When building a bathhouse, the main factor influencing the choice of material and construction method is the financial costs of construction. This is the main reason why the frame method is used in construction.
The main tasks of the bath are rapid heating and slow cooling. It is advisable that you do not have to spend a lot of firewood for this. You also need to know whether the bathhouse will be used only for its intended purpose - for washing, or whether the project provides for a guest room where guests can be accommodated for the night. In this case, it is important that the room is quickly ventilated, “breathes” and that changes in temperature and humidity do not destroy the walls or damage the finishing elements.
Positive and negative in frame baths
A frame bathhouse trimmed with artificial stone looks very presentable.
Frame construction comes to the aid of buyers who want to have a bathhouse or a house on their site, but cannot afford an expensive building. There is a lot of talk about such baths on forums. A large number of positive reviews say that construction has inherent advantages, but there are also disadvantages. We will find out why some of the buildings are criticized below.
Advantages of frame construction of a bathhouse
- All positive reviews about bathhouses with frames are mainly related to their advantages:
- The bathhouse turns out to be light, so the lightest foundation is installed under it.
- When assembled correctly, it retains heat no worse than lumber or logs.
- Construction is carried out in the shortest possible time, along with insulation and finishing.
- The bathhouse will cost from 5,000 rubles/m².
- Assembling a frame bath is 2-3 times faster than a similar one made from timber or brick.
A frame bath is assembled from timber and boards with insulation. The heaviest part of the structure is timber with a section of 100x100 or 150x150 mm. The load on the foundation is ultimately 5–6 times lower, which means there is no need to make it massive.
Disadvantages of frame construction of baths
The frame bath is assembled, but without finishing it does not look aesthetically pleasing.
The negative thing about frame construction is mainly related to costs. Yes, at first glance, such a structure is cheaper. But if you carefully calculate the costs of insulation + finishing (external and internal), then the difference practically disappears. Of course, timber baths also need to be finished over time, but they can simply be painted, and this is cheaper than panels or decorative plastering.
The second big disadvantage of frame construction is poor-quality insulation. If you use inexpensive mineral wool, then you shouldn’t vouch for the beneficial side of the bath. You cannot use inexpensive polystyrene foam, as it is highly flammable.
The third important point is the shrinkage of the bath. It is impossible to leave the insulated frame without finishing for more than 1–2 weeks, and shrinkage can last up to 2 years. Moreover, if you use a beam of natural humidity, then the bathhouse can shrink by 10 cm. In this case, the paneling will crack or become deformed. This can be avoided by building a bathhouse from chamber-drying material, but then the point of saving is lost.
In order to avoid troubles, the frame construction of a bathhouse must be carried out in accordance with all the rules.
Blocks or wood?
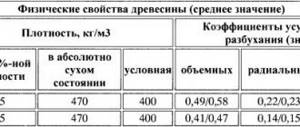
The properties of a building for bath procedures are influenced by the structure of the materials used - the spatial arrangement of particles, size, location of pores and capillaries, microcracks, and other structural elements.
Wooden sauna
The properties of wood are different in different directions. The sound and heat insulating qualities of wooden products vary along and across the fibers. Pores in wood are both closed and interconnected.
Advantages of wood:
- low thermal conductivity;
- high heat capacity;
- moisture capacity;
- porosity.
Attention! Wood and products made from it are flammable. When heated to 100 °C, wood dries out, loses weight, and becomes deformed. With a further increase in temperature, the rate of change in wood increases greatly, and the intensity of the release of volatile substances increases. Heating to 350 °C leads to spontaneous ignition of the material.
Block sauna
Masonry made from small blocks of artificial stone is an alternative to wooden walls. Industrial blocks are used; it is possible to make lightweight concrete yourself.
The stone becomes light due to the large number of voids, or due to the porosity of the filler: expanded clay, sawdust. (The use of slag concrete is often avoided since the composition of the slag is only approximately known).
Highly porous concrete (for example, expanded clay concrete) has a low heat transfer coefficient, and air permeability is not greatly reduced.
If the pores arose under the influence of special additives (air-carrying or pore-forming), then they are large, spherical, most often closed, occupying up to 50% of the volume of the porous substance. Expanded clay pores are small, also closed.
The predominance of closed voids in the wall material makes the bathhouse more inertial - it will take longer to warm up, but will cool down only a few hours after the end of the fire.
Walls made of aerated concrete blocks or ceramic blocks do not require post-installation treatment with antiseptic primers or special anti-cracking compounds, unlike a log house.
Concrete does not rot or burn, and does not attract insects and mice.
Block walls require plastering on the outside - with a sand-cement mixture.
A good, but more expensive option is lining a block wall with clinker bricks, imitation of natural stone (with an air gap, because the porosity of the finishing layer is lower). Artificial stone is characterized by good adhesion to plasters, ease of cladding, and stable geometric shape.
The disadvantage of porous concrete is its high water absorption. The larger the block of closed pores, the lower it is. But often a foam block bathhouse needs constant heating. Unloading and storing blocks requires space; shrinkage of the walls lasts 1–2 years (only after this is insulation and cladding carried out).
On a note. Concrete based on cement and lime loses the least volume.
Construction of a frame bath
Since frame construction is lightweight, all work can be done with your own hands. You need to build a frame bath in the following successive steps.
Foundation for a frame bath
Ready-made columnar foundation for a bathhouse with a top frame.
The easiest way to assemble a lightweight foundation for a frame bath is from asbestos-cement pipes (with a diameter of 100 mm or more) reinforced with concrete. This is a columnar type of foundation. The outline of the bathhouse is marked and holes are drilled with a drill to a depth of 1–2 m. The depth depends on the proximity of groundwater and the type of soil.
The pipes are placed in wells and covered with coarse sand. The sand is compacted thoroughly. The entire structure is poured from above with concrete, which should consist of:
1 part waterproof cement M200; 4 parts sand; 7.5 parts of fine crushed stone; 3 parts water.
The pipes are poured one at a time and allowed to dry completely. At the pouring stage, an iron plate is installed on top of each. The first link is subsequently laid on them. Only after this can you make the lower harness.
Installation of the bottom trim
Bottom frame made of timber for a frame bathhouse.
For the bottom trim, you can use a beam with a section of 150x150 mm, but in order to save money, you can take 50x150 boards and join them with self-tapping screws. The entire structure must be treated with an antiseptic and waterproofed before installation. For waterproofing, roofing material is laid on the pillars in 2 layers.
After this, logs for future floors are attached to the harness. Between the lags and the strapping you should also lay roofing material or coat it with mastic.
The piping can be secured to the pipes using special screws or brackets.
Installation of frame walls of a bathhouse
Frame walls of a bathhouse without a rafter system - assembly.
All material, including edged boards, is dried and treated with antiseptics before installation. Instead of timber, you can use the same spliced boards as a basis. They are selected according to the specified dimensions for the racks and rafters.
Assembly is carried out in the following steps:
- Stands are installed in the corners, they are secured together with the top trim.
- Intermediate ones are installed between the racks; they will strengthen the structure.
- The resulting structure is sheathed with boards or particle board using self-tapping screws.
- The remaining racks are installed and also sheathed with boards or OSB.
So, gradually adding links of racks, the entire bathhouse is assembled. In this case, it is necessary to take into account openings for windows and doors; in frame construction they should be made immediately.
Roof installation
Rafter system for the roof of a frame bathhouse made of timber and boards.
The rafter system for a frame bath is installed in parts. Each is assembled at the construction site, gradually lifted and mounted on the roof. Each truss is mounted on its own frame stand. When installing the last truss, OSB is attached to it to create a pediment.
It is more convenient to assemble the roof by first laying rough flooring made of boards on the frame.
It is better to make the roof structure ventilated; for this, a vapor barrier is placed in the gap between the rafters and the counterbeam, and the sheathing is mounted on the beam.
For the roof of a frame bath, it is better to use lightweight material: ondulin, corrugated sheets, soft tiles. After this, the gables are installed using OSB or boards.
Insulation and finishing
Insulation scheme for a frame bath - main layers.
A frame bathhouse must be insulated and finished. Initially, OSB sheets or boards are sewn onto the inside of the ceiling; this will be a rough ceiling. It must be insulated in 3 layers of fire-resistant insulation. The walls are insulated with 2 layers of insulation and glassine. In the steam room, an additional layer of foil insulation is made. Only after this can finishing be done with clapboard or imitation timber.
A stove is installed, which serves as a fireplace in the dressing room and as a heating element in the steam room. To protect the wood of the frame from fire, the partition with a built-in stove is laid out of brick.
Do not forget about ventilation and holes in the ceiling for the pipe. It is treated on all sides with special fire-resistant compounds and lined with iron plates and asbestos paper.
If the bathhouse is built without an attic, then a hatch is made into the attic and additional lighting is installed. The ceiling in the burning room can be lowered to a level of 210 cm, this will make it possible to insulate it and cover it with linden clapboard. It is also better to make all parts in the steam room from linden.
Additional Tips
And finally, a few more tips:
- When choosing the size of the bathhouse, you must take into account that it can accommodate at least two people. The room should not be less than 10 sq.m.
- The steam room should be larger than the dressing room.
- Ceiling height - 2 m.
- Windows and doors should be smaller than standard sizes.
- The threshold in the bathhouse should be high, about 20 cm.
If you follow the recommendations for construction, insulation, and finishing of a frame bath, it will serve the owner for many years.
- Economical do-it-yourself panel bath
- How is a floor installed on wooden logs?
- Features of a wooden floor
Bathhouse construction period
Frame construction is considered one of the fastest. But if you compare it with others, it will become clear that the difference is small. Let's look, for comparison, at some stages in tabular form:
| Type of work | Time spent on constructing a bathhouse from various materials, minimum, days | ||
| Frame | timber | Brick | |
| Foundation installation | 3 | 3–4 | 7–10 |
| Installation of piping, joists and wall assembly | 3–4 | 7–10 | 10–20 |
| Installation of rafter system and sheathing | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Finishing walls and gables | 5–6 | 1 | 1 |
| Insulation and interior finishing | 4–5 | 2–3 | 2–3 |
| Total: | 17–20 | 15–17 | 22–30 |
It turns out that assembling a frame without finishing will be faster than other types, but insulation and finishing will equalize the work period with the installation of a bathhouse made of timber. The price for this will be lower, but the amount of work will be greater.
We have considered all the pros and cons of frame construction. It is up to the owner to decide whether to build a frame bathhouse for permanent use or not. But we recommend using this one for summer cottages or garden plots. It is better to equip residential private houses with baths made of more massive structures.
Finnish sauna - what are its features
For a residential building, the normal difference in maximum and minimum temperatures during the day is 6 °C. In a bathhouse, even if it is heated constantly, the microclimate parameters change in a range that is an order of magnitude larger. Building codes classify a bathhouse as a damp or wet room, the relative humidity of which is greater than 60% at temperatures above 24 °C.
The peculiarity of steaming in a sauna - at relatively low humidity and high temperature - makes the presence of a shower or washing room necessary. It is impossible to combine a steam room with a washing room.
A large group will have to be more crowded in a sauna than in a “Russian bath” with equal energy costs: heating a large room to 100 °C is time-consuming and expensive.
The sauna has the same requirements for building materials and structures as the “Russian bath”. Water vapor inevitably condenses on the walls, tends to moisten the finish, penetrate deep into the enclosing structure, and involuntarily increase its thermal conductivity.
Which timber to choose - video instructions
The main requirements for the floors and walls of a bathhouse are a high level of thermal protection, durability with the lowest possible energy consumption. The need to protect the wall from the foundation does not depend on the material. The embedded crown of a log or cobblestone bathhouse will begin to rot from contact with ground moisture, the block wall will be damp and will lose its strength prematurely.
Any walls need precipitation removal. In the second bottom crown of the log house, select a groove, insert a sheet of roofing steel or a board into it to form a canopy over the base at least half a meter wide.
Both brick, block and wooden walls are covered with wooden beams.