A reliable roof protects the building from bad weather and hot sun. Naturally, the bathhouse should also have a roof - a good-quality and practical one, built in accordance with all the rules of construction. What type of roof to choose, what materials to pay attention to, what are the main stages of construction - this is what will be discussed in our material. The purpose of this article is to give you simple instructions for building a roof for a bathhouse with your own hands.
The roof is the upper part of the building, insulating, enclosing and protecting it from the adverse effects of precipitation, wind and ultraviolet radiation.
Roofing materials for baths: choosing the best
The bathhouse is a rather complex structure with a lot of features and nuances in its structure. In order for the bathhouse to function well and not malfunction, you need to put a lot of effort into the process of its construction.
So, even at the design stage, one of the most important questions arises - how to cover the roof of the bathhouse?
The modern market offers the consumer a lot of different roofing options for bathhouses: soft and hard, roll and sheet, for every taste and color. It’s quite easy to make a mistake here, since each manufacturer claims that its material is the safest, most durable and of the highest quality.
In order to soberly evaluate all the advantages and disadvantages of each coating, we will analyze them in order and choose the best one.
Next, we’ll find out which roof is best for a bathhouse.
What to choose?
Which roof is best for a bathhouse? It is impossible to give an exact answer to this question, since the choice of a specific design depends on many factors. Most often, the roofing system is gable, which is traditional and modern, and its installation is quite simple. But some people prefer to build multi-slope structures, which look more attractive and original. This decision is made especially often if the bathhouse is built with an attic.
The roof of the bathhouse can have an attic or be built without it. In the first case, installation of ceilings for the under-roof space will be required. In the second case, that is, without an attic, the roof and ceiling of the bathhouse are combined, the roof itself is left pitched. On the one hand, the attic space creates a more aesthetic appearance of the entire structure, and more effective thermal insulation is provided. On the other hand, when constructing a country bathhouse that is used only in the summer, an attic space is not needed.
Main selection criteria
Before you evaluate the quality of the main roofing materials, you need to decide which types are suitable specifically for your bathhouse. The assessment must be based on the following factors:
- Amount of precipitation in the construction area;
- The type of roof structure, as well as its angle of inclination;
- The material with which the remaining roofs on the site are covered.
For the most part, the design of the roof of the bathhouse is not complicated and is either single-pitch or gable. It is better to entrust more complex structures to professionals, since without certain skills it is almost impossible to complete the roof of a complex roof.
Important! To cover the roof with a rigid roof, sheathing must be installed. In turn, rolled soft roofing should be laid in a continuous layer on boards or plywood sheets.
When choosing the type of structure for a bathhouse roof, you must be guided by the following criteria:
- If the bathhouse is separate, it is better to install a roof with two slopes. If the bathhouse is an extension - with one. The angle of inclination should not exceed 65 degrees and be at least 45;
- For a bathhouse with an area of more than 12 m2, a gable roof is suitable, for smaller ones - a single-slope one;
- If precipitation in the construction area is heavy, then the roof must be at least 45 degrees, otherwise precipitation will accumulate on the roof, which can lead to damage to the roof;
- If strong winds prevail in the construction area, then the angle of inclination should be less than 40 degrees. This way, the wind will not affect the roof as much.
How to make and install rafters
If the bathhouse design assumes the presence of an internal load-bearing partition, then a layered rafter structure is used. It consists of a mauerlat, vertical posts, a ridge girder and rafters. On standard buildings with load-bearing external walls, a more complex hanging system is used, like making rafters for a bathhouse.
How to properly install rafters on a bathhouse with your own hands:
- The load-bearing walls along the upper end are formed with a support beam and a beam. To secure them, you will need long metal studs or anchor bolts.
- Installing racks on top of the bed. To give them a vertical position during installation, special supports are used.
- Laying on ridge girder posts. During this procedure, you need to constantly check the building level.
- Installation of rafters. The installation step is 60-120 cm, which makes laying the insulation more convenient. To fix the rafters, nails, staples, metal plates or sliders are used.
Before placing the rafters on the bathhouse, it is more convenient to assemble the trusses on the ground. After this, the finished structure is lifted and installed on the Mauerlat.
Types of roof structures for baths
Let's look at the types of roofs that are most often used in bathhouse construction:
- Shed roof;
- Gable roof.
A lean-to structure is installed if the bathhouse is an extension to a residential or any other premises. The relatively low cost is the main advantage of this type of structure.
Also, a small roof area allows you to significantly save on covering materials.
Gable roofs are used if the bathhouse is a separate building.
The abundance of materials for gable structures allows you to use your imagination and choose the appropriate type of roof based on color and appearance.
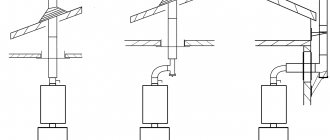
Features of fastening rafters on a bathhouse made of round logs
The main difficulty in attaching rafters for a bathhouse made of round timber is the difficulty of fixing the lower part of the rafters (heels). It is impossible to firmly fix the flat surface of the board to a round log; the elements only touch at one point. And this does not provide reliable support; the rafter system loses stability. In addition, if the bathhouse is made of ordinary, and not rounded, logs, then the upper crown does not lie in the same plane. As a result, it is necessary to prepare special supports for the rafter legs.
Fastening rafters on a bathhouse made of round logs
There are two options for attaching the rafters to the timber: making cuts in the logs under the heels of the rafters or mounting the roof on the ceiling beams. The second option is considered by professionals to be more reliable and simpler. How is it done?
Step 1. Mark the location of the ceiling on the top crown. It’s better to make marks with a laser level; if you don’t have one, you can use an ordinary water level.
Important. Pay attention to two factors. First, all beams must lie strictly horizontally and in the same plane. Second, logs cannot be sawed to a depth exceeding one-third of their diameter.
Step 2. Drive in nails at the outer marks and stretch the rope between them.
The photo shows a stretched rope
Step 3. Mark the installation locations of all rafter legs. Place the level on the rope and rest the end against the frame. Set the horizontal line and mark it on the top crown of the bath.
Marks are applied
These marks should be used to control the depth of sawing of logs. Thanks to this simple technology, all ceiling beams will be located in the same plane and strictly horizontally.
The log is sawn through
Next you need to work with a small ax
This is what the installed rafters will look like
Further work on fastening the rafters can be continued using one of the methods described above.
Metal tiles are strong and aesthetically beautiful
This type of roofing is a cheaper prototype of expensive ceramic tiles. In some cases, it is almost impossible to distinguish them.
Attention! Tiles are a time-tested material, because they were used for roofing houses by the ancient Romans and Greeks several thousand years ago!
The composition of metal tiles is quite complex: steel sheet with galvanized and polymer coating, as well as a primer and aluminum coating.
A protective varnish is applied on top of all layers. The weight of the finished sheet is relatively small - approximately 4-5 kg per 1 m2.
Advantages:
- Quick and easy installation;
- Ability to withstand temperature changes;
- Durability – able to withstand heavy loads and impacts;
- Relatively small mass;
- Hassle-free loading and transportation;
- Durability – service life varies from 25 to 50 years;
- Variety of colors and shades.
Flaws:
- High thermal conductivity;
- Low sound insulation;
- High price;
- Corrodes.
A rather interesting variety of this type is composite metal tiles. Instead of a polymer coating, the protective function here is performed by stone chips.
Metal roofing is quite popular, but it is not the most suitable option for a bathhouse.
Profiled sheet - an inexpensive analogue of metal tiles
The composition of the corrugated sheet is similar to metal tiles: it also consists of galvanized steel sheet. Each side of the corrugated sheet is coated with either a zinc layer or an aluminum-zinc layer.
Corrugated sheets are mostly used to cover the roofs of sheds, garages and other outbuildings.
Advantages:
- The corrugated sheet is quite easy to install;
- High strength of the material;
- Service life reaches 50 years;
- Low cost.
Flaws:
- Low sound insulation;
- Low thermal insulation;
- Susceptibility to corrosion.
Of course, roofing a roof with corrugated sheets has a number of advantages, but it cannot be said unequivocally that it is best suited for a bathhouse.
Ondulin – is resistant to moisture and environmentally friendly
Ondulin, as a material for roofing, is attractive due to its natural composition, as well as a fairly reasonable price.
Ondulin consists of cellulose fibers impregnated with bitumen and polymer substances.
The weight of the sheets does not exceed 7 kg, height – 2 m, width – 1 m.
Ondulin is ideal for roofs of complex structures, as it bends easily and without problems.
This material is widely used in the construction and roofing of bathhouses, garages and sheds.
Advantages:
- Easy installation;
- Resistance to moisture;
- Ondulin is an environmentally friendly material;
- Service life exceeds 40 years;
- Ability to withstand temperature changes;
- High strength;
- High noise insulation;
- Reasonable price.
Flaws:
- Flammability. Ondulin is incapable of spontaneous combustion, but it supports combustion well;
- Gradual loss of color.
Ondulin is best suited for the roof of a bathhouse, as it can make it beautiful and as durable as possible.
Slate is strong and durable, but contains asbestos
Slate is widely used in the construction of buildings for various purposes, including baths.
It is very popular because, relative to other representatives of roofing materials, it is very cheap.
Slate consists of approximately 80-85 percent cement and 15-20 percent asbestos.
Slate is mainly used to cover industrial premises, as well as sheds and toilets. Very rarely used to cover private houses.
Advantages:
- Slate is not flammable and does not respond to high temperatures;
- Not subject to corrosion;
- Service life – more than 40 years;
- Soundproof;
- Easy to install.
Flaws:
- Asbestos, which is the main component of slate, is dangerous to the human body;
- Fragility;
- Heavy weight;
- Over time it becomes covered with moss.
Frame design
The basis of the roof structure is the rafter frame, which bears the weight of the roofing covering, evenly distributes the load between the load-bearing walls and the foundation, and is also used to fasten the waterproofing material. It is made of wood and consists of the following elements:
- Mauerlat. This is a kind of support beam that distributes the weight and softens the pressure of the rafters on the load-bearing walls of the bathhouse. It is made of square pine beams onto which the rafter legs are attached.
- Racks. Racks are the vertical supporting elements of the frame that support the ridge girder or the central part of the rafter leg. This element is used only in layered rafter systems.
- Rafters. Rafter legs are made from boards with a section of 50x150 mm or 100x150 mm; one end is installed edgewise on the mauerlat, and the other rests against the second leg of the pair or on the ridge girder.
- Struts. Struts are the supporting elements of the frame, located at an angle to the rafter legs and preventing them from bending under their own weight.
- Puffs. The horizontal elements pull the rafter legs together in pairs and compensate for the bursting load acting on the load-bearing walls.
Important! Since the bathhouse is considered a structure with a high risk of fire, it is necessary to make the wooden rafter frame resistant to fire. To do this, all parts of the structure are treated with a fire retardant.
Construction of the rafter system
Flexible tiles - a type of soft roofing
Important! Flexible tiles, which no longer surprise anyone, appeared more than a hundred years ago in America.
Flexible tiles consist of fiberglass coated with bitumen and stone chips, which gives the tiles color, volume and resistance to ultraviolet radiation.
The fabric has a self-adhesive surface on the reverse side.
This type of roofing is ideal for complex roof structures due to its flexibility and softness.
Advantages:
- Service life can exceed 70 years;
- Good sound insulation;
- Aesthetic beauty;
- Does not corrode;
- Low price.
Flaws:
- Becomes brittle when exposed to low temperatures;
- Flammability;
- Melts under high temperatures.
Hard surface installation process
Let us examine in more detail the process of installing a rigid roof using the example of a slate roof. The slope of the sheathing under the slate should be at least 27 degrees, preferably more.
The distance between the beams should be approximately 1 m. Slate sheets are attached directly to the sheathing using nails specially designed for this purpose, which do not corrode.
Small rubber washers are placed under nails about 10 cm long.
The slate is laid staggered depending on the flatness of the slope. Next, all the cracks are coated with mastic with a layer of 5 mm.
The process of installing a soft roof
As an example of a soft roof, let's take a relatively inexpensive material called roofing felt. Roofing felt rolls are a dense carpet with a layer of waterproofing.
First of all, a ridge is installed on the wooden flooring, then a layer of bedding is laid out on the flooring. Glue it with hot mastic.
Important! Under no circumstances should you lift mastic onto the roof with full buckets! Also, when working with mastic, you must use protective gloves and boots!
The underlying layer is applied across the ridge in separate strips. It is attached to the ridge with nails.
Next, hot mastic is again applied to the bedding layer, on top of which the roofing material is directly attached. It is laid out in the same way as the underlying layer - overlapping across the ridge.
Next, the layer of roofing material needs to be smoothed out to avoid the appearance of bubbles.
At the place of descent, the roofing material is folded under the sheathing and secured with the same nails.
The essence of the rafter system for a bath
The system is a supporting structure for securing the roof. Rafters for a bathhouse roof are beams that make up the base (frame) of a pitched roof. They give it the desired shape, take on all the loads and redistribute them to the load-bearing elements of the structure.
The rafters are installed obliquely, forming rafter legs, which are secured at the lower end to the upper frame of the walls. The required tilt is ensured by vertical posts. The legs are connected into a common rigid, strong system using purlins, tie-rods, struts, post-rafter horizontal beams (crossbars) and other additional elements - headstock, fillet, flange.
The design of the supporting system depends on the type of roof. With the appropriate arrangement of the rafter legs, a single-pitched and double-pitched version can be provided. In the first case, the system consists of elements in the form of right triangles, composed of an inclined rafter and a vertical post. The elements of a gable roof are formed from two rafters connected at a certain angle to each other, with the free ends resting against the frame of the load-bearing walls. There are several ways to install rafter elements:
- Hanging type. In this option, two rafters are connected to each other, and rest on the walls only with their free ends. The system is used provided that the distance between the supports does not exceed 6 m.
- Inclined type. It assumes the presence of a vertical stand in the middle part. This additional support is installed when the span exceeds 5 m. It allows you to extend the rafter legs to a distance of up to 12 m, and when installing 2 racks - up to 15-16 m.
In the vast majority of cases, a wooden beam is used to make a supporting structure, which has sufficient strength and is easily assembled into the desired structure. The main disadvantage is the tendency to rot when exposed to moisture. To eliminate this drawback, the wood must be impregnated with a special composition.
Coniferous wood is most suitable for rafters. Pine is most often used as a fairly cheap and accessible material. The ideal option is larch, but it is expensive. The size of the timber is selected with a width of at least 10 cm and a thickness of at least 5 cm.
conclusions
Based on the above advantages and disadvantages, certain conclusions can be drawn:
- Each of the presented materials, one way or another, is suitable for roofing single-pitch or gable roofs. There are differences only in the slope angle. For example, for most sheet materials the slope angle is equal to 12 degrees, and for piece materials - 20. The exception is soft tiles, the slope angle of which is from 12 to 90 degrees;
- The most expensive material is considered to be natural roofing – ceramic tiles. Metal tiles are slightly inferior to them;
- Budget options include corrugated sheeting and ondulin. Quite high quality materials and also economical. In cases where staying within budget is the most important thing, these materials are perfect;
- During the installation process, the easiest way is to lay soft tiles, since it takes less time and even a non-professional can handle it;
- Ondulin is the most environmentally friendly. Corrugated sheeting comes next, but slate is in last place, since the asbestos content makes it unsafe for the human body.
Having analyzed the prices and types of roofing materials, we draw conclusions: they can all find application in one segment or another.
There is no clear answer to the question of what is the best way to cover the roof of a bathhouse, since each material has its own characteristics.
However, the most important thing remains that, regardless of the material chosen, its quality must fully meet that declared by the manufacturer.
Now you know what is the best way to cover the roof of a bathhouse.
Laying the Mauerlat
The roof structure is quite heavy, so the rafters are not installed directly on the load-bearing walls. To evenly distribute the load and prevent deformation of the supports, a Mauerlat is placed on the upper belt of the box. Mauerlat is a strong, even beam with a cross-section of 100x100 mm or 150x150 mm, mounted on a log house to soften the pressure on the walls of the roof rafters. The installation process of this element of the rafter frame of the bath is as follows:
- First, the support beam is cut into pieces of the required length. The length of the Mauerlat corresponds to the length of the bathhouse, and the quantity corresponds to the number of roof slopes.
- Then the Mauerlat is impregnated with deep penetration antiseptic preparations. The treatment is carried out twice to protect the wood from fungus, mold and rot.
- The Mauerlat is secured to the top row of load-bearing walls with metal studs or anchor bolts. Moreover, the locations of the attachment points are calculated so that they are located between the rafters.
- After installing the Mauerlat beam, you can proceed to assembling the roof rafter frame.
Mauerlat devices
Mauerlat fastening technology
Please note that if a log house acts as a bathhouse, then it would be correct to use the upper crowns, reinforced with metal brackets, as a mauerlat. However, if the roof structure is complex or heavy, then this frame element cannot be avoided.