Finnish sauna is dry heat with a tonic effect, hammam is an oriental ritual aimed at relaxation. It is impossible to say unequivocally which is healthier, a sauna or a hammam - there are too many differences both in the surroundings of both rituals, and in the mechanism of action of each bath.
To choose “your” steam room, you can go in two ways - based on a specific goal (indications) or conduct an experiment and make a choice based on personal feelings. For example, the gentle warmth of a hammam is ideal for getting to know bath culture in general, and a sauna is for seasoned people with a strong cardiovascular system.
Differences between a Russian bath and a Finnish sauna and Turkish hammam
Every major civilization has its own recipes for healing, cleansing and beauty, but only the Finnish sauna, Turkish hammam, and, perhaps, Japanese Shinto can be compared with a Russian bath. Although cleansing and healing occurs everywhere with the help of steam, there are differences in the principles of construction, temperatures and importance.
Russian bath
What and how are they built from?
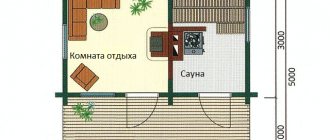
From the point of view of construction, the Finnish sauna is most similar to a Russian bath: both are built of wood, the interior decoration is also made of wood.
They have a separate room with a high temperature, where they stay for a short period of time: a steam room. There is a separate dedicated room for water procedures and another one for relaxation.
In this, both the Russian bath and the Finnish sauna are similar.
Turkish hammam is a clay or stone (brick) structure, lined with different types of stone. Ideally it is marble, but any stone or ceramic tile will do. There is a dedicated dry changing room, and the rest is a vast hall with adjacent open rooms (without doors), where they wash and rest. There is another room in the hammam - a technical one - it contains a stove and a steam generator.
Finnish sauna
Air condition
More differences in the principles of the steam room:
- The Russian bathhouse does not have the highest air temperature - about 50-70°C, the air humidity is high from 50 to 70%.
- In a Turkish hammam: the temperature is not higher than 45°C, and the humidity is close to 80-90%.
- The Finnish sauna is distinguished by high temperatures - up to 100 and even 120 ° C and low humidity - no more than 15%.
What do these different states provide from a physiological point of view? Different states. In a dry-air sauna, even its high temperatures are easier to tolerate. There is little moisture in the air and a lot of oxygen. Therefore, a person with a healthy heart and vascular system can sit longer. Finns, by the way, do not heat the air above 90°C. 120-140°C is already too much for us.
When the ambient temperature rises above 36.6°, intense sweating begins. This is the principle behind the “working” of the steam room.
At such a high temperature, sweat, of course, is released.
But it instantly evaporates from the surface of the skin. All these vapors are in the air of the steam room. By inhaling, we get a significant part of them back.
Good ventilation improves the situation slightly, but vapors are still present in the air.
In a Russian steam room, sweat does not evaporate. Firstly, the temperature is not enough for this, and secondly, there is almost nowhere: there is so much moisture in the air. Therefore, sweat flows on the skin and needs to be wiped off.
In a Turkish hammam, the temperatures are very low, and there is a lot of moisture in the air. It condenses on all cool surfaces. The human body with its temperature is just such a surface. Most of what flows over the skin in the hammam is condensation, not sweat.
From the point of view of sweating intensity, the Russian steam room is an ideal compromise between a sauna and hammam.
Turkish hammam
Technical details
The main difference between a bathhouse and a sauna is the thermal regime. In a sauna it is necessary to heat the air to a high temperature. Here you need a powerful stove that quickly transfers heat. To speed up the heat transfer, a metal casing is made around the furnace body, which is located at some distance from the furnace body.
Cold air, which is located near the floor, is sucked into this gap from below. Passing along the hot wall of the oven, it heats up, quickly rises, hits the ceiling and spreads throughout the steam room. The transfer of heat through air is called convection, and these screen-casings are also called convective.
With this structure of the furnace, heating occurs really quickly.
In saunas, the air warms up quickly due to active air movement
In Russian doubles the task is more difficult. You need to get a lot of steam, which requires very hot stones and active combustion. But, on the other hand, you cannot overheat the steam room - the temperature should be within 40-60°C. Such conditions are easily created by a brick oven.
In the firebox, inside, stones are placed, which heat up quite quickly from the fire. The stove itself heats up slowly: there is a lot of brick, it has a heat capacity.
After a few hours, the stones are already red-hot, and the wall of the oven and the walls of the steam room only have a temperature of 50-60°C.
But today, a brick oven and its long heating are not a pleasure for everyone. Metal stoves are installed much more often. But they are suitable for a sauna. For a bathhouse, they need to be completed: reduce heat transfer from the walls. This can only be done by shielding it. There are two ways to reduce heat transfer:
But that's not all. Stoves with a closed internal heater are suitable for this modification. Only in it will the stones heat up enough to produce a sufficient amount of steam.
Heaters located around the body or on top are not suitable for this purpose. Firstly, they cool down quickly, and secondly, the steam turns out damp and heavy.
This is the main difference between a sauna and a bathhouse from a technical point of view.
A brick stove creates ideal conditions for a Russian bath
With a Turkish bath the situation is completely different. In the hammam, to produce steam, a special steam generator is installed, located in a special room. Steam is supplied to the steam room through pipes, which at the same time warm the room.
A steam generator is a large vat in which heated water boils. The temperature of such steam is 100°C and no higher. There is no talk of any ease here. The steam is wet and heavy. It swirls and stays mostly at the bottom. In a Russian steam room, all the steam is concentrated under the ceiling. It is from there that they take it out with a broom and drive it along the body.
There is also a difference in heating. In the sauna and Russian bath, the air is heated from the stove, and in the hammam the walls and floor are heated, as well as special stone seats and loungers, from which the air is already heated.
Source: https://baniwood.ru/otlichiya-russkoj-bani-ot-finskoj-sauny-i-tureckogo-xamama.html
Benefits and harms
Doctors confirm that hammam has a positive effect on the human body. According to experts, the Turkish sauna helps treat colds, asthma, bronchitis and cholera.
Unlike the Finnish sauna, the Turkish bath has a gentle temperature regime, which the body tolerates much more easily. A person relaxes here, and heated sun loungers and the floor contribute to this even more (for more details: “How a Turkish hammam is built - about construction and properties”).
Which bathhouse is better - Russian, Turkish or Finnish?
Nowadays three types of baths are popular in Russia - Russian, Finnish and Turkish hammam. Their difference from each other is only in humidity and air temperature (the situation does not count here).
The different ratio of the percentage of vapor in the air and its temperature determines the different effects of baths on health.
Many people continue to visit the bathhouse they entered for the first time, but they could choose a more suitable option for themselves if they understand this topic a little. So, briefly about the features of different types of baths and their effect on the body.
Russian bath
The Russian bath is characterized by high air humidity combined with moderate temperature - no higher than +50 C. There are several other aspects that are unique to the Russian bath and have an impact on the body. For example, in a Russian bath it is practiced to use a broom, which has a powerful cleansing and massage effect on the skin.
In addition, compared to a Finnish sauna, where people simply lie on the surface, a Russian bath involves movement in the steam room - following groups, dispersing stagnant air with a sheet, climbing onto shelves, whipping yourself with a broom, jumping into an ice hole, and so on. And movement in a hot room puts a slightly different load on the body's systems.
The effect of a Russian bath on the body is still contained in the genetic memory from previous generations, so adaptation to it occurs quite quickly. High humidity puts increased stress on the cardiovascular system, but it perfectly heals the lungs and bronchi.
Vapors from aromatic plants add an effect for the treatment of pulmonary diseases. The therapeutic effects of the Russian bath are also used to relieve attacks of rheumatism, arthritis and osteochondrosis.
If you have skin problems, then you need to choose a Russian bath, since the combination of mechanical treatment with a broom with hot, humid air (and even better, if cold procedures are added) gives the best cleansing effect.
Complete cleaning of the pores makes the skin “glowing” and healthy in appearance, while massage and cold water increase tone and elasticity.
Turkish hammam
In Turkey, probably due to the hot climate, the softest and most humid bathhouse has traditionally developed. The temperature here does not exceed 45 degrees, but the entire room is shrouded in thick clouds of steam.
There is no sharp effect on the body, as in a Russian or Finnish bath (broom, cold water or extremely high temperatures). That is why the Turkish bath is recommended for those who are just starting their bath experience or for people with heart problems.
To begin with, a Turkish bath is an ideal option to get a taste for and enjoy the bath, but after a Russian bath it may seem too “fresh” and soft. The effect of a hammam on the skin and musculoskeletal system is similar to a Russian bath, but a little weaker.
There are no harsh or tonic factors that can harm heart patients or unaccustomed people.
Finnish sauna
Although it originated from the Russian bathhouse, it has undergone significant changes over the centuries. The peculiarity of the Finnish sauna is that it is not a steam room in the usual sense of the word. That is, steam is not used at all.
Dry air heats up to a very high temperature (70-90 C), which activates sweating. The Finnish sauna does not use a broom, frequent dousing with water directly on the shelf and cold procedures. The atmosphere of a traditional sauna is dry, intense heat with the aroma of pine trees and lying motionless.
Low air humidity creates the best conditions for the treatment of rheumatism, arthritis, osteochondrosis, ankylosing spondylitis, radiculitis and other diseases of the musculoskeletal system. Strong dry heating generally has a positive effect on any inflammatory processes, causing them to decrease.
Many people physically tolerate hot dry air in a sauna more easily than the humid “stuffiness” of steamy Russian and Turkish baths.
To summarize: when choosing “your” bathhouse, you can go two ways. The first is to try them one by one and, based on personal experience, choose the most suitable option for yourself. For such lovers, the Turkish bath in Moscow has created all the conditions. The second way is to start from a specific goal.
For example, the Turkish hammam is for starters (gaining experience and getting involved in the bath culture) and for those with heart problems, the Russian bath is for vigor, hardening, improving the condition of the skin and blood circulation, the Finnish sauna is for lovers of dry heat and for the treatment of diseases of the musculoskeletal system.
Source: https://laguna-spa.com/kakaya-banya-luchshe-russkaya-tureckaya-ili-finskaya
Roman bath
One of the most ancient types of baths. In fact, the baths are prototypes of Turkish hammams. These are also stone buildings with central heating and heated floors and walls. The modern Roman bath is distinguished by marble-clad rooms with heated marble loungers. The thermal bath was divided into separate rooms that had to be visited sequentially. They were called: caldarium, tepidarium, frigidarium.
The modern caldarium is a room decorated with ceramic tiles, heated floors and a large bathtub with water. Humidity in the caldarium is kept at 80-100%, temperature 37-45⁰С. The room is usually filled with the aromas of essential oils of healthy herbs and plants. Great importance is attached to design; caldariums are usually decorated in warm colors, with picturesque paintings from the life of Ancient Rome placed on the walls.
Tepidarium is a room with dry warm air. The temperature here, just like in the caldarium, is maintained at 37-45⁰C, but the humidity is much lower, only 30%. The tepidarium is equipped with marble beds and armchairs. Heating, as in all rooms of the Roman baths, is carried out from below. The tepidarium is comfortable for a fairly long stay. After visiting it, the body will require replenishment of moisture.
Frigidarium is a cool room with a swimming pool, where you go after visiting the tepidarium and caldarium to refresh and relax.
What is better than a hammam, a sauna or a bathhouse: what are their differences?
Beginners to the bathing business often wonder how the hammam differs from the Russian bathhouse and sauna, mistakenly considering them identical. In fact, steam rooms of different nationalities have a number of characteristic differences. Before you start getting acquainted with different steam rooms, it is worth studying their features.
Historical summary
It is a mistake to believe that the ancestor of the bathhouse is Ancient Rus'. History proves that steam rooms existed in ancient historical times among different nations. Each nationality modified and added new elements in creating their own steam room.
A bathhouse called “hamam” was inherited from Turkey, which means heat source in Arabic. The forefathers of eastern “hot” places are considered to be Roman baths. Muslims believed that in steam rooms sinners were washed from evil spirits that consumed body, soul and mind.
The Finnish sauna has been known for many years. Since its origins, the steam room has undergone few changes. The main features and features have been preserved to this day. In Finland, visiting the steam room is considered a mandatory ritual, a centuries-old tradition that should not be neglected.
In Russia, for a long time, the construction of a house began with the construction of a steam room. In many European cities, there were cases when visiting the bathhouse was banned, but the Russian steam room was still held in high esteem and people did not stop visiting it.
Features of steam rooms from Russia
The humidity in Russian baths is prohibitive. At temperatures of 50–70°C, humidity reaches 80%. For Russians, the main accessory for a steam room is a broom. As soon as you think about steam procedures, you immediately remember twig pats on the body. Some people use tied rods for their intended purpose, others steam the product and enjoy the pleasant aroma that spreads throughout the room.
In a Russian bath you can’t just lie down on a shelf and relax peacefully. Each steam session involves following the gang, lifting to disperse air accumulation, and sudden jumps into the ice hole.
Russian bathhouse attendants are distinguished by the fact that they like to sharply shock their own body.
In addition to the high air temperature, which puts intense pressure on the heart and blood vessels, constant movements also force the heart to work at an accelerated rate.
High humidity helps normalize the respiratory system. Many doctors prescribe a course of treatment in the steam room. The use of aromatic oils enhances the effect of hot steam on the body, reducing pain in arthritis and osteochondrosis.
For cleansing the skin, a Russian sauna is an indispensable option. The pores are completely cleaned in conditions of high humidity, the body covers acquire a healthy appearance, massage helps restore the tone and elasticity of the tissues.
What is a Turkish steam room?
The steam room, commonly called a hammam, is considered a traditional place of ablution in Turkey. The indigenous people consider the steam rooms a sanctuary, suggesting that if you enter the hammam, shrouded in sins, you can emerge from it as clean as a baby. It is enough to steam the body for a few minutes for the sinful evil spirits to free the soul and mind. This is stated in the holy book of Muslims, the Koran.
The microclimate inside the steam room was influenced by the hot natural conditions inherent in Turkey. In order not to cause harm to health, soft and moist air is maintained in the steam room. The steam filling the steam room warms up to 45°C. Such conditions do not have a strong effect on the body.
Attention! It is not customary to use a broom when steaming. The gentle conditions in the steam room are a suitable solution for those new to the art of bathing and people with heart disease.
What kind of steam room did the Finns give?
The difference between a Finnish sauna, a Russian bath and a Turkish hammam is that the steam is not used for its intended purpose. The air in the sauna is dry, the temperature is about 100–110°C.
Often lovers of super-hot conditions prefer to heat the sauna to 130°C. Excessive heating of the air causes increased sweating. It is not customary to use a broom in the sauna.
If a beginner whips hot rods over a steamed body, a burn will instantly appear. It is also not customary to douse yourself with cold water.
To cool down after the steam room, it is customary to dive from the pool, which should be built in every sauna. If the steam room is located on the banks of a river or lake, lovers of high-temperature procedures after steaming dive into the abyss of natural waters.
Steam sessions are accompanied by constant lying on a shelf, inhaling the aromas of pine needles. Reduced humidity helps to cope with discomfort associated with arthritis, rheumatism, osteochondrosis, and radiculitis. Strong heating with dry air reduces the inflammatory process. For most people, the dry, hot air of a sauna is easier to tolerate than the humid microclimate of a sauna.
When is it better to choose a steam room from Finland?
The steam room from Finland, according to most doctors, has a good effect on the body of people who do not suffer from cardiovascular diseases. Dry hot air makes breathing difficult, despite the large accumulation of oxygen masses and a small amount of water vapor. Therefore, people with diseased lungs and bronchi are also prohibited from visiting Finnish steam rooms. Indications for visiting the sauna:
- poor vascular functionality;
- excess waste, toxins;
- contamination of skin pores - under the influence of excessive temperatures, pores open to the maximum;
- depression, frequent stress;
- fatigue, loss of vitality;
- metabolic disorders;
- decreased performance;
- deterioration of the immune system;
- pathologies of the urinary and musculoskeletal systems.
The benefits of the Turkish steam room
Hammam and sauna differ in the amount of wet vapor. While Finnish steam rooms are filled with dry air, Turkish baths maintain a humid microclimate.
Due to the bath conditions, sweating is minimal, and the body gets wet due to the formation of condensation. The skin and hair do not dry out, so the hammam is a good alternative to the steam room for people suffering from allergies and increased sensitivity of the body.
Despite the slight heating of the room, under the influence of moisture the pores expand faster.
It is advisable to arrange steam sessions in Turkish steam rooms:
- For people who prefer to accompany steam treatments with aromatherapy. The hammam provides the opportunity to visit the solarium.
- In order to strengthen the functioning of the heart and blood vessels.
- For complete warming up of muscles and joints.
- In order to relieve stress, conduct relaxation sessions.
- To combat the symptoms of bronchitis and runny nose at an early stage.
- For girls who want to thoroughly cleanse their skin pores of dirt.
- In order to normalize metabolism and rejuvenate the body. Weight loss occurs faster if you combine training and a balanced diet with a visit to the hammam.
Essential oils for aromatherapy
Comparative analysis of Finnish and Turkish steam rooms
To understand whether a sauna or hammam is better for health, a comparative analysis should be carried out. If a lot is already known about the Russian steam room, then only a few know about the Finnish and Turkish ones. Comparative analysis of sauna and hammam:
| Comparative factor | Sauna | Hammam |
| Peculiarities | – dry steam; – temperature 1300 C; – wood interior finish; – pleasant aroma of wood. | – high humidity; – temperature up to 500 C; – interior decoration made of stone using marble tiles; – the ceiling is shaped like a dome; – the air is aromatized with herbs. |
| Who is it suitable for? | experienced bathhouse attendants. | for beginners. |
| Indications for visiting | – chronic nonspecific lung diseases (chronic bronchitis, asthma); – frequent colds; – vegetative disorders; – mental disorders; – hypotensive syndrome; – obesity; – gastrointestinal tract disorders; – chronic skin diseases; – pathologies of the urinary system. | – sports injuries; – deterioration of heart function; – period of pregnancy; – contamination of the skin; – excess weight. |
| Duration | – 1 session – 10 minutes; – number and frequency of sessions – no more than four repetitions in one session. | – 1 entry – 20 minutes; – there is no special limitation on the number and frequency of entries. |
| Contraindications | – exacerbation of chronic pathologies; – oncology; – pregnancy; – tuberculosis; – hypertension; – body temperature above 37°. | – vein diseases; – atherosclerosis; – inflammation of the skin; – oncology. |
Analyzing the data obtained, it becomes clear what distinguishes a hammam from a Finnish bathhouse. If you plan to just start getting acquainted with the “hot” world, there is no need to rush. It is better to slowly get used to the steam, starting with the eastern steam room, where the conditions are more gentle.
Interesting video
Source: https://probani.guru/intersnoeipoleznoe/hamam-sauna-i-banya/
How is a sauna different from a hammam?
To make the right choice, you need to understand the operating principle of the Finnish sauna and Turkish hammam. These two types of places for resting and washing give different sensations and have different effects on the body. The microclimate of a sauna and hammam varies significantly, as do the methods of steaming.
Those who like to take a steam bath and have a good rest often experiment by visiting both the Russian bathhouse and sauna, and the hammam. And if there is much in common between a Russian bath and a Finnish sauna, the structure of the hammam is fundamentally different. Because of this, the microclimate in the hammam is special and many ultimately prefer this particular Turkish version of the bath.
Microclimate of sauna and hammam
Sauna and hammam differ in the temperature and humidity of the steam room. Different combinations of ambient temperature and humidity give very different sensations.
Sauna
The traditional Finnish sauna is known for its very dry and hot air. Temperatures reach 90-100 C°, while humidity remains at 15-20%. Due to the low humidity, it is easy for even an unprepared person to be in the sauna steam room - this is one of the significant advantages of the Finnish sauna.
Even if the air temperature exceeds 100 C°, such a microclimate is quite well tolerated.
However, the Finns themselves usually do not heat the air in the sauna above 90 C°, since in this case the sweat secreted by the body begins to quickly evaporate from the surface of the skin, and breathing such fumes is not very useful.
Due to the dry air in the sauna, people with respiratory diseases should avoid visiting this type of sauna.
On the other hand, such a microclimate perfectly helps with joint problems and is very relaxing - in the steam room of a Finnish sauna, visitors are at rest, performing some active actions (like a massage) already in the relaxation room. For this reason, the sauna helps fight nervous tension and related disorders.
Hammam
In the hammam, the temperatures are not as extreme as in the Finnish sauna - only 40-45 C°, but the humidity reaches approximately 80%. The heavy and humid air of a hammam may seem unusual after a sauna experience, but the lower temperatures compensate for the high level of humidity. With so much moisture in the air, it condenses on the steamed skin.
The milder microclimate of the hammam is well suited for people who have certain problems with the cardiovascular system. The Turkish bath also has a beneficial effect on people suffering from colds and various respiratory diseases. In addition, hammam is loved by many women because of its mild conditions and the ability to carry out effective cosmetic procedures.
Installation of sauna and hammam
The differences in the sensations that a sauna and hammam give lie in the different principles of construction and arrangement of bath rooms.
Sauna arrangement
A sauna is always made of wood - at least the entire interior is made of wood. The stove in the sauna heats the stones, which release heat to the air. There is no steam generation as such in a Finnish sauna.
Wooden benches are provided as places for visitors, on which they most often sit, although sometimes they lie down.
In addition to the steam room, the sauna usually has two more rooms - a room with a pool filled with cold water (for contrast procedures after the steam room), and a relaxation room.
Arrangement of the hamam
The hammam is much more complex than the sauna. The main source of heat in the hammam is steam. A steam generator or boiler with boiling water is installed in a room separate from the main hall.
Steam is supplied to the hall through pipes running inside the floor and walls - thus, the steam reaching the hall simultaneously heats all surfaces. The surfaces themselves are made not of wood, but of stone, in the classic version - of marble. The beds, the so-called “supa”, are also made of stone.
They warm up well and lie on them in order to properly sweat and warm up the body.
The steam in the hammam is quite heavy, concentrating closer to the floor. In the conditions of a heated bed, enveloped in moist steam, you can relax well and use the services of a massage therapist - in Turkish baths, massage therapists perform the same role as a bathhouse attendant with a broom in a Russian steam room.
Most modern hammams have a swimming pool. Sometimes there may even be several of them - with warm, cool and cold water.
conclusions
The Finnish sauna and the Turkish bath are quite different from each other. The microclimate of the sauna is much harsher, despite the ease of tolerance of hot dry air by a healthy person. The microclimate of the hammam, in turn, is more gentle due to the relatively low temperature.
At the same time, being unaccustomed to it can be difficult due to high humidity and lower oxygen content compared to a sauna.
However, a lot depends on how moderately and adequately the sauna and hammam rooms are heated - with the right approach to this issue, it will be comfortable to be in both types of baths.
Source: https://himall.ru/info/chem_sauna_otlichaetsya_ot_khamama/
Peculiarities
The sauna is known as the Finnish bath; it is present in almost every Scandinavian home, public institution and hotel. There are saunas in many sports facilities, clinics and factories. They are distinguished by hot, but dry steam. The heating temperature in the steam room can reach up to 140 degrees, while the humidity level does not exceed 15%.
The principle of operation of a sauna is quite simple - the fire in the firebox warms up the stones, they release the resulting heat inside the steam room, thus heating the air to the required temperature. Saunas are equipped with chimneys that allow steam to be safely removed from the steam room.
When the desired heating level is reached, sauna visitors sit on benches and from time to time add hot water to the firebox to obtain a new portion of steam. Many people add essential oils to it, which improve the functioning of the human respiratory system. Heated air causes intense sweating - this principle forms the basis of the entire bath procedure.
Most often, after a steam room, visitors take a cold shower or plunge into ice water (a pool or even an ice hole) - this way the body cools down to normal temperature.
Hammam
The operating principle of the Turkish hammam differs in many ways from the traditional sauna, but this did not stop it from gaining a huge number of fans. The popularity of this bath is explained by its inherent oriental flavor and the specific effect on vital human organs and systems.
The temperature in a Turkish hammam varies from 32 to 52 degrees, and the humidity remains at around 90-95%. The ceiling in such a bathhouse remains cool - this allows steam to settle and condense on its surface.
A hammam in classical technology includes several rooms, which are conventionally divided into technical rooms and bath rooms. In the utility block the equipment is located and hot steam is generated, from there it is supplied through equipped channels to the bathhouses. In the past, steam was obtained by maintaining the boiling of water in a large boiler; nowadays, a steam generator is installed for this purpose.
The bathhouse part includes three rooms, each of them has its own purpose. There is a comfortable locker room near the entrance; the temperature in it is maintained between 32-35 degrees. The design provides for the installation of a shower so that users can wash off sweat and dirt.
Next comes the steam room itself, here the heating level is higher - 42-55 degrees. In spacious hammams there are additional rooms where, if desired, the temperature can be increased to 65-85 degrees, but such conditions are the exception rather than the rule.
Highly humidified air is pumped into the steam room, so the steam is felt physically. In addition, the air can be additionally scented - this allows the vacationer to fully relax.
The third zone in the hammam is a relaxation zone, where you can fully relax and unwind after treatments, drink a cup of herbal tea and chat with family and friends.
Hammam, sauna or Russian bath: we are looking for steam to suit our souls and hearts
“Saturday - dacha - bathhouse” - for many, the logical chain of weekend pleasures looks exactly like this. But are you sure that you are going to the bathhouse that is most beneficial? Sputnik found out which relkas is more useful: on the floors of a Russian steam room or on a marble slab of an oriental hammam.
If you have no contraindications from the cardiovascular system, you do not suffer from high blood pressure, then regularly visiting the steam room is a great way to exercise your blood vessels and reduce the risk of colds, and at the same time heart disease.
© Pixabay
What good does a bathhouse give us?
Numerous studies confirm that those who regularly visit the steam room improve the functioning of the heart muscle, reduce the risk of blood clots, and experience virtually no depression.
In the final analysis, good and regular steam prolongs life. Research is now being conducted to show that regular exposure to high temperatures can destroy tumors.
But we do not recommend checking it - this is still only an assumption that has not yet been proven by clinical trials.