The history of building wooden houses began several thousand years ago. Not far from the stone blocks of Stonehenge, scientists have discovered several wooden buildings. One of the oldest log buildings still remains. the Horyu-ji Buddhist Temple in Japan. Its history goes back about 1400 years . The Norwegians began building wooden houses more than 1000 years ago . Written sources of Ancient Rus' mention similar houses in the 5th century. The oldest examples of wooden architecture have still been preserved. Towers, temples, palaces, huts, baths, and fortresses were built from wood. Wood construction technologies have reached our times and have become fundamental.
In ancient times, wood was not the only building material, but it firmly won the palm due to the fact that wood is a universal material that can solve many architectural problems. Even with the advent of new building materials, the popularity of wood has not decreased. As before, it is used for the construction of a wide variety of structures. High-quality wooden buildings are environmentally friendly, light, cozy, and warm.
Anyone who begins the construction of a building made of wood is faced with the dilemma of choosing a cushioning material - inter-crown insulation . The construction market offers various insulation materials. Each of them has its own characteristics and behaves differently. How not to make a mistake in choosing the best option? For a long time, only natural material played the role of insulation in wooden buildings. Insulation materials of plant origin help the tree to breathe and ventilate the air.
Today, two natural insulation materials are used, which are placed between the crowns. These are flax and jute, as well as their derivatives.
Jute
Jute grows in Asian countries and India. This plant is very similar to reeds or reeds. It is tough and grows in water. Jute contains 49% lignin (a substance that increases the strength of the plant and prevents it from rotting), antiseptics, this is its amazing resistance to moisture. The scope of jute is wide. It is actively used both in everyday life and in various fields of industry and agriculture. But the main use of jute is as insulation between the crowns in wooden buildings made of timber and logs. Jute fiber is crushed, crushed, cut, and rolled. This is how jute felt is made.
Jute is not brittle, it does not require pre-moistening, it is flexible and soft. Convenient for installation, as it is sold in the form of a tape. Jute is a water-repellent material; after getting wet, it dries quickly, maintaining its properties. To achieve a tighter fit of logs or beams, additional insulation, eliminate further blowing, as well as less moisture ingress, the jute tape is taken wider than the groove of the log. Jute has another important feature. Birds and rodents do not like it.
Jute insulation is popular among builders .
It is easy to use, strong, durable, does not rot, repels water, is not subject to deformation, and does not contain straw. Jute has an attractive appearance, it has the color of a freshly cut tree.
Artificial materials
When answering the question - how to choose inter-crown insulation for timber, you cannot ignore artificial materials. Today this option is the most popular. One of these materials is called “holofiber”.
This insulation is made from polyester fibers using the non-woven method. The material is produced in rolls and plates, each type has its own density.
Holofiber has high elasticity. This feature is very convenient for thermal insulation of crown joints, especially when using laminated veneer lumber or non-profiled timber.
This material has no pores, which means it can warp when drying. If insulation made from natural material is used, then the appearance of cracks is inevitable. When using holofiber, additional sealing of the crown joints after the timber has dried is not required. The fibers of this material will fill the cracks that appear on their own.
Holofiber does not absorb water and retains its thermal insulation properties
In addition to a high degree of elasticity, holofiber has a number of other advantages. Experts include the following among the most significant of them:
- has low water absorption rates, less than one percent. This means that holofiber will not absorb moisture and will retain its thermal insulation properties longer even in a humid climate;
- the material does not burn even at high temperatures. This property is very important for thermal insulation of wooden buildings;
- Insects “don’t like” the material; they definitely won’t live here. In addition, holofiber is not afraid of mold;
- not only has high thermal insulation properties, but is also an excellent sound insulator;
- Holofiber has a long service life, and even over time does not require additional caulking.
You should not think that holofiber can have a detrimental effect on human health. This material does not cause allergies, does not emit harmful substances and is absolutely environmentally friendly. There can only be one drawback. If wood that was too damp was used during construction, it may be prohibited. Holofiber does not allow the walls of the house to “breathe”.
Another common inter-crown insulation for wooden houses made of profiled or laminated timber is “shelter”. This material is made from polyester fiber. Just like holofiber, it has high elasticity, which allows you to fill all the cracks newly formed as a result of shrinkage of the house. Shelter does not rot, does not absorb moisture and retains heat perfectly.
There are also more modern materials, for example, “polytherm”. At its core, it is a type of holofiber, but with greater elasticity. According to the manufacturers, the material can last 50 years. But polytherm appeared not so long ago, only about ten years ago, so it is not possible to test this in practice.
Inter-crown insulation “Polytherm” can last up to 50 years
Linen
Flax is a plant growing in Russia, Belarus, and Europe. Linen is very durable, has heat-saving, heat-transfer, and antiseptic properties. Linen fiber is used to produce fabrics that are used in various branches of light industry. Insulation (flax wool and tow) is made from flax. Ligin in flax is only 7% , which makes it unstable to the conditions of our climate. Rolled insulation – flax wool – is used as insulation in wooden houses and bathhouses. This is a special material for inter-crown gaskets. Linen is the most unstable insulation material. The service life of flax fiber is 1-3 years . It quickly rots when moisture gets on it and quickly disintegrates. Birds and rodents love this material.
It is loved by bedbugs, moths and many other insects. In view of this, it is necessary to antisepticize wood and all lumber. The roof extension in buildings where flax was used as insulation must be at least a meter. The main advantage of this material is environmental safety and excellent thermal conductivity.
Flax fiber insulation has proven itself to be excellent when caulking seams between logs, filling gaps when installing windows, doors, and insulating roofs, floors and ceiling surfaces. Linen is an excellent soundproofing material.
Lnovatin
This insulation is made from flax fiber and is usually sold in the form of strips of different widths. This material is environmentally friendly, its thermal conductivity is simply excellent and is 1.0 W/mK. Linen batting is a cheaper material than jute, although it has poorer workmanship. The overall density of flax wool will be less than that of jute, so the cost is not so high. If the density is less than 300 grams/m3, then the quality of insulation is poor. The thickness of flax wool is usually 4-12 mm, its average density is 400 grams/m3, and its width is 0.1-1.6 meters or more.
What do jute and flax have in common?
The technology for laying jute tape is similar to the technology for laying flax. The width of the tape should be wider than the groove of the log so that the edge is not cut off. Laying insulation from jute and flax does not require knowledge of special technologies; any builder can easily cope with these materials. Both materials are natural and therefore environmentally friendly. Both insulation materials are produced in a form convenient for installation - tape tow or batting.
Both flax fiber and jute fiber have a beneficial effect on the human body due to their natural properties. They have antiseptic properties, are breathable, and resistant to sunlight.
Insulation for a house made of edged timber
Linen and jute tow, batting and peat moss are used as inter-crown insulation for houses made of edged logs.
Moss is used to insulate baths and auxiliary buildings. For a residential building, flax or jute material is better suited; strips of batting or tape tow are laid between the crowns, corners and irregularities are caulked with tow. After shrinkage of the log house, additional “finishing” caulking of the seams is done from the outside and inside.
When asked which material is better, experts do not have a unanimous opinion. Jute fibers are more elastic, and linen fibers are soft and elastic; it is better to use flax as tow. When building from edged timber with roughly processed layers, it is recommended to use jute batting; for planed timber, linen insulation is recommended.
The best solution when choosing inter-crown insulation may be flax-jute batting; when constructing from three-edged timber or timber-laft, the inter-crown seams are additionally caulked with linen rope with a diameter of 20 mm.
Comparison and how they differ between jute and linen
- Jute fiber is more durable; it will last more than 70 years . Flax fiber will last 1-3 years . Due to the content of a large amount of ligin, jute is resistant to rotting and is able to release moisture. Linen absorbs moisture perfectly, it is susceptible to rotting and destruction. In buildings where flax is used as insulation, logs require mandatory antiseptic treatment.
- Unlike jute, the appearance of flax fiber leaves much to be desired.
- Jute fiber is denser in thickness and more elastic.
- Mice, birds and many insects are partial to flax, which cannot be said about jute fiber.
- Jute insulation is more rigid, therefore less pliable in installation and more difficult to work with.
- Flax fiber is a less expensive insulation material than jute.
How to caulk a bathhouse correctly and when to do it
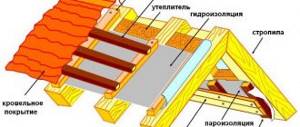
Putting up a log house from a log or timber is not the whole task. It is also necessary to properly caulk this log house: to seal the gaps between the crowns and the cracks that form when the wood dries out. This is done so that the log house of the bathhouse loses as little heat as possible. The quality of the log house's assembly is determined by how the crowns are laid. It is important not only to cut out the bowls and grooves correctly, but also to lay inter-crown insulation between two rows of logs or beams.
The insulation is installed during the assembly stage of the log house
What it will be - moss, tow or jute - is up to you, but such a layer must be present. When building a log house, you need to lay insulation in two layers:
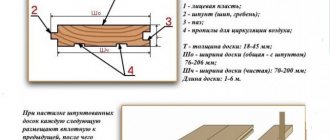
- on the lower crown so that the edges of the insulation protrude beyond the edges of the bowl by 3-5 cm, the width of the insulation, in general, is taken 5-10 cm more than the width of the bowl;
- Insulation is also placed in the bowl of the upper crown; its edges protrude beyond the bowl by 3-5 cm.
Please note that when using moss or tow, there is no need to “tap” the material. When tapped with a hammer or an ax butt, the moss fibers break and dents form on the wood, which are directed across the fibers. Such damage can lead, in the future, to the development of foci of rotting. It is enough to simply compact the fibers with the palm of your hand, leveling and probing the layer; if you come across large foreign objects (cones or sticks are often found in moss), simply remove them.
Laying moss when assembling a log house
When using tape insulation, you can fix it using a construction stapler - damage to the wood from the staples is minimal, and the material is held securely. It is advisable for two people to lay the “insulated” crowns so that they can take the log from both ends and lower it so as not to move the insulation.
How to caulk a log bathhouse
All materials for caulking can be divided into two main categories: natural (tow, hemp, moss, jute, etc.) and industrial sealants. Sealants are applied faster and easier to work with. Usually, to reduce the consumption of sealant, a cord is placed in the gap between the rims, and only then a sealant is applied on top of it, which, when wet, is leveled with a special spatula.
When caulking, it is not appropriate to have a spatula-scalpel at hand. The working part of the tool is made of hardened carbon steel
Synthetic sealants have a number of disadvantages:
- some of them do not tolerate exposure to ultraviolet radiation - when irradiated, they lose their properties, crumble and are blown away by the winds. The problem is solved by strengthening strips that will cover the seams from ultraviolet radiation;
- Some sealants for log houses, when dry, form a monolith, which, when wood expands/contracts (depending on weather conditions), interferes with the process and contributes to the destruction of adjacent wood fibers. For this reason, it makes sense to use flexible sealants.
Elastic joint sealant for wood from EUROTEX
The video shows how to use Eurotex sealant.
As shown in the video above, you can use a regular tablespoon as a tool to level and remove excess sealant.
If you decide to use one of the sealants, carefully read the instructions and description, make sure that it is compatible with the type of wood from which the log house is built, can be used in your region (temperature regime) and has the necessary qualities.
The use of sealant is justified in the case when it is used to seal caulked cracks: after caulking the log house twice with tow, moss or jute, wait for the log house to completely shrink and acquire operational dimensions, after which a cord is laid in the seams, and then the sealant is applied.
Natural materials for caulking also have their advantages and disadvantages, in addition, each of them requires certain preparation.
Moss
The most proven material for caulking a bathhouse is moss. It has been used for centuries. Today, many other materials have appeared, but they have not surpassed moss in terms of characteristics. It is more convenient to work with new materials (especially tape materials). This is undeniable, but the qualities of moss remained unattainable for them. Chief among them is the ability to resist bacteria and high resistance to rotting.
Not aesthetically pleasing, but practical
The moss is first dried and then wetted again before use. This restores elasticity to the stems. The soaked moss is laid out in an even layer so that its ends hang down on both sides of the log/beam. After completing the collection of the log house, too long stems of moss are trimmed, everything else is tucked in and tucked into the cracks of the log house - the initial caulking of the log house is performed. This is followed, after six months and after a year and a half, by repeated caulking.
Jute
Jute is increasingly being used in the construction of wooden bathhouses and houses. And not just jute fibers, but rolled material. Jute fiber has good characteristics: it has good heat-insulating properties, due to the large amount of lignin - a natural resin that serves as a binding element - it is practically not subject to rotting and has low hygroscopicity. Even at high humidity, jute remains dry to the touch.
Jute insulation can be of several types:
- Jute tow. When making this material, the fibers are not torn, but combed, giving them the required direction. With this processing, jute retains its properties to the maximum extent. But such material is inconvenient for caulking: it is hard and not dense enough, working with it is quite difficult, caulking has to be done several times: firstly, the birds pull the fiber into nests (the material is natural), secondly, it shrinks and becomes compacted ( due to the rigidity, it is not possible to immediately achieve the required seam density in one go).
Jute tow
- Jute felt. This is a material consisting of 90% torn jute fibers and 10% long flax fibers. The material is dense and flexible at the same time. It is much easier to work with, but if the fibers are not long enough, it tends to clump and fall out. When choosing jute for caulking, pay attention to the length of the fibers - only fibers longer than 2 cm will provide the required elasticity. Material made from shorter fibers will become denser and lose most of its properties, and short fibers will simply spill out or be blown away by the winds. Another disadvantage is that this material often becomes a breeding ground for moths. Therefore, before use, it is advisable to treat it with impregnation against moths and rot.
Jute for baths - jute felt
- Flax-jute . A combined tape material consisting of half soft flax fibers and half hard jute fibers. This combination attracts many builders, but this material is prone to rot and is often attacked by moths. So, just like jute felt, flax-jute requires treatment against rotting and moths before use.
Tow
Tow is waste that is generated during the primary processing of natural fibers. For caulking log houses, tow made from jute, hemp and flax is used. The characteristics of the material and its quality depend on the source raw materials, the degree of purification of the fibers and their length. Construction tow is pressed into square blocks. To use when caulking a log house, a strip of material is pulled out from a common block, twisted into a rope and placed in the seam. Combed tow, which is sold in rolls, is more convenient to use.
Tow for a bath
It is inconvenient to work with such material: it is difficult to achieve a uniform layer when used as inter-crown insulation, and for caulking a log house, tow is excessively rigid, which is why it is almost impossible to achieve a dense filling of the seam the first time and you have to periodically re-caulk it. If the choice is between moss and jute tow, then we can definitely say that moss is better for a bath - it has the ability to inhibit the development of putrefactive bacteria and fungi.
When to caulk a bathhouse
The log house is assembled, when is the first time you can caulk a fresh log bathhouse? If the log house was assembled using moss or tow, then remnants of material of different lengths stick out between the crowns. In this case, you can perform the initial caulking immediately: trim the overly long fibers, tuck them inward and tuck them into the seams. There is no need to be zealous about this. This is preliminary work, the purpose of which is to remove fibers. But this must be done following the rules of caulking. If the log house is assembled on tape insulation, nothing needs to be done.
Bath after initial caulking
The first “serious” caulking is carried out approximately six months after the collection of the log house. During this time, the logs/beams will lose most of the excess moisture, new cracks will appear, the crowns and corners will basically “sit” in place. At this time, the first caulking is carried out. After this process, you can install doors/windows.
A second caulk will be needed about a year after the first. A year and a half has passed since the construction of the log house, the log house has become stable. Now all seams and cracks are checked, all defects are eliminated. Depending on the material and quality of work, it may be necessary, in another five years, to caulk the seams again. But there have been cases (usually this is the result of the work of “shabashniks”) when caulking errors are corrected for several years in a row. Most often, this need arises if the log house was built without inter-crown insulation.
How much tow do you need for a bath?
Any natural material for caulking is compressed many times during installation and a large amount of it can fit into a log house, even with good inter-crown insulation. No one can say exactly how much tow is needed for a bathhouse: it also depends on what material the log house is assembled from and how the grooves are cut out in the logs. When manually cutting grooves, as a rule, more material is wasted. Also, a sanded log requires more material compared to a rounded one. Less is required for a log house, but even here the amount of tow or moss that will be used to seal the cracks depends on the accuracy of the geometry of the beam and the depth/number of cracks that appear during drying.
Caulking rules
Caulking a log house is not a very difficult task, but it is long and tedious. Everything needs to be done thoroughly and slowly, so it takes a lot of time - it took 10 days to caulk a small 5*4 bathhouse (one worked for 7-8 hours).
The main thing is not to overdo it in the efforts made when hammering in the insulation, which can lead to the log house rising by 15 cm or more.
Rules for caulking a log house:
- You need to start from the bottom crown, moving along the entire perimeter, first from the outside of the building, then caulk the same crown from the inside. And only after that start processing the next crown.
- When caulking, pay special attention to the corners - these are often where the most significant gaps are located.
- During primary caulking, you first need to pick up the hanging material, bend it down and tuck it into the gap. The tool should be used as needed. Perform this operation on a section about a meter long, then move on to the next section.
- In the same area, use caulk and a wooden mallet (sometimes a hammer is used, but the mallet does not knock off your hands so much) to compact the material. You need to hit the caulk until the material begins to spring back. Then move on to the next section.
- After compaction, a gap formed. A piece of insulation is again placed in it. If it is tow, you need to roll it into a rope of the required thickness or tear off a piece of the required length from the tape. This piece is also hammered with caulk and a mallet until a springy effect appears. Repeat this operation until the gap is completely filled and move on to the next section.
Like every business, caulking requires certain skills. Since there will be more than one such procedure, you will eventually gain skills. As you gain experience, you will notice the mistakes that you made at the beginning of your activity - this will be your chance to eliminate them. Actually, it is not the gods who burn the pots, but it is possible to caulk a log house more or less efficiently even if you have no experience.
baniwood.ru>
Jute tow
Jute tow is 100% made from jute. On the one hand, this is its significant plus, on the other hand, it is a minus that can become a problem when working with insulation. The fact is that jute tow itself is very rigid, which complicates the process of laying it on the work surface. It is for this reason that jute tow can most often be found with some additions of flax, which softens the insulation.
On the other hand, jute tow is most often produced in the form of rolls (tape), the thickness of which is ideally selected. It is for this reason that the tape is easy to install, and during its installation we will not have problems with level differences in a certain inter-crown crown of a wooden house. In turn, when choosing the width of the tape, we can take a larger value, which will allow us to place it with a slight overlap inside and outside the bath. This will be useful to us at that moment in time when the wooden structure shrinks.
Note that jute itself is not afraid of moisture. In addition, jute tow is an example of secondary production, which makes its cost very low and even budget-friendly. That is why any owner of a wooden bathhouse in our country can afford to use jute tow.
Advantages of jute as inter-crown insulation for a bath:
- the composition of jute is very close in composition to wood - logs, timber, lumber;
- environmental purity of natural jute;
- good thermal protection performance;
- durability.