More recently, the winter period became a kind of rest for builders. The work stopped, everyone was waiting for suitable conditions to continue. Today, even frosts are not a hindrance, and workers continue to build various structures. Modern technologies have advanced, but ordinary people still argue whether it is possible to pour a foundation in winter.
When it is necessary
If you take this issue seriously, then pouring a foundation in winter turns into a rather profitable undertaking. First of all, there is no need to worry that the walls of the trench will not be strong enough - the soil practically does not crumble. The reason is clear - the frozen soil composition acts as a formwork structure. It happens that in certain areas, excavation work is possible precisely in the cold season, when frost sets in.
Note that foundation work in winter is cheaper, since during the construction season the cost of materials is high, and teams of craftsmen are not idle.
Laying a foundation in winter is the only option to build an object in regions with a harsh climate, when the warm season occurs no more than two to three months. In these cases, preserving the finished foundation for the winter is a stupid and unfounded decision.
The use of additional means that make it possible to fill the foundation in winter
Another way in which the answer to the question of whether it is possible to fill a foundation in winter will be positive is to ensure that the foundation is heated. It is known that concrete gains its highest strength during the first two days. It is during this period that the foundation especially needs protection from low temperatures. To heat the base along the entire perimeter, special equipment is used - a thermal gun. With its help, the temperature required for hardening of the concrete solution is ensured and maintained. The larger the foundation, the higher the power of the device should be
You can also heat the foundation using electronic current. This method allows you to maintain the temperature required for hardening by transferring heat (from hot to cool). The concrete is heated by reinforcement rods, to which an electric current (380 V) is supplied.
Advantages and disadvantages
We propose to understand the pros and cons of building a foundation in winter.
Benefits include:
- convenience of preparing a pit or trench in an area where the soil composition does not hold its shape well in the warm season;
- during the winter season, building a foundation in the North is a completely justified decision;
- acceptable cost of materials for which demand temporarily falls;
- availability of free time.
Unfortunately, there are also certain disadvantages. If in the summer it is possible to prepare a trench with your own hands, then in the winter season it becomes necessary to use special equipment to cope with frozen soil. The risk of purchasing low-quality building materials that suppliers were unable to get rid of during the season increases. Added concerns about how to preserve the foundation for the winter.
Negative aspects of pouring a foundation in winter
So, the answer to the question “is it possible to pour a foundation in winter” is obvious. However, despite many positive arguments in favor of this process, there are also some negative aspects:
“Although the savings in the cost of building materials are obvious, at the same time the price of excavation work in frosty weather increases greatly. You will also incur additional costs for heating the concrete solution and structures, so in general, the savings in construction in winter are very doubtful.
— The efficiency of work in winter is much lower than in summer, since working in cold weather is much more difficult.
— The price of additives and modifying substances that affect the properties of concrete is low, but to build even a small foundation, quite a lot of them are required. And therefore the price of building materials increases significantly.
— Sometimes it is necessary to use special equipment, in particular for digging a pit.
Therefore, before thinking about whether it is possible to fill the foundation in winter, you need to calculate all the costs and consider all the pros and cons of this idea.
What types of foundations are poured in winter?
As a rule, certain types of foundations are built in winter. A common option is a strip foundation, the installation of which in winter has its pros and cons. The main disadvantage is associated with the low level of productivity and the need for frequent rest for the construction team. In addition, certain operations will require significantly more time to complete than in the summer.
It is recommended to minimize the volume of “wet” operations and use ready-made reinforced concrete products.
A pile foundation also has its pros and cons in winter. It is good for light structures built from wood material. If you meet all the requirements of SNiP, in winter you can install a pile-screw foundation on any difficult soil using bored and drilled supports. The first type is concreted into prepared wells, the second is simply driven into the soil. This option is more convenient in that there is no need to mix the solution - the supporting elements are purchased ready-to-use.
The nuances of concreting in winter
It is not for nothing that winter was considered not the best period, both for pouring a monolithic structure and for constructing supporting elements of bored and pile types of foundations. The reason for this is the crystallization of water, one of the main components of the concrete solution. By turning into ice, water not only interferes with the normal course of the hydration process of the concrete mixture - that is, the formation of reliable molecular bonds due to its work. Due to the formation of ice crystals, the dimensions of which increase the initial volume of water by 10%, porosity increases. This fact in no way contributes to obtaining the planned strength of the foundation, but significantly reduces it.
Let's understand the mechanism of hydration
Concreting is the process of gradual transition of a mixture of cement with sand and crushed stone from the liquid phase into the solid stone state assigned to it by rank. At a temperature background of + 15º and at a humidity level favorable for setting, the following occurs:
- first, a kind of sodium hydrosilicate shell is formed on the surface of the poured structure;
- then the upper layers of the poured mass are involved in the reaction - the hard grains of cement gradually suck out the moisture, due to which the components of the solution “stick together”;
- then the outer shell, losing evaporating water, begins to shrink;
- then deeper layers react;
- and further in the same sequence until after 28 days the concrete structure gains maximum strength.
If the foundation has to harden on a hot, dry day, the rate of hydration increases. But the water also begins to evaporate more actively, leaving in its place pores unfilled with bound concrete. At low temperatures, the reaction slows down, but pores appear due to the formation of ice crystals. To avoid this, the foundation is poured in winter according to special rules that make it possible to obtain the temperature of the solution required for normal hardening inside the poured concrete mass or individual pillars.
Hydration is accompanied by a spontaneous increase in temperature. The greater the thickness and dimensions of the concrete structure, the more heat the concrete generates and the slower it cools. Therefore, you should not get carried away with pouring support pillars in cold weather; it is advisable to prefer tape or monolith. If you install heat-saving formwork from insulating mats or slabs around massive structures, with minor drops in temperature you can do without additional tricks.
Concrete preparation
Not all solutions are suitable for work related to concreting, but only those to which the necessary modifiers have been added.
Their presence allows the concrete mass not to harden ahead of schedule and to have time to gain the required qualities. In addition, the presence of such substances in the solution greatly simplifies the supply of the mixture to the formwork structure.
When choosing modifiers, pay special attention to frost resistance and hardening speed. As a rule, the manufacturer puts such information on the packaging material.
Thermal mats for heating concrete
Wires embedded in concrete often burn out, and when electrodes are used, microcracks appear in the concrete, which sharply reduces the performance characteristics of the products. These problems can be avoided by using electric heating mats for concrete.
In our store you can purchase FLEXICHIT thermomats for heating concrete. Contact us!
Russia was one of the first to start producing these products. Its engineers offered construction organizations FlexiHeat heating mats made from a special resistive material. The products are produced in a standard size of 1.2x2.75 m and are equipped with built-in temperature controllers.
Use of additives
When using them, certain factors are taken into account:
- additives that are resistant to low temperatures reduce the need for water required for preparing the concrete mixture by ten to fifteen percent;
- the minimum temperature regime allowing the use of such additives is twenty-five degrees below zero;
- it is prohibited to use modifiers if the air humidity level exceeds sixty percent;
- take into account the fact that certain types of additives can react with metal;
- By adding additives, you do not eliminate the need for additional measures.
Technology
After pouring the concrete solution into the formwork, its surface is covered with a vapor barrier and heating mats for concrete are laid (working side down). Connected to a 220V power supply, thermomats smoothly increase the temperature to the set value and switch to isothermal mode. By periodically turning on and off, the mats consume less electrical energy. When the required concrete strength is achieved, the devices are unplugged and waited until they cool to a safe temperature. After this, the thermomats can be removed from the concrete surface and prepared for a new cycle of work.
In the same way, using thermomats, frozen soil is heated, placed on the site and connected to the network.
The undeniable advantage of thermomats in comparison with cable heating is the possibility of their reusable use. That is why this method is gaining more and more popularity.
Pouring technology
Soviet engineers figured out how to fill the foundation in winter. The need to carry out such work and the growth of their volumes dictated their own conditions related to the continuity of the cycle, weather conditions, time of year and temperature conditions.
The construction of the foundation in winter was based on three technologies:
- use of heated formwork in winter;
- concreting with a mixture resistant to low temperatures;
- installation of pile supports.
The first option is based on increasing the temperature by artificial means. In this case, it is necessary to install a tent on the site, isolating the heated area from the surrounding air. It is advisable to carry out such construction work at temperatures below five degrees below zero.
In its technical design, winter concreting resembles conventional casting of a monolithic tape. First, excavation work is carried out, after which the formwork is installed, into which the reinforcement frame is laid and the mortar is poured. True, there is one distinctive feature - a heating device is connected to the metal frame, maintaining the temperature of the concrete. After a few days, the tent is dismantled and the heat supply is stopped. The question arises: is it necessary to cover the foundation for the winter? Builders advise covering the entire site with a heat insulator. Resistant to water. This measure will help maintain the temperature of the foundation.
This technology is used in any weather conditions, but its cost increases due to energy consumption. Naturally, pouring without heating is cheaper, but the foundation loses its quality and is only suitable for a bathhouse.
When determining whether it is possible to lay a foundation in winter, many use additive technology. Mortars with such modifiers can be poured without additional heating, because the additives allow the concrete to set even at low temperatures.
Note that for the construction of a columnar foundation in winter, concrete is used, the moisture content of which is reduced, which reliably protects it from frost. And if you still doubt whether it is possible to make a pile foundation in winter, rest assured that such work is completely justified. True, you will have to clarify how to properly preserve the base in order to prevent it from becoming waterlogged.
The process of this method of pouring does not cause any difficulties, but the moisture level of the concrete will have to be kept under constant control.
Whether concrete is poured in winter and how this is done is clear to us. But there is another technology that allows you to build a foundation in winter on screw piles. In this case, there is no need to heat up the concrete, the volume of excavation work is minimized, and you don’t have to worry about how to insulate the foundation for the winter.
Such a foundation can be left unloaded for the winter; it does not require waterproofing.
If you have to pour a foundation for a bathhouse, consider this technology.
How to pour a foundation in winter: methods for aging the mixture
Antifreeze additives and careful preparation of the foundation pit/formwork alone are not enough for normal concrete hardening. It is necessary to maintain the required temperature and humidity conditions during the hardening process of the material.
When introducing additives into the mixture to accelerate hardening, the temperature of the concrete mass should be maintained at +10...+15 degrees for 1...1.5 days or not lower than +5 degrees for 2...3 days.
Depending on the surface modulus, that is, the ratio of the external (in contact with the outside air) area to the volume of the poured mass, the most rational method of maintaining structures is chosen.
Thermos method
It consists of maintaining the desired temperature of the concrete mixture until it reaches critical strength with the help of covering materials. Thick polymer film, bitumen sheets, roofing felt, and tarpaulin are used as such materials. You can also use mats, felt, polystyrene and foam plastic for insulation, but in this case a frame is required for laying the insulation and careful sealing of the cracks. Bulk heat insulators are laid on top of film-roll materials and protected from the wind with shields or a second layer of film/tarpaulin.
It is believed that the minimum temperature at which a foundation can be poured using the thermos method should be within the range of 0...-10 degrees at night and at least 0 during the day.
Features of the method:
- the formwork must be pre-insulated (or the insulation materials are prepared so that they are installed as they are poured);
- formwork and reinforcement are cleared of ice and snow, dried and heated using steam or heat guns;
- the supplied mixture is heated to a temperature above standard and immediately, within no more than 1.5 hours, poured with obligatory vibrating rammer;
- Open surfaces are immediately covered and thermally insulated after pouring.
It is possible to pour a foundation in winter at sub-zero temperatures using the “thermos” method only based on the results of a thermal engineering calculation - the ability of the mixture to gain critical strength at a given initial temperature of the concrete and selected insulating materials must be confirmed.
Pouring the heated mixture
How to pour a foundation in winter with heating
To do this, as already mentioned, it is necessary to pre-mount the greenhouse. Heat can be supplied to the working volume in two ways:
- air heating - heat guns, steam. Steam or air, heated to a temperature of 100...120 degrees, is supplied to the open surfaces of the concrete, to all surfaces of the formwork. The more uniformly the heating occurs, the faster the concrete gains strength. In favorable conditions, it is possible to gain critical strength in 1…2 days;
| Ambient temperature, degrees Celsius | Rated power of the heat gun, kW per 100 sq.m of heated area | Gas consumption, liters per day |
| Up to 15 | 10 | 16…20 |
| Below -15 | 30 | 60…70 and more |
| Under these conditions, the temperature inside the greenhouse is positive, about 2...5 degrees Celsius | ||
- electrical heating. There are through and peripheral heating. In the first case, rod or string electrodes are laid inside the formwork, and the current passing through them heats the entire mass of concrete. In the second case, strip electrodes are laid on the surface of the foundation, and heating occurs due to the thermal conductivity of the concrete.
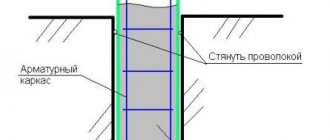
String electrodes inside the formwork
Rod external electrodes with connected generator
Important: when using electrical heating, it is necessary to take into account the presence of anti-frost additives in the concrete! With them, the conductivity of the mixture increases up to two times; accordingly, it is necessary to reduce the current strength.
Below are diagrams of the location of electrodes in different structures during concreting and diagrams of their connection.
Preservation of the foundation for the winter
It is necessary to understand how to prepare the poured foundation for the coming winter.
Actions related to deciding how to preserve the foundation for the winter are most often directed at how to cover concrete, especially that built on heaving soil. If the soil was not replaced with a sand cushion before pouring the base, there is a possibility that the structure will collapse. And if you doubt whether it is possible to leave the foundation for the winter without load, then you have already received the answer to your question.
Prevent the possibility of destruction by erecting temporary shelters. How to cover the structure, everyone decides for themselves - hay, expanded clay, straw, slag and other materials are suitable for this. An excellent solution is to insulate the foundation strip for the winter with sawdust.
How to prepare a strip foundation for winter? As soon as the concrete hardens, the formwork panels are dismantled. Conservation of the structure is carried out in several stages:
- A reliable waterproofing barrier is constructed from roofing felt or polyethylene. The material is laid on the foundation with an overlap, pressed down so that it does not blow off the wind;
- foam plastic is laid under the waterproofing or expanded clay stone is poured so that the heat in the concrete is retained for as long as possible.
If you decide to leave the foundation for the winter, you should take care to drain excess water from it. To do this, a pit is built a few meters away, and trenches are connected to it, designed to collect moisture.
Remember that only the foundation that has managed to gain final strength is insulated for winter.
How to protect a screw pile foundation for the winter? It is believed that such a design is not dangerous from frost, and such work is not necessary.
Possible options for filling at negative temperatures
The optimal method of winter concreting, which can be used for a relatively small cottage foundation in cold weather, is a “warmhouse”:
- a timber frame is constructed over the building site;
- immediately after laying the mixture and compacting it with the tips of deep vibrators, a canopy made of materials that retain elasticity in cold weather is put on;
- There are several heat guns inside that maintain a positive temperature for 3–5 days.
Tepljak is a greenhouse for pouring the foundation in cold weather.
The main difficulty of this technology lies in the need for round-the-clock duty to control the temperature in cold weather and provide a wet compress to the upper surface of the foundation. You can rent heating formworks with heating elements built into the panels, but this is unreasonably expensive for the limited budget of an individual developer.
For slab foundations, a heating cable and underfloor heating systems are used (USHP slab with ready-made communications). If the cable is laid inside a floating slab, it becomes irremovable and remains in the concrete for its entire service life, which increases the cost by 20 - 30%.
In an insulated Swedish slab, the contours of the heated floor are intended for further use, so additional costs can not be taken into account here. However, the slab must be sanded to achieve its final strength. This is difficult to do in cold weather, especially when snow falls immediately after pouring.
At the same time, it is necessary to take into account that in 70% of cases, the contours of a water heated floor are laid in the USP, into which there is nowhere to supply boiling water in winter. Electric heating is always more expensive, so it is less in demand among individual developers, even as additional heating.
What to do in winter if you need to fill the foundation?
What should builders do in the winter? Especially for those who intend to construct the foundation with their own hands? After all, winter frosts are a real obstacle.
You can, of course, close the construction site until the frost subsides. Preserving the foundation for the winter is a completely effective and quite popular option. But situations are different.
Frost outside does not always begin exclusively in winter. Sometimes it begins in the fall and lasts for a long time, even after the onset of spring. In addition, as we noted above, a single frost is not as dangerous as temperature fluctuations themselves.
The foundation does not freeze in a day or two. In the best case, it is necessary that after pouring it, the temperature outside remains above zero for at least two weeks. And even after that you need to be careful.
High-quality greenhouse for concrete mortar
What should all those people do whose goal is to concrete the foundation of a bathhouse, a private house or any other structure? Do not postpone construction for an indefinite period.
Fortunately, modern technologies used in concreting foundations make it possible to work efficiently and efficiently even after the onset of real frost.
There are such solutions to the problem of sub-zero temperatures:
- Adding plasticizers and more cement.
- Warming up the concrete.
- Construction and installation of greenhouses.
Each option provides its own temperature regime and its own approach. The first option is the simplest, the last is the most difficult. The construction and installation of greenhouses takes a lot of time and effort, but in some situations it is worth it.
We will consider these methods using the example of building a bathhouse. Baths are very often erected in winter, since the structure is small and its installation causes a minimum of inconvenience, even if you work exclusively with your own hands. The structure of the bathhouse is most often placed on a strip foundation, which has its advantages. But it also happens differently when the walls of the bathhouse are mounted on piles, using a pile screw foundation as a supporting structure. We will also mention him.
Improving the quality of the solution
The simplest solution is to improve the concrete solution. Not the cheapest, of course, but believe me, compared to other options, you will definitely win.
The advantages of this approach are obvious. The minimum labor intensity of the process of strengthening the structure comes down to adding more cement, purchasing premium grade cement, frost-resistant cement, etc.
The more cement, the faster the solution sets and the faster it cools. If there is no constant winter temperature outside, or it fluctuates, sometimes rising from +5 degrees, then dropping to slight minuses, then this solution will suffice.
The concrete will set even at the moment of pouring; then it is enough to cover it with a cloth and leave it overnight . In most cases this is more than enough. All the processes under consideration can and should be done with your own hands.
Electrodes for heating the foundation strip
An equally useful method is the addition of plasticizers. Plasticizers are special chemicals that perform a variety of tasks. With their help, natural waterproofing of the foundation is carried out in winter, strengthening it and speeding up work processes.
The brands of frost-resistant cement that are common on the market today consist of approximately 10% plasticizers.
The option of increasing the frost resistance of the solution is good when the cold winter season has not yet fully arrived. In real frosts such decisions are of little use.
Warming up the concrete
Warming up concrete involves a slightly different method of action. Here you will need a heating unit that runs on electricity. Special electrodes are immersed in uncured strip or pile foundations (the installation is generally used in any reinforced concrete structures, with the exception of installation of screw piles), and then they are heated.
Heating the electrodes increases the temperature inside the concrete and keeps it at an acceptable level for as long as you need.
High-quality heating is expensive. The installation itself costs money, heating the concrete requires a large amount of electricity, the workers also need to be paid, and you cannot complete the work with your own hands.
However, heating with electrodes makes it possible to do its job even in winter, when there are hard minuses outside and installation of structures by other means is impossible. Even after overcoming the critical point, heating the concrete mixture remains quite effective.
An example of assembling a foundation in winter (video)
Assembly of the greenhouse
When pouring massive structures, for example, forming a strip foundation for a large private house, it is recommended to make something like a greenhouse for concrete.
Builders call greenhouses for mortar greenhouses, and the process itself is referred to as installation of greenhouses.
The design of greenhouses is very similar to the design of a conventional greenhouse for vegetables. Except that the surface of the greenhouses is stronger, the frame is more reliable, and it weighs much more than a standard greenhouse.
Installation of greenhouses is an expensive business. We do not recommend doing it with your own hands, unless you are going to pour the foundation for a bathhouse or any other small building.
The influence of temperature on the condition of concrete
Let's look at why there is a belief that foundations need to be laid only in the warm season and nothing else.
This belief is justified by a mass of scientific literature and personal experience of people. It's all about the features of monolithic structures.
Standard cast-in-place concrete cannot be used until it has completely hardened. The setting or hardening process takes a decent amount of time. As a rule, the structure completely hardens on the 15th day, and on the 25th day it can already be fully exploited, that is, work loads can be transferred to it.
However, the design of a standard construction site does not allow us to properly protect the structure from external influences during concreting. In the summer, when people don’t even remember about sub-zero temperatures, builders don’t have any problems in this regard.
Another thing is building a foundation in winter, when sub-zero temperatures or real severe frost significantly affect the quality of concrete.
Frost acts on the foundation during concreting in a unique way. As you probably know, in liquid form, a monolithic mortar is a mixture of cement, sand, gravel and water.
Water is the binder in this formula; when it comes into contact with cement, it provokes a special chemical reaction. Then the solution hardens and the water evaporates . During hardening, the structure must be left alone.
Preparation for heating a concrete slab with electrodes
If it’s frosty outside, you won’t be able to simply leave the structure. In cold weather the water freezes. It freezes both on the street, turning puddles into frozen mirrors of ice, and inside a concrete structure. Small microcrystals of ice or even entire frozen floes the size of a mobile phone may well form inside a concrete block, thereby undermining its strength.
After the cold weather subsides, the water will melt and evaporate, but this will not make it any easier. In place of the frozen ice, medium and small voids will remain. The presence of voids provokes the appearance of cracks as soon as work loads are applied to the structure.
Leaving a foundation destroyed by winter frosts just like that means taking a deliberate risk.
Temperature
So at what temperature can the foundation be poured? Surely you ask.
The temperature regime is divided into several groups. Let's mark them all and then look at them individually.
So, there are the following temperature regimes:
- adverse;
- moderate;
- favorable.
Unfavorable temperature conditions are usually recorded in winter, when there is real frost outside. By and large, it is generally impossible to make concrete structures in minuses on the street. Unless, of course, you took care of the preliminary preparation.
As soon as the temperature drops to below zero and real frost sets in, the work should be reorganized, the loads should be redistributed and special equipment should be used, with the help of which it will be possible to get the job done even in extreme conditions.
Moderate temperatures range from +4 degrees to zero. This temperature most often occurs in autumn and early spring. It is still possible to make concrete structures in this mode, but you need to be careful and not leave exposed elements behind, at least overnight. However, in most cases (if there is no frost at night), it is enough to take minimal protective measures, for example, covering the formwork with fabric.
Favorable temperatures in winter are extremely rare, especially in our climate zone. We are talking about temperatures above +6 degrees. In this case, no restrictions are placed on the builders and they are free to take the steps they consider necessary when concreting monolithic structures.
Warming up concrete with a welding machine and PNSV wire
The operating scheme here is exactly the same as when using oil transformers. All the subtlety is in the calculations. So, to heat concrete with a welding transformer along with a wire, we will need a 150-250 A welder, a PNSV cable, an aluminum cold-end cable, an ammeter (pliers) and fabric-based electrical tape.
As an example, I will give a calculation for heating a 3.8 m 3 slab measuring 4x5x0.19 m at an air temperature of about -12°C and a 250 A welding machine. So, we cut the PNSV wire into sections 18 meters long. The length was determined empirically and may be different for your case. Each of these segments is capable of withstanding a current of up to 25 A. Accordingly, for a total of 250 amperes it is possible to use 10 segments. But in order not to go to extremes and leave a small margin, we will focus on 8 wires.
To each piece of PNSV we screw an aluminum wire on both sides of such a length that the twist itself is in the concrete and the cold ends reach the transformer. We insulate the twist itself with electrical tape.
How long does it take to heat concrete?
To save money, the heating time of concrete needs to be reduced to a minimum. But in each case, time is calculated separately, which is due to certain factors. These are the outside air temperature, the possibility and quality of thermal insulation, and the power of heaters.
Heating concrete with wire depends on how it is laid inside the structure and the power consumption. In general, the calculation of time depends on the temperature of the structure. In most methods, the monolith is heated to 60ºС, but this is done slowly, no more than 10 degrees per hour of heating. This ensures its uniformity, increasing the quality of the material. After the mixture reaches 50% strength, it is gradually cooled at an even lower rate of 5ºC per hour, using thermal insulation. Thus, warming up can take place over several hours or days.
Is it possible to build a house in winter?
Construction of a country house is a complex and rather long process. And if in European countries building a cottage in winter has long become commonplace, in Russia they are still wary of this. the reason is ignorance of modern technologies and materials that allow building in any weather. Let's try to find out for what period it is best to schedule the work.
Advantages and disadvantages of summer construction
Undoubtedly, summer is the optimal time to build a house. Favorable temperature, lack of precipitation, long daylight hours and other factors contribute to the prompt completion of work and help reduce their cost.
Other advantages of summer construction include:
- when constructing the foundation before the cold weather, it will have time to give the necessary shrinkage (a monolithic foundation gains its maximum strength in 28 days in summer, longer in winter);
- working with concrete in the warm season does not require the use of special anti-frost additives, which means it reduces the overall cost;
- entrances and traffic intersections are in normal condition in dry weather, thereby not disrupting the delivery schedule of construction materials;
- the construction of warm workers' cabins is not required, and electricity costs are lower; the creation of special shelters (warmhouses) is not required;
- It is easier and more efficient to maintain order on a construction site in the summer.
However, completing a full cycle of construction work in one season is only possible for small houses. In addition, if a high level of groundwater has been identified at the site, then it is more rational to construct a pit for the foundation in late autumn. Also, a significant disadvantage of construction in the summer season is the higher cost of contract work and the materials themselves.
Pros and cons of winter construction
Of course, the weather is unpredictable, but in recent years, winter in our country has become significantly milder and shorter: frosts mainly arrive in mid-December, and thaws begin in early February. Traditionally, the foundation is laid during the warm period, but today there are many technologies for effective winter construction.
The main problem in the cold season is the freezing of water at subzero temperatures (below 0°C) and, as a result, expansion in volume, causing powerful pressure. Therefore, the main task is maximum heat retention in concrete or mortar. There are several solutions to this problem:
- the use of special anti-frost additives that allow working with concrete even at –15°C (there are additives down to -20°C);
- preliminary constant heating of the concrete mixture in the formwork using electrodes, thereby increasing the time period required for the solution to set;
- construction of greenhouses (structures made of scaffolding covered with plastic film or special awnings);
- temporary insulation of masonry at the end of each working day;
- installation of heat guns under a special awning for the construction of individual structural elements.
In winter, if necessary, you can even carry out excavation work. It is known that the soil freezes by an average of 30 cm with sufficient snow cover. The soil is heated to this depth, and further work proceeds as usual.
Among the advantages of winter construction are:
- significant reduction in tariffs for contractor and labor services;
- promotions and discounts on building materials.
Winter construction has several disadvantages, the main one is that carrying out work during this period requires highly qualified specialists, experience and professionalism, knowledge of modern technologies and materials. Finding real masters is not always easy, but it is necessary because the risks in this case are too high.
In what cases is it definitely worth building in winter?
If you are planning to install a log house, then the ideal time for this is a dry, frosty winter. Thanks to slow freezing, moisture from freshly sawn timber evaporates gradually, and the structure itself shrinks evenly. In the off-season, there is a high probability of mold and mildew; in summer, the heat can cause the log to crack and become deformed. The same applies to construction from laminated veneer lumber.
Another argument in favor of winter construction if the cottage is large, if continuous work is planned until finishing is completed. Then, depending on the start of construction, some stages can be safely attributed to the winter period.
For example, if the start of construction is planned for late autumn, then monolithic foundation construction work can be safely carried out in the winter, rolled metal is significantly cheaper during this period, and by spring you can leave the ground, reach the zero level and begin masonry work, moreover, As a rule, building materials for masonry (blocks, bricks, mixtures, adhesives) can be purchased at special promotional prices at the end of winter - beginning of spring.
Thus, already in the fall you can install utilities, start heating and next winter carry out finishing work inside the house, that is, the full cycle of building a “turnkey house” will be shortened by at least 1 construction season.
Choosing the optimal solution
Despite the fact that construction in the cold season requires certain costs for the purchase of special equipment and frost-resistant additives, additional energy costs, the cost of constructing a cottage will be lower than similar work in the high season. But this is relevant in most cases only for fairly large, over 200 m2 country houses.
The ideal option is to clearly divide the construction stages by season. For small cottages, it’s time to start construction in April-May, get a finished frame of the house by the fall, either carry out conservation in the fall, or start heating and continue work inside the house in winter; if the facade is wet, then work on the facade next season (late spring - summer ).
Cooperation with Wood House Group
The construction of a country house, regardless of the time of year, requires the participation of real professionals. By choosing, you get:
- free consultations on any issues;
- accurate calculation of the estimated cost without hidden costs and additional expenses;
- a high-quality project, worked out in the smallest detail;
- a full range of turnkey construction, installation and finishing works using the latest materials, equipment, and technologies;
- strict control over the progress of each stage of construction.