. There must be a note stating that the composition is allowed to be used inside houses and apartments. If necessary, it is better to consult the seller.
In most cases, the surfaces will have to be primed before varnishing.
A number of craftsmen prefer to use factory-made varnishes and impregnations based on oil and wax. They penetrate deep into the pores of the wood, flow into all microcracks, and provide protection from moisture and mechanical stress.
For example, alkyd-oil solutions have a beneficial effect on the properties of aspen lining, protecting it from cracks and deformation. It is believed that treating wood with impregnations and varnishes can extend the life of products by 3-4 times.
Varnishes are applied in accordance with the rules:
- On dry and clean surfaces;
- After applying the primer;
- The ends are painted first;
- Temperature not lower than +5 degrees;
- Humidity not less than 70%.
An antiseptic is applied before varnishes. In addition to a brush and roller, you can use a spray bottle; with good skill, you will get the most even surface without defects.
For the dressing room or kitchen, water-based or wax varnishes are suitable.
In some cases, aspen lining is coated with special fire retardant compounds. There are combined mixtures: fire protection + antiseptic.
When finishing wood products, common mistakes occur. Firstly, the use of cheap products from the Chinese chemical industry, which can cause harm. It is not recommended to purchase varnishes, paints, impregnations and primers in markets without the appropriate certificates.
Secondly, the type of impregnation/primer does not match the finishing varnish or type of paint. Otherwise, high-quality coverage will not be achieved.
Use of aspen in industry
The main consumers of aspen are the construction industry. Various lumber is produced from it: round timber, timber, boards, particle board, fiberboard, peeled veneer. Bathroom equipment is made from timber, for example, benches, ladders, shelves, grates and pallets. Aspen slats are used to produce packaging boxes and containers for storing and transporting goods. Until recently, before the advent of computer technology, drawing drawing boards were made from dense white aspen.
The shavings are a by-product of production and are used as fuel for thermal power plants, as well as insulation in rural and country construction. Wood shavings used for combustion at thermal power plants are considered an environmentally friendly material, and wood is a renewable natural resource. For heating private houses, chopped wood, scraps from production, and fuel pellets are used.
Aspen wood is a raw material for the production of cardboard and paper. In the shoe industry, crushed aspen shavings are used as a material that absorbs moisture well. Peeled aspen veneer is used to make plain and laminated plywood, matches, and toothpicks. It is used to make caskets, baskets, gift boxes and packaging. Sliced veneer is used for the manufacture of various household items. Bent, shaped parts of furniture and decorative boxes are made from thin aspen plywood.
When burned without access to air, aspen produces charcoal of good quality. It is used in the chemical industry and for artistic works.
Aspen and lumber made from it
Aspen and lumber made from it
Aspen boards and beams are quite rare on the lumber market today. This tree has been undeservedly forgotten by woodworkers, but in vain. Aspen wood has a number of technical and consumer advantages that are not inherent in every hardwood species. It is not for nothing that in the old days it was one of the main building materials - aspen was used to make well log houses, bathhouses, cellars, and peeled shingles for roofs. In addition, various utensils were cut out of it - buckets, ladles, troughs. All this speaks, first of all, about such an irreplaceable quality of wood as high water resistance. Aspen was used to make hammer handles, ax handles, and handles for various garden tools, which means that the wood is highly durable. Now woodworkers have begun to pay more attention to this species and are increasingly using it to produce lumber for various purposes.
Biological features and geography of growth
Common aspen is a deciduous tree belonging to the Willow family, Poplar genus. Aspen is often called “trembling poplar” - this is how the Latin name of this plant (Populus tremula) is translated.
Aspen is a tall, large tree; its height can reach 35 meters, and its trunk diameter is 1 meter. Trembling poplar grows relatively quickly and lives relatively short - the age of the oldest specimens reaches 80-90 years. The main disadvantage of this species is that the wood is often infected with various fungal diseases, so high-quality large-sized sawlogs are very rare.
The root system of the tree is powerful, located deep, forming root shoots of great length. Young trees have smooth bark, and its color can vary from greenish-gray to light green. With age, closer to the base (butt), the bark cracks and darkens.
The leaf arrangement of aspen is alternate, the leaves are characterized by a round or rhombic shape, their length is 3-7 cm. In young shoots, the leaves can be much larger, up to 15 cm long. In autumn, the foliage acquires different bright shades - from golden to bright red.
Aspen blooms before the leaves bloom into earrings containing many small flowers. This tree is dioecious, male catkins are reddish, female catkins are greenish. The fruit is a very small capsule containing seeds equipped with a tuft of hairs.
Aspen is an important forest-forming species in Russia; this tree is found throughout the country, most often in the steppe and forest-steppe zones. It also grows on the border of the taiga and tundra.
This breed “loves” soils with high humidity; the tree feels great on the banks of reservoirs, near swamps. Often found in forests, ravines, less often on dry sands and in mountainous areas. Aspen is part of mixed forests, where it grows adjacent to coniferous species (pine, spruce, larch) and deciduous species such as birch, oak, and alder. It is found throughout Russia and Europe, and also grows in Mongolia, China, Kazakhstan, and the Korean Peninsula.
Physical and technical indicators and appearance
The structure of the wood structure of aspen is of the coreless, scattered-vascular type. The color of the wood is whitish, often with a slightly greenish tint. The texture is not particularly impressive or particularly expressive. Heart-shaped rays and growth rings are poorly visible here, so the wood pattern, unlike other hardwoods, looks rustic - aspen products are practically not used for decorative purposes.
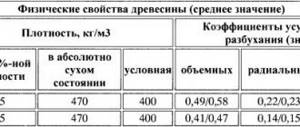
The structure of the wood is uniform; there are usually about 5.5 growth rings per square centimeter (if you look at the cut). The density of aspen with 12 percent humidity is within 495 kg/m2.
This material is quite soft, and in terms of strength it is very close to linden. The mechanical properties of aspen lumber are approximately as follows:
- Static bending strength - 76.5 MPa
- Compression limit along the fibers – 43.1 MPa
- Tensile limit – 121 MPa
- Impact strength – 84.6 kJ/m2
- End hardness – 25.8 N/kV.mm
- Tangential hardness – 19.6 N/kV.mm
- Radial hardness – 18.7 N/kV.mm
- Percentage of radial shrinkage - 2.7%
- Density – 495 kg/m2.
With an average moisture content of a freshly cut trunk of 82 percent, aspen does not dry out too much. Based on the drying coefficient, it can be classified as a medium drying rock. In terms of load resistance, aspen can be compared with spruce and pine; it bends well and does not lose its strength characteristics with prolonged application of force. At the same time, the wood is highly resistant to abrasion and lends itself well to cutting and turning. Its structure is homogeneous, due to which, in the production of lumber, it is possible to saw workpieces in different directions, at different angles. In this case, a small number of knots get into the products.
Having assessed the above figures, we can conclude that builders are wrong to treat lumber from this species with distrust. Apparently, this is explained by the fact that the tree often grows in wetlands and is susceptible to fungal diseases. In this case, infection occurs precisely from the core, which makes the infected sawlog unsuitable as a raw material for production. But, if the round timber is prepared of high quality, then it can adequately compete with coniferous raw materials.
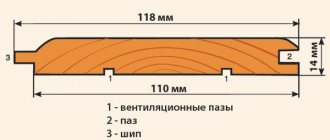
Aspen cannot be called a unique tree; it is a good average among competitors that deserves to be used. It is most often used to make timber and edged boards intended for special purposes. Baths/saunas are built from aspen timber. Edged boards, floor tongues, and various small moldings (plinths, platbands, fillets) are made from this wood.
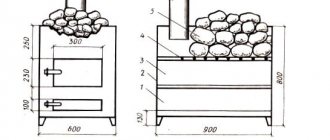
Aspen baths
One of the main positive qualities of aspen wood is its ability to withstand high humidity, even without any special treatments. Therefore, you cannot find a better tree for building a bathhouse or sauna (at least in terms of practicality and price). For the installation of the log house, aspen timber is used, while the interior finishing is carried out using aspen edged boards. All kinds of bath utensils are also made from this wood - barrels for cold water, containers for steaming brooms, ladles, chairs, hangers, etc.
A bathhouse made of aspen will keep heat perfectly. In addition, in this case, one cannot fail to take into account such a feature of aspen wood as the ability to have a bactericidal effect due to the content of a large amount of tannins and aromatic essential oils. It is believed that the substances released when this wood is heated have a pronounced antitussive, anti-inflammatory and choleretic effect.
An important point is the low cost of timber and boards, so building a bathhouse from aspen will cost very little.
Houses made of aspen timber
Aspen is widespread throughout Russia; lumber made from it is inexpensive and easy to process. However, aspen timber is used very rarely for the construction of houses. This is explained by two reasons:
- It is quite difficult to find the required amount of high-quality timber, since the tree is still susceptible to fungal diseases during the growth process;
- The natural moisture content of aspen wood is high, therefore, if insufficiently dried lumber is used for construction, cracks may form in the supporting structures during the drying process and the geometry may change.
In addition, in certain circles there is a strong opinion that aspen has negative energy - this may scare some people away from using it as a material for construction and decoration.
How is aspen edged board used?
In addition to finishing baths and saunas, edged aspen boards, due to their increased moisture resistance, are often used for arranging various outdoor buildings. It is used to make floors in open verandas and gazebos, and to lay garden paths in the form of wooden paving stones. Aspen lumber is also used to make various outdoor furniture and decorative buildings. Benches, tables are made from it, and used as finishing for well covers. They say that a better material than aspen timber cannot be found for constructing a well frame. After all, even in ancient times it was noticed that it is in such wells that the water always remains clean and fresh.
Thick boards are suitable for assembling frame walls and interior partitions. Aspen edged boards can be used to install sheathing when arranging a rafter system. Dry products are suitable for the manufacture of furniture elements and stairs.
Industrial processing of aspen wood
Aspen is an accessible and inexpensive raw material, and its wood lends itself well to various types of mechanical processing (cutting, peeling, sawing, planing). Therefore, this material is widely used for the manufacture of matches, paper, cardboard, containers of various shapes and purposes.
In match production, aspen wood is especially highly valued due to its ease of processing. Considering that aspen easily peels into veneer, it is sometimes also used in the manufacture of plywood sheets.
Aspen wood is distinguished by its natural white color and sufficient fiber length, which makes it an excellent raw material for the production of paper and cardboard. The wood of this species does not contain resins, which makes it possible to make barrels and boxes from it.
Aspen lumber TU
As already noted, aspen wood, especially sawlogs of large age and diameter, is often infected with rot. Therefore, when sawing logs into lumber, a lot of unprofitable wood remains, and this significantly increases the price of lumber.
Any product made of wood, as is known, must be manufactured in accordance with the indicators specified in state standards (GOSTs) - this applies to size, grade, geometry, etc. Considering the characteristics of aspen wood, doing this without increasing costs is very problematic. In order to reduce costs and the price of lumber, each lumber manufacturer, depending on the capabilities of its existing equipment, develops its own technical specifications - technical specifications. Such documents make it possible to produce products that differ in size from GOST requirements. The main task of the technical specifications is to reduce the amount of non-commercial wood and increase the production of usable lumber, which is especially important in the case of aspen wood. The developed technical conditions allow the manufacturer to reduce the price of products.
Each buyer, in addition, has the opportunity to order lumber at the enterprise according to individual sizes, which will allow him to reduce the cost of installing individual structures and reduce waste to a minimum. As we can see, the main difference between GOST and TU is the ability to satisfy to the maximum the needs of the consumer, who needs to have the required number of high-quality piece products, while the “standard” dimensions are not important for him.
Pros and cons of aspen wood
From all of the above, it becomes clear that the characteristics of aspen wood are far from clear. For example, it is characterized by increased resistance to humidity, but is often affected by fungal diseases.
This material has few disadvantages, but they are a fundamental factor when choosing:
- it is very difficult to find high-quality lumber in the required quantities, especially when you need a lot of it;
- The high natural humidity of aspen wood leads, if the products are not dried correctly, to warping, cracking and changes in the geometric shape of structures.
Let us highlight the main advantages of aspen as a building material:
- decent moisture resistance;
- good thermal insulation abilities;
- ease of processing and installation combined with strength and elasticity;
- the absence of resins in wood and high moisture resistance makes aspen an ideal material for baths and saunas;
- When processing aspen wood, the cutting residue of the tools does not become dull and does not require constant cleaning.
Some consider aspen wood to be very beautiful, while others, on the contrary, say that it looks rustic and is not suitable for design. Well, this, as they say, is a matter of taste. In this case, each consumer has a choice and the opportunity to purchase what he likes and is suitable for each specific purpose.