The foundation is poured into pre-arranged formwork. This structure must be installed in compliance with a number of established rules and regulations. Familiarize yourself with the features of existing types of formwork, the procedure for their calculation, instructions for the construction of the most common structures and get to work.
DIY foundation formwork
Of course, before erecting the formwork, you need to decide on the type of foundation that you will build. We recommend reading the following materials on our portal:
How to make a strip foundation with your own hands - first of all, we suggest you familiarize yourself with the step-by-step technology for constructing a strip foundation. In which, among other things, it talks about the method of constructing wooden formwork.
In addition to the strip foundation, we recommend that you familiarize yourself with the material on constructing a columnar foundation with your own hands, because This is a fairly popular type of foundation in Russia.
Purpose of formwork
The design is designed to prevent liquid material from spreading. Due to the limited space, concrete maintains its given geometry and position in space, dries evenly and acquires the required strength.
Basic requirements for formwork for strip foundations:
- high strength, resistance to the pressure of the liquid mixture inside a given volume and external influences;
- stability of the dimensions of the internal space (the geometry of future base elements);
- the possibility of unhindered pouring of the liquid mixture into the mold, reinforcing the monolithic foundation.
Technical requirements for formwork are collected in GOST 52085-2003, but they relate to industrially used auxiliary structures. For self-installation of formwork, only basic conditions must be met.
Features of different types of structures
There are removable - removed after hardening - and permanent formwork.
Removable formwork for foundation
This name refers to auxiliary structures that are removed after the concrete mixture has gained partial strength. Removable elements consist of panels (solid or plank) and fastening and fixing elements connecting them. If reinforcement is provided (almost always for strip bases), supplies and spacers are added to the standard set to prevent contact of the reinforcement grids with the soil and the inner surface of the pouring forms.
Important: the removal of the formwork occurs before the final curing of the concrete, therefore, when carrying out further work, you should focus on the “maturation” time frame of the foundation, depending on the grade of concrete, weather conditions and the dimensions of the structural elements.
Permanent formwork
Fixed forms are considered to be pouring molds that remain in the building structure after the mixture has cured. This type of structure provides additional strength to the building, its heat, sound and waterproofing properties, and other characteristics. Typically, special blocks made of polystyrene foam, fiberboard and other materials are used as material for permanent structures.
Important: constructing a house using permanent forms significantly speeds up construction, improves the operational characteristics of the building, but at the same time increases the cost of the work.
Asbestos sheets or flat slate
These materials are also used for both removable and non-removable structures. However, it must be taken into account that such sheets have good adhesion, so they are difficult to separate from the finished concrete base. In this regard, when creating removable formwork, the panels must be treated with a composition that makes it easier to dismantle structures.
If we talk about the advantages of such materials, then it is worth highlighting their low cost and ease of processing. The sheets can be easily cut directly during the formwork process. But it takes quite a long time to build. The fact is that in order to secure the spacer and thrust elements, holes for the screws will have to be made first. Since the material is highly fragile, there is a risk of damage to it.
Also today there are ready-made formwork structures made of synthetic materials on sale. They are lightweight, easy to install and can be used repeatedly. They are not cheap. Therefore, everything depends on the budget. But, one way or another, you need to take into account the characteristics that removable formwork should have.
Calculation of formwork for the foundation
In this case, calculation means the calculation of the required thickness of the boards or boards of the structure, taking into account the distance between the supports, the specific gravity of the mixture being poured and the resistance ability of the mold material. The traditional, simplest formwork design consists of panels installed at the bottom of a pre-dug trench, held in a vertical position by special supports.
The choice between stakes or braces depends on the volume of the mixture being poured and the type of soil: for small foundation strips (250...400 mm) and dense soil that is not prone to shedding or sliding, stakes are sufficient. If in doubt, it is better to give preference to braces, since they are able to hold the panels in place even with increased load.
Formula for calculating the thickness of shields (minimum)
h = √((0.75×G×n×l^2)÷T)
Here
- G is the load of the liquid mixture on the formwork, it is assumed to be maximum and is defined as the product of the specific weight of concrete and the thickness of the poured layer G = qx H. The specific gravity is q = 2500 kg/m3, H is the height of the foundation strip in meters;
- n is the compaction coefficient of the concrete mixture. If vibration compaction is not used, the coefficient is equal to one;
- l – distance between shield supports, in meters;
- T – load resistance of the board material; for wood it is assumed to be 8 x 105 kg/sq.m.
Taking into account the difficulty of independently determining the grade of concrete, respectively, its density, as well as the lack of accurate data on the resistance of the material of formwork panels, calculations are carried out approximately, for average values. Typically, the thickness of the board is taken to be 25 mm.
The second part of the calculation is determining the required number of boards of a given thickness and the number of fasteners. For these calculations, it is necessary to know the length of the foundation strip and the height of the fill. The length of the tape is multiplied by two, since the shields are located on both sides. When installing a strip foundation with a step, the calculation is carried out twice - for the first and second stages of pouring. The amount of lumber is determined based on the data on which board for the foundation formwork will be used (dimensions).
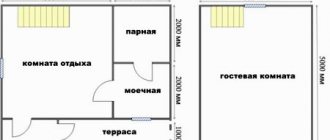
Drawing up a plan similar to that shown in the illustration will help you navigate a more accurate calculation of the required length of the form, the number of connecting and supporting parts.
Renting formwork panels is a great opportunity to avoid mistakes and save your time!
Although making shields yourself can reduce the cost of the construction process, it is still not an easy task and requires skills. Otherwise, you risk losing both money and your time. ]Ordos Formwork offers you to rent formwork panels[/anchor]. All of them are in excellent technical condition. Delivery, installation, dismantling and maintenance of equipment are included in the rental price. Linear panels are always available for both small-panel and large-panel formwork. The kit includes a full range of fastening elements. To get more information regarding rentals, contact our consultants.
Do-it-yourself formwork for a strip foundation
In order to correctly form the base of the building, it is necessary to correctly install the base for pouring. We will analyze two design options, based on removable wooden and permanent foam formwork.
Regardless of what type of form is used, part of the work performed is carried out according to a single scheme.
- Site marking. It is done using stretched cords or fishing line (in the illustration “cast-off strings”) according to the building construction plan.
- Digging a trench. In this case, it is necessary to dig out a ditch according to the depth of the future foundation, taking into account the cushion under the foundation and the depth of soil freezing (you can read in more detail about the principles of constructing a foundation and preparing a place for it in the article). Since creating strictly vertical walls is practically impossible, they try to create a slope with a minimum slope, about 15...30 degrees to the vertical.
- Compaction of soil at the bottom and walls of the ditch. Tamping is done manually or using special mechanisms. This process is especially important for loose soils. Tamping can be replaced by the use of geotextiles - a special material that prevents soil shedding.
- Creating a foundation cushion. For it, sand of large (1...3 mm) fractions, fine crushed stone or granots, pre-washed and dried, is used. To enhance the load-bearing capacity of the base, the cushion is poured with a liquid cement mixture; in especially critical cases, concreting is performed.
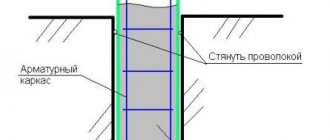
- The formwork is being installed. Slots and gaps between structural elements should not exceed 2 mm, the strength of the structure should correspond to the required one, taking into account the thickness of the poured layer.
- The fittings are being installed. The installation of rod systems and meshes is planned with the obligatory preservation of the protective layer of concrete from the metal to the external environment. You can read more about the rules for tying reinforcement and its protection against corrosion in the feature article.
- Pouring concrete mixture.
- Vibration compaction (if possible).
Depending on what type of forms is used, the nuances of the technological process of installing the formwork and, in the removable version, its removal change.
Installation of formwork from boards or plywood
Due to the successful combination of load characteristics and price, edged boards for foundation formwork are the most popular and popular option. The wood used is water-resistant species (pine, alder, birch) with an initial moisture content of 18...25%. Boards made from boards are assembled using bars on nails or self-tapping screws. In this case, the points of the fasteners should extend to the outer (facing the ground) side of the boards.
The knocked down panels are installed on the prepared cushion, reinforced with braces or stakes with a pitch of 800...1000 mm. To prevent the structure from spreading under the weight of the poured mixture, the opposite panels are connected by spacers.
As an option, first a box is mounted on the base of shields and cross braces, after which the finished structure is laid in a trench and fixed with stakes.
Important: there should be no gaps between the boards! Otherwise, the solution will begin to flow into the gaps, and the consumption of concrete will noticeably increase. Possible formation of voids inside the poured form, violation of the strength calculations of the foundation.
Proper formwork can easily withstand the pouring of concrete mixture and is easily separated from the hardened base after initial curing. The period for stripping (removing formwork), depending on temperature and humidity conditions, is 8…20 days. At subzero temperatures, it is undesirable to disassemble the form-building structure, since the time it takes for concrete to gain design strength slows down in proportion to the decrease in temperature.
How to assemble formwork for a foundation from foam blocks or panels
Industrially produced foam blocks or panels are manufactured with their own tongue-and-groove fastening system. Thanks to this, connecting the elements of the future form is not difficult:
- the first row is laid according to the markings so that the line is perfectly straight;
- the second and subsequent rows are mounted taking into account the location of the reinforcing bars - they must pass strictly through the cavities in the blocks. For panel options, displacement is allowed;
- concrete is poured only by hand, after installing every three to four rows of foam blocks.
Important: low-quality (crumbling, irregularly shaped) blocks are only suitable for low-impact buildings with low loads.
If you want to create permanent formwork with your own hands, you should choose the option with a two-layer structure. The outer layer is a sheet material that defines the geometry (as is the case with removable formwork), the inner layer is sheets of foam plastic or expanded polystyrene. Concrete is poured into the cavity between the internal heat-insulating layers, which are not subsequently removed. The outer layer is dismantled after the mixture has cured.
Nuances of formwork installation for different types of foundations
In low-rise private construction, a strip base is the most common option. However, he is not the only one. Slab and columnar foundations are also used.
Formwork for columnar foundations
In this case, in addition to the general trench, deep holes are dug for columnar supports. They are located along the perimeter of the future building so that there is a support at each corner or intersection of the walls.
The formwork itself is also made from boards, plywood or other sheet materials using the technology described above. The difference is the arrangement of the limiting elements in the form of a vertically located tetrahedral prism (a column of rectangular or square cross-section) or a cylinder. Filling is done from above. Reinforcement of a columnar foundation is carried out separately for each support, followed by piping.
In this case, the column has either the same cross-section throughout its entire height, or an enlarged lower step.
It is mandatory to place a cushion under the foundation supports; the lower step can be poured into the ground without formwork, but at the same time reinforced. Formwork is installed for the upper part of the support, and the reinforcement of the upper and lower parts is tied together. Supports that are simple in shape and have a limited load can be concreted without reinforcement.
If it is planned to install a monolithic grillage on top of a columnar foundation, the formwork for it is carried out separately, in the form of a box.
Formwork for foundation slab
The main difference between this type of limiter is its one-sided arrangement: the shields outline the shape of the future slab along the outer sides.
Important: when installing this type of formwork, you should be more careful when calculating the strength of the structure, since the load on the panel stops increases in proportion to the size of the slab.
Foam blocks are not used as permanent formwork for slab foundations. If it is necessary to make the limiters non-removable and at the same time use them to insulate the base, use flat sheets of foam or polystyrene.
Self-production of formwork on the construction site
Photo of making a panel structure from boards for the base
It is not difficult to make wooden small-panel formwork yourself, and many private developers often do this. To do this you need to prepare:
- dry larch logs or other moisture-resistant wood;
- cardboard or film;
- a regular construction stapler or hammer;
- bars for connecting panels;
- fasteners and clamps.
First you need to prepare and cut the boards to a given length, and you need to buy them with a thickness of at least 1 cm. The thicker the board, the stronger it will stand, and the fewer fasteners you will have to use. Then the shields are nailed down with the head facing the inside of the structure. The board is fixed with beams, forming perpendicular connecting links. To ensure the most even and smooth surface of the board, a thick film or cardboard is glued over the wood and secured with a stapler.