The standards for building a bathhouse on a site are quite numerous, and this is not without reason: this is the only way to ensure the proper level of safety and durability of all building structures.
In order to choose the optimal location of the building and not violate the norms of SNiP and the requirements of various supervisory authorities, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with the relevant regulations or consult with competent specialists. This will avoid mistakes and costs for eliminating various violations.
>
In the photo, the distance between the bathhouse and the fence should be 2.5 meters
If a design organization is planning the location of buildings on your site, then there is nothing to worry about - all requirements and standards will be met, but if you do everything yourself, then you should familiarize yourself with the basic requirements before drawing up a site plan.
Documents regulating the rules for building baths on the site
As you know, both in residential and garden areas, the distances between buildings must meet the requirements that are regulated by the following documents:
- SNiP 30-02-97, which contains complete information on the basic rules for planning and development of garden and personal plots. This is the main document that every developer needs to study most carefully.
- SP 11-106-97 - this regulatory act will help you create a site development project that will comply with all basic standards, which will save you from alterations and improvements in the future. In addition, after studying this act, you will know all the intricacies of the approval and approval procedure - where to go, what to provide and how to speed up the process.
Let's look at the basic requirements in more detail.
Main regulatory regulations
There are quite a lot of regulations regulating the activities of bath and sauna organizations.
The main ones are:
- ZPPP No. 2300-1.
- SanPiN 1.2. 3150-13 (a document regulating both the design and operation of saunas).
- SNiP 31-05-2003 (rules for the construction of housing and communal services).
- SP 118.13330.2012/SNiP 31-06-2009 (requirements for public buildings).
- Federal Law No. 123, pay attention to table 11. This law is a technical regulation of fire safety (fire safety).
- NPB 110-03 (list defining the types of knowledge to be protected by automatic fire extinguishing systems and automatic fire extinguishing systems).
Before starting work, make sure that local authorities have not provided you with a SNiP specially developed for the city or region.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytcreatorsru
The requirements of the SES are organically linked to the provisions of current legislative and by-laws, departmental documents and standards. Among the main documents it is necessary to note:
- Law No. 52-FZ, dated 03/30/99. the document is valid as amended on July 29, 2017;
- SaNPiN: registered under No. 2.1.2.3150-13. The text was approved by Decree No. 70, issued by the Acting Executive Office of the State Service for Military Inspection of the Russian Federation on December 20, 2013. regulates a set of requirements for baths of various types;
- rules number 2.1.2.1188-03. They set out the requirements for the quality of water that fills the pool (if any);
- 2.1.4.1074-01. The document, as amended on June 28, 2010, regulates the requirements for cold water supplied to the bathhouse;
- 32670-2014. This GOST is valid as amended on July 13, 2017 and regulates the general specifications that bathhouses must comply with;
- 118.13330.2012. The mentioned joint venture was approved on 12/29/11. The document represents a revised version of SNiP numbered 06/31/2009 and establishes requirements for individual bathhouse premises;
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Penoplex for a bath, floors in a bath made of Penoplex, insulation of a bath with Penoplex
Fire safety - basic requirements
Fire safety standards should be strictly observed when building a bathhouse, because any violations can lead to a fire in the room.
First of all, you should take care of the safety of the stove, since this is by default the most important part of the bathhouse. The walls of the oven should not heat up to a temperature exceeding 120 degrees.
All walls of the building adjacent to the stove must be additionally protected from high temperatures using several methods:
- Plastering with cement mortar on a metal mesh.
- Sheet of galvanized sheet over moderately fire resistant surfaces.
- The entire contact area between wooden walls must be covered with asbestos cardboard.
Basic fire safety standards
A sheet of tin measuring no less than 50*70 must be attached to the floor in front of the firebox. Much attention is also paid to chimneys, which must have grooves in places where they pass through ceilings and retreats when burning structures are close to each other.
In addition, it is best to additionally protect the junction of the chimney with the ceiling with a sand trap around the perimeter at a distance of approximately 70 cm. This will protect the building from sparks if cracks occur in the chimney.
Advice: the chimney is the most dangerous place in a building, so after completing the work it is wise to invite a competent specialist who will inspect the quality of the structures. This will ensure that the chimney is safe.
Fire safety regulations prohibit the use of asbestos or metal pipes as a chimney in a bathhouse due to their danger and high surface temperature. The exception is the pipes of the coaxial system, that is, inside the large pipe there is a smaller pipe, and the space between them is filled with fire-resistant heat-insulating material (most often it is stone wool).
It is unnecessary to remind that all baths must be equipped with fire shields or, at a minimum, must have fire extinguishers.
SES requirements for baths and saunas (SanPiN 2.1.2. 3150-13)
Section III
Sanitary requirements for equipment, maintenance and operating hours of baths and saunas
3.1. To decorate bathhouses, materials are used that are resistant to moisture, temperature, detergents and disinfectants.
3.2. Furniture installed in bathhouses must have smooth surfaces that are accessible for wet cleaning and resistant to treatment with disinfectants.
3.3. Changing rooms must be provided with separate seats and hangers for the clothes of each visitor.
3.4. Soap bars are equipped with benches made of materials that are resistant to moisture and disinfectants.
Soap rooms are equipped with water taps and showers with mixers at the rate of one tap and one shower for no more than 8 people. It is recommended to provide a separate tap in the soap room with hot and cold water supply for washing walls, equipment and floors.
3.5. Baths and basins intended for washing must be made of materials that are resistant to corrosion and treatment with disinfectants. The number of cans is taken at the rate of at least two cans per washing area. Basins intended for washing feet must be marked “For feet.”
3.6. Steam rooms are equipped with shelves or seats. The steam room is decorated with materials that are safe for humans.
3.7. The staff room is equipped with individual lockers for separate storage of personal clothing and workwear of bathhouse workers.
3.8. The following microclimate parameters must be maintained in the bathhouse premises: in the dressing room - the air temperature is 25 - 28 C, in the soap room - not lower than 25 C.
3.9. Separate rooms (hereinafter referred to as linen rooms) must be allocated for storing clean and used linen.
3.10. Linen rooms for storing clean linen must be equipped with closed cabinets or racks at a height of at least 30 cm from the floor, with a coating that allows wet cleaning and disinfection.
3.11. Linen rooms for storing used linen must be equipped with racks at a height of at least 30 cm from the floor, with a coating that allows wet cleaning and disinfection.
When storing used linen for more than a day, provision must be made for drying the used linen.
3.12. In dressing rooms and soap rooms, containers with lids should be installed to collect used linen, brooms, and bath accessories.
3.13. Baths are provided with cleaning equipment, which must be marked and used in accordance with the marking depending on the purpose of the premises (toilet, entrance group of premises, soap and steam room, dressing room), stored in specially designated areas or in a separate closet.
3.14. During the working day, routine cleaning should be carried out in the bathhouse premises: washing the floors, benches in the dressing rooms, as well as washing the floors, benches with a hose in the soap and steam rooms. At the end of the working day, in the absence of visitors in the bathhouse, all premises are cleaned using disinfectants.
3.15. Once a week a day is allocated for general cleaning. During general cleaning, the surfaces of floors and walls in all rooms, as well as benches in changing rooms, soap rooms and steam rooms, are washed using disinfectants.
Elimination of current finishing defects (elimination of leaks on walls and ceilings, cracks, crevices, etc.) is carried out during general cleaning.
3.16. Deratization and disinfestation are carried out at least once a month.
3.17. Waste generated as a result of bathhouse activities must be collected and disposed of.
3.18. Bathhouse workers must undergo preliminary, upon employment, and periodic medical examinations in the prescribed manner2; certification for knowledge of these sanitary rules at least once every 2 years.
Bathhouse workers must be vaccinated in accordance with the national calendar of preventive vaccinations, as well as according to epidemic indications3.
Each bathhouse employee must have a personal medical record, which must contain the results of medical examinations and laboratory tests, information about vaccinations, previous infectious diseases, information about undergoing professional hygienic training and certification, and permission to work.
3.19. Bathhouse workers must be provided with special clothing and personal protective equipment. Laundry of work clothes must be organized.
Where should the bath be located?
There are certain standards for building a bathhouse on a plot of land, compliance with which is regulated by regulations. Violation of these provisions is highly undesirable and may result in the most severe sanctions from supervisory authorities.
Distances from buildings to the fence
So, there are the following standards for the construction of a bathhouse from a fence:
- According to the standards, the distance must be at least 3 meters, this is due to the peculiarities of draining wastewater from the building. The optimal solution is a separate drain or gutter, in which case the distance to the fence can be reduced to 2.5 meters.
- Any deviations from the norms must be agreed upon between neighbors in writing to avoid problems in the future when the owner of the property changes.
- In any case, the distance to the fence should not be less than 1 meter; this minimum permissible distance must be observed.
You should not save space between the bathhouse and the fence in order to avoid violation of norms and requirements
In addition to the distance to the fence, there are other standards for the location of the bathhouse on the site:
- The distance from the residential building to the bathhouse must be at least 8 meters.
- There must be a distance of at least 12 meters from the well to the bathhouse building.
- If the bathhouse is located on a dacha or garden plot, then the borders of the neighboring plot must be at least 8 meters.
Requirements for ensuring epidemic well-being
These requirements imply:
- monthly activities to exterminate rodents and parasites;
- ongoing elimination of defects in floors and walls (as cracks form);
- weekly general cleaning;
- routine cleaning during the working day;
- the final “promenade” of the cleaning employee at the end of the working day, the last cleaning is done with the mandatory use of disinfectants.
The SES will definitely check the disinfection log and the consumer’s corner in the sauna.
Sanitary requirements for the construction and operation of a bathhouse
As is known, sanitary standards for baths affect mainly public institutions, while structures for personal use are affected much less, which often leads to violation of various norms and rules that affect the quality of recreation and safety of operation.
Basic sanitary standards for the construction of buildings on the site
What needs to be considered during the construction process
- The instructions for a public bath pay great attention to a high-quality ventilation system; this is no less important in small buildings, because the durability of the structures and the quality of their drying directly depend on this. In addition, musty air is not conducive to a good rest in the steam room.
- The installation of high-quality drainage is also important; defects can lead to the appearance of fungus and the proliferation of various pathogenic bacteria.
Advice: you should not skimp on materials for thermal insulation of the steam room; the durability of the structure and the quality of ventilation directly depend on them. The low price of insulation is the first indicator of its low quality.
Why compliance with sanitary and building codes is so important
During construction, first of all, it is necessary to take into account all the features of the project. It is worth understanding that compliance with all standards is intended to ensure the maximum level of safety during operation, as well as ensuring the best quality of rest. Any deviations can reduce the benefits of bath procedures and make staying in the steam room dangerous.
All distances between objects should be carefully checked
Factors to consider when building a public bath
To ensure high popularity and stable profitability, public bath projects must meet the following conditions:
- All premises must be spacious and comfortable for visitors. In addition, the presence of both male and female sections significantly increases the comfort of the bathhouse for clients.
The spacious locker room will be appreciated by clients
- Anyone who runs a bathhouse as a business will confirm that good repairs and the use of quality materials are no less important than a good steam room. Only an attractive environment can make a bathhouse popular - black spots on the walls and old furniture will not appeal to any client.
- Good instructions posted in the rest room or near the cash register will allow visitors to better understand the intricacies of the process of visiting the bathhouse. This is important, since there are many misconceptions among the population regarding visiting the steam room.
- Additional service in the form of trade in related products: from towels and washing supplies, to drinks and brooms. The latter are also very important; some people prefer to do them themselves, but most visitors will choose a bathhouse, where you can purchase a broom on the spot. The price of the broom should be reasonable, which will also be appreciated by customers.
- The relaxation room is just as important as the steam room. Visitors really value convenience and the level of service is judged both by the quality of the steam and by the relaxation room, in which they spend much more time.
TVs are increasingly being used in modern lounges to attract sports fans.
Design of a modern Russian steam room
Previously, it was believed that the interior should strictly correspond to the traditional ideas about the bath culture of a particular people. In the modern world, this statement is not so legitimate, since designers skillfully use all fashion trends to harmoniously combine them with traditions. For example, when it comes to the interior of a Russian bathhouse, the first thing that comes to mind is the abundance of natural wood. It is present in the interior decoration, functional pieces of furniture and decorative elements of all rooms of the bathhouse. Indeed, often they try to decorate bathhouses with the help of simple wooden tables and benches, and be sure to place a wooden tub in a prominent place. But if you use a little imagination, you can turn a traditional Russian bathhouse into an ultra-modern, eco-friendly interior.
The main requirement for the modern design of a Russian bath or Finnish sauna is that their interior does not distract a person from deep relaxation with objects of rough shapes or complex designs. In finishing, comfort and naturalness of all materials should play the first fiddle. Therefore, wooden decorative items and furniture, first of all, should not have an unpolished surface or sharp corners.
If you are a follower of minimalism in the interior, then limit yourself to the most necessary things that you cannot do without in the bathhouse. Look for contemporary furniture designs with smooth surfaces, rounded edges and flowing shapes. And if you prefer decoration in a traditional Russian style, then furniture of rougher, simpler shapes would be appropriate.
The color scheme needs to be soft; the warm color of natural wood is best. Avoid using plastic buckets or metal containers as decorative items. Use wooden tubs instead.
Do not overdo it in the number of decorative elements, so as not to turn the bathhouse into an exhibition of folk crafts. Try to adhere to reasonable minimalism in the interior.
This recommendation is especially important for a steam room, since there should be no unnecessary items in it. Well-chosen spot lighting will help modernize the interior of the steam room. It is important to light the space in such a way that the room remains dark and maintains an aura of calm and intimacy. It is recommended to decorate wall lamps with simple shades made of natural wood. The lighting built into the multi-tiered shelves in the steam room also looks beautiful.
In the interior of a modern Russian bath, the washing room is not much different from the same Finnish sauna. It is customary to install a shower and washbasin here, and you can also organize a bathroom. In the simplest version, there should be a drain in the washing room and a large container with cool water. The dressing room or relaxation room is traditionally equipped with comfortable upholstered furniture, as well as a table for organizing a friendly tea party.
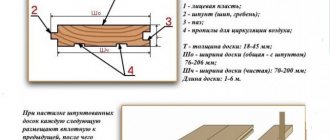
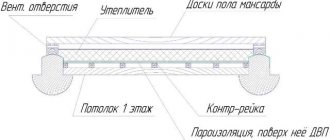
Rules for building walls and procedures
Frame wall pie with additional insulation.
Before starting the construction of a frame bath, you need to make sure that the wood used in the work is completely ready. It must be well dried. The type of wood can be any; in this matter you can rely on your own preferences. The main thing is not to use birch, which rots very quickly, and all other types of trees are suitable for work. Most often, the choice falls on linden, larch or aspen, which are characterized by low thermal conductivity and long-lasting shape retention.
For external cladding it is better to use pine or larch, and for internal cladding all types of trees will do, but in most cases aspen is used.
After all the work is completed, the outer boards must be coated with an antiseptic, and the inner lining, if possible, must be sanded and then coated with furniture varnish, preferably in two layers. It would also be advisable to use special impregnation, which is necessary for all rooms except the walls in the sink and steam room.
The bottom trim will be stronger if it is made of strong timber; a timber with a cross-section of 10x10 cm is suitable. It will need to be connected in the corners and fastened with nails. The resulting bottom trim must be securely fastened; for this, the corner posts must be installed on steel pins, so they will not move.
The simplest and most affordable material for the outer cladding of a bathhouse is considered to be lining (imitation or decorative). The placement of the lining along the external wall is carried out in a horizontal direction, having previously laid down parchment, which will act as waterproofing. The sheets must be laid out overlapping and glued with tape to prevent moisture from penetrating inside.
Site marking and excavation work
When the documentation is completed and the site for the construction has been chosen, you can begin the actual implementation of the project. The first step is to make markings for excavation work. You will have to dig trenches for the foundation itself, for water supply and sewerage. You need to think about such things in advance - after the building is built, it will be much more difficult to supply water and sewerage to it.
Marking
Before marking, you need to clean and level the area to be marked. Next, decide on the location of at least one wall. The entire outline of our foundation will subsequently be built from it. To do this, we hammer in two pegs at a distance slightly exceeding (30–50 cm on each side) the length of the wall and pull the lacing between them. This will be the boundary of the outer foundation wall. Next, using the “Pythagorean triangle” (a triangle with sides 3:4:5 is rectangular), we build two segments perpendicular to the base of the wall. And again, the pegs are driven 30–50 cm beyond the border of the future trench. In the same way, we close the contour of the straight line showing the boundary of the rear wall. The intersections of the lacing will coincide with the outer corners of our foundation. We check the correctness of the formed contour with diagonals. In a rectangle they will be equal and when intersecting they will be divided in half. In a similar way, the internal contour of the foundation is marked, as well as trenches for water supply and sewerage. By the way, when marking, it is better to use pegs with a height no less than the planned height of the base; this will save you from additional labor costs.
Sewerage
When all the trenches are dug, they begin to install water supply and sewerage systems. For the manufacture of the latter, PVC pipes with a diameter of 40–50 mm are quite suitable. Both the sewer riser itself and the connection to the drainage pit are made from them. The installation depth of the drainage system depends on your region, more precisely on the depth of soil freezing (according to paragraph 4.8 of SNiP 2.04.03–85, a tray for a sewer pipe with a diameter of up to 500 mm should be located no higher than 300 mm from the maximum freezing depth of the soil, but no less than 700 mm to the top pipe points). The slope is chosen as standard for this diameter, 30 mm per linear meter. This is done as follows: wooden pegs or pieces of reinforcement 70–120 mm high are driven along the marked area under the trench at intervals of 1.5–2 meters, “0” is stamped on them using a water level, and then the slope itself is modeled with lacing. Now, when carrying out excavation work, it is easy to control the depth of the sewer trench simply by measuring the distance to the string attached to the pegs.
1 - 1 m; 2 – slope 30 mm
By the way, the depth of the trench should be fifteen centimeters deeper than the planned depth of the sewer pipe; this is done specifically for the sand cushion. The pipe never rests directly on solid ground. The bottom of the trench is filled with sand, the latter is leveled at the required slope. Next, a pipe is installed, which is again covered with a ten-centimeter layer of sand. All this is compacted and only then the trench is filled with solid, previously selected soil.
Water supply
The situation with water supply is more complicated. There will be a constant column of water in the water pipes. And for an irregularly heated room, this state of affairs is fraught with at least the formation of ice plugs, and even damage to the plumbing system itself. The situation will be saved by a self-regulating heating cable placed under the thermal insulation of the pipe. Since you will only have to heat the area from the freezing depth to the tap, such a system should not really ruin you. But if you think that this is still unjustifiably expensive, then you don’t have to supply water to the bathhouse at all, using the supplied water. Anyway, it will be easiest to heat it on the heater itself, and you can fill the shower tank directly from a bucket.
If necessary, installation of water supply is carried out by analogy with installation of sewerage, except that there is no need to maintain the slope.
Capital buildings
These are independent buildings, erected on a buried foundation and equipped with basic communication systems. Unlike “temporary buildings”, a permanent structure cannot be moved to a new location.
The owner of a capital object must register it with Rosreestr, and in the future - pay tax on the ownership of real estate.
Let's look at the catalog again. Capital buildings - projects of two-story bathhouses made of timber and those one-story ones that are built on a permanent foundation.
Important. *The construction of a one-story bathhouse is considered a secondary building, and a building permit is not required"