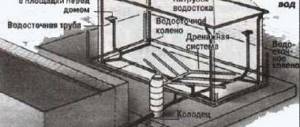
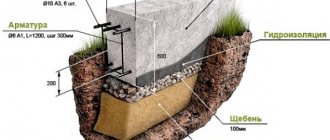
Waterproofing is an important part of construction work, which protects the foundation and the entire building from the effects of groundwater and precipitation. The choice of type of waterproofing depends on the level of groundwater and the level of its seasonal fluctuations. If groundwater lies close to the surface, it is necessary to use a more expensive and complex type of waterproofing - vertical. In cases where groundwater is located at great depths and there is little precipitation, it is possible to get by with only horizontal waterproofing for a bathhouse - a simpler and cheaper method. In this case, it will be necessary to remove precipitation using a blind area.
Foundation waterproofing is an important part of construction work
When performing any type of waterproofing, it is necessary to ensure that the material is placed in a continuous sheet. When connecting individual canvases, they must overlap and be carefully connected. In some regions, groundwater can be aggressive towards concrete. In this case, it is necessary to use special materials that have high resistance to this environment.
According to the method of implementation, waterproofing can be:
- lining (roofing felt, geotextiles, membranes, etc.);
- painting (for example, bitumen mastics and emulsions, penetrating solution, protective water-repellent impregnation, etc.);
- combined (using materials from both groups).
Vertical waterproofing
This type of protection is applied to the entire height of the foundation, starting from the sole. Its upper limit is determined by the level of splashing when precipitation hits the walls. Select the type of application depending on the amount of moisture in the soil. Before applying any type of waterproofing, it is necessary to carefully repair all defects: potholes, chips and sinkholes. If the foundation is block, the joints must be sealed with special moisture-resistant plaster. Waterproofing materials are laid on the outside of the building, providing protection against water penetration into the building.
Vertical waterproofing of bathhouse foundation
The most economical option for vertical waterproofing is mastic coating. It protects well from moisture penetration into the structure, but is easily damaged already at the stage of backfilling the foundation: the soil contains stones, fragments of broken brick or other building materials that can damage the protective layer. The protective bitumen film is also damaged when the soil shifts during operation. To avoid any damage, a layer of insulation or geotextile is placed on top of the mastic, and sometimes a pressure wall is built from brick (a rather expensive option). Instead of bitumen, you can use various penetrating water-repellent solutions and mastics. They provide a high degree of protection, but are more expensive.
Vertical waterproofing using roll materials
The next most expensive option is adhesive waterproofing using rolled materials: roofing felt, technoelast or isoelast.
There is also plaster waterproofing, in this case, a mineral-cement mortar with special additives is applied to the walls in several layers (total thickness up to 22 mm). Plaster insulation is applied hot - this helps to avoid cracks.
Using water-repellent impregnation: effective, but expensive
Other waterproofing methods
There are lesser known waterproofing methods that are also worth mentioning.
The first method is a clay castle , which does not allow pressure water to reach the base. To build such a castle, you need to dig a trench around the base with a recess of 60 cm, and fill the bottom with crushed stone. Then, using fatty clay, compact the bottom and walls of the trench. It is advisable to do this in several layers. After this, you should fill the free space with gravel. The resulting structure will serve as good protection against moisture during floods.
The second method is protective screens. Bentonite mats, which are made from clay, are used here. They are recommended to be combined with other protective materials. Similar to the previous method, you must first prepare the foundation, and then fix the clay mats on it using dowels. Near the base, you can install a concrete pressure wall to prevent the mats from swelling from moisture. During the first few days of operation, the paper part will collapse, and the clay will cover the entire surface of the foundation, thereby protecting it from water.
Horizontal waterproofing
Horizontal waterproofing protects the structure from capillary penetration of moisture. If you are building a bathhouse with a basement, then the first level is under the ceiling of the basement. The second level of horizontal waterproofing is at the level of the junction of the walls and the foundation. Particular attention should be paid to sealing the connection between horizontal and vertical insulation. All joints must be carefully coated and glued.
Horizontal waterproofing of the foundation
The simplest and most popular method is roofing felt laid in several layers. Next in popularity is impregnation with bitumen mastic or other water-repellent compounds. Also popular are the latest generation membranes, which provide reliable insulation. To install, just heat them on the burner, press them tightly to the surface and carefully level them with a roller. Membranes provide a good degree of protection, but small cracks and pores still remain, making these materials less effective than bitumen. The greatest efficiency can be achieved by combining materials: coating and film.
Bathroom floor waterproofing
Wooden flooring does not require any additional waterproofing. For them, the main condition for long-term operation is an effective ventilation system for the underground space.
Waterproofing bath floor
There are projects with other floor coverings, in some cases ceramic tiles are used. Such floors must be separated from concrete or cement-sand bases. For waterproofing, you can use mastics or roll coatings.
Waterproofing floors under tiles
When choosing a specific solution, you should take into account the operating characteristics of floor coverings, the material they are made of and the presence or absence of heating systems. In some cases, it is recommended to use membrane waterproofing. But this is a rather expensive material; in most bathhouses, the floors are insulated with cold-use mastics, which can significantly reduce the estimated cost of the building.
Waterproofing mastic
Waterproofing between foundation and masonry
Any concrete, even with excellent water-repellent properties, contains some amount of water. Moreover, he also absorbs it. Inside, it spreads both vertically and horizontally through tiny pores that penetrate the concrete stone. If the walls are made of hygroscopic material - and this includes brick, wood, and almost all building blocks, then in the absence of waterproofing, moisture will be absorbed by them. The walls will be constantly wet, the development of mold and fungi will begin, and the destruction of materials will begin.
The result of poorly done foundation waterproofing
To avoid such a development of events, waterproofing between the foundation and the wall is mandatory. This is the option when it is better to play it safe, since correcting something poorly done is very difficult and expensive.
What materials to use
Traditionally, in bathhouses and houses, roofing material is laid in two layers on a strip foundation. It is cut into a strip twice the width of the tape, folded in half lengthwise and glued to the mastic. Before laying, you need to remove all debris and foreign small objects from the surface: if you get a pebble, it will sooner or later break through the waterproofing. And this will lead to “suction” of moisture into the wall. Therefore, if the surface of the tape is very uneven, it is better to level it by pouring a thin screed, and it is better to take care of this at the stage of pouring the foundation. In order not to level the surface manually, but at the same time improve the characteristics of the solution, use a concrete vibrator. As a result, the surface will be smooth and the concrete will have improved frost resistance.
For horizontal waterproofing between the foundation and the masonry or the first crown, you can use modern materials:
- Hydrobelt is a dense, durable film made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC). Operating temperature range from -40°C to +80°C.
- Ruberit is a modern bitumen-polymer roll material, with a use temperature from -35°C to +90°C.
- Aquaizol is made from fiberglass or polyester. The scope of use is similar.
These are the most popular, but in general, the list goes on. In principle, any of the modern rolled euroroofing felts can be laid between the foundation and the wall, only without backfill, but underlays, which are used for waterproofing roofs.
For lovers of ancient recipes, there is also one method that was used in the northern regions of the country. When building a log house, soak the board twice with hot salt-bitumen solution on both sides. And in this form, place it under the lower crown. In addition to waterproofing, such impregnation also provides antifungal protection.
Foundation for a log house: which one to choose, waterproofing
The construction of the house is taking place in stages. The foundation is laid first. It determines how strong and durable the finished building will be.
It is important to understand: the foundations of a log, brick or block building are different. The specific gravity of wood is lower, therefore, the pressure on the foundation is low. The bases for log houses are classified into: screw; pile; tape;
columnar.
Each foundation has specific benefits. But disadvantages cannot be ruled out. When choosing a foundation for a log house, it is necessary to take into account the following factors: soil quality, proximity to groundwater, weight of the building. And, no matter how trite, the material costs of the event.
Pros and cons of screw, pile, strip and column foundations for log houses
Heaving soil that can freeze deeply requires the installation of a strong frame. For this purpose, pillars made of different materials are used: from wood to concrete (FBS). The pillars are strengthened at the support points of the log frame. Advantages of a columnar foundation: cost-effectiveness; convenient on difficult terrain; speed of installation. Cons: designed for one-story buildings; cannot be installed at low temperatures; unsuitable on loose soil. When constructing a building with a basement, a strip foundation is the best option. It is laid in the form of a solid frame, which is able to support the overall structure. Advantages of strip bookmarks: low cost; uniform distribution of log weight;
there is no need to remove the soil under the entire house.
Cons: cannot be used on heaving soil; high labor costs. How to build a house made of timber on marshy soils? A foundation on piles will help resolve the situation. This will require experienced craftsmen and considerable labor costs. Justifies itself in case of: sudden changes in terrain; “floating” soil at the construction site. The disadvantage of such a foundation is that there is a need for special equipment for installation. On wet soils, it is advisable to use a screw foundation. The basis is a steel pile. For ease of screwing, it has a screw tip and a wide blade. The diameter of the pile is calculated depending on the complexity and dimensions of the structure being built. The following factors speak in favor of a screw foundation: site leveling is not required; no need for waterproofing; low labor costs; simplicity and speed of the device.
An unpleasant point, a disadvantage of a pile-screw foundation, will be, over time, the corrosive destruction of the pile. Subsidence of the foundation due to poor quality work will also bring a lot of trouble.
Optimal choice of foundation for a log house: price vs quality
When choosing a foundation, it is fundamentally important to pay attention to the following parameters: soil composition, load and area of the structure, terrain of the site. Don't forget about the price-quality ratio. A profitable solution when building a small house or cottage would be a columnar foundation. A more solid structure with a long-term future would be better placed on a strip foundation. The amount of costs will be ¼ of all costs. You will be pleased with the quality and reliability, as well as the good possibility of constructing a basement or garage or basement. Labor-intensive, requiring considerable costs - a pile foundation. The price is justified only in the presence of unreliable soil, where another option cannot be secured. A screw foundation is economically beneficial: at minimal cost you get a reliable, earthquake-resistant, quickly erected frame for a house. Its cost is half lower compared to other types of foundation.
Regardless of the type of foundation chosen for the log house, a quarter of the costs will go towards installation. A reasonable approach and correct calculations will reduce costs without sacrificing quality. The price is influenced by:
material used; type and size of the building being built; foundation width; installation method.
An important point when carrying out work is waterproofing.
Waterproofing the log house from the foundation
The quality, strength and durability of a log house directly depend on the isolation of the log house from the foundation. Neglect at this stage of construction leads to problems such as: dampness; cold floor; the presence of condensation on the basement walls;
formation of mold and mildew.
Pile-grillage foundation
Waterproofing between the log house and the foundation will help to significantly reduce or avoid the above problems. There are two types: anti-filtration and anti-corrosion. The first is used when installing a log house on soils with a high content of chemical elements. The second one protects the wood directly from rot. Anti-corrosion waterproofing of a log house from the foundation provides two methods: coating; glued. The coating method requires heated bitumen mastic. The finished foundation is carefully coated in two or three layers. Accordingly, the initial layer must dry well before applying the next one. Then put the log house coated in the same way.
With the glued method, roofing felt is used. It is heated and placed between the base of the foundation and the lower crown of the frame. It is advisable to lay three such layers.
Popular projects on our website
Project a1 Project a2 Project a3
Maximum service life without repairs
The safety of the foundation for timber without repair depends on the assembly method and compliance with technical parameters. The strip foundation has proven to be the most durable. Its “life expectancy” reaches 150 years.
A columnar foundation will last less, which is why it is not recommended for a residential log house built “to last forever.” On average, stone pillars will last 50 years, brick pillars - 30. Repairing such a foundation is possible using formwork and adding a cement mixture, which will preserve the structure. Steel screw piles treated against corrosion will last up to 100 years. During operation, it is imperative to monitor their condition. It is easy to periodically check the area near the ground surface. Repairing a damaged pile is possible by installing a steel coupling on its top.
Experienced craftsmen know how to pour mortar and install a steel coupling. The restoration of the foundation takes place without disturbing the frame.
Strip foundation. Choice and basic rules
Our website presents a number of log house projects, for example: https://www.domastroim.ru/category/proekty-domov/proekty-srubov-domov-ploshhadyu-svyshe-200-kv-m/ Or you can see all prices for log houses . You can calculate the house or bathhouse you need with maximum accuracy using our log house cost calculator. To order and buy a log house, call:
- Vologda
- Moscow,
leave a comment
Also read with this material:
Waterproofing a brick foundation
Waterproofing of a brick foundation must be carried out in full and very carefully: the brick, in the presence of moisture, quickly collapses, and it is even worse affected by freeze/thaw cycles. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully limit the flow of water.
They start with waterproofing the cushion, which is made under the base of the foundation. Roofing material is laid on compacted and leveled soil. Can be done in two layers. A leveling cushion of crushed stone and sand is poured on top. Then the concrete base strip is poured. After it is ready, roofing material is also rolled out onto the base or the surface is coated with bitumen-polymer mastic. Then they begin laying the brick foundation.
Under a brick foundation, the first layer of waterproofing is laid on the ground, the second - under the brickwork
After the walls are erected, external waterproofing work must be carried out. Two layers are used - one of bitumen-polymer mastic, GIDROPLAST or other similar material, the second - rolled material (eurorubberoid or polymer spike-shaped membranes) is glued onto it.
Since the mastic must be applied to a relatively flat wall, sometimes it needs to be leveled. This significantly increases the cost of construction and takes a lot of time, since a dry base is required (the humidity of the wall on which waterproofing is applied should often not exceed 5%). You can find cement-based compositions that will simultaneously level the foundation wall and serve as waterproofing.
Video: Seal the gap between the log house and the foundation
2. The second option is familiar in understanding - the wood should not come into contact with water. Waterproofing a log house from the foundation is done by creating layers between two different surfaces. This process has several methods - coating, glued and gasketing.
- For the first, bitumen mastic or liquid resin is used. Having brought them to the state of paint, the prepared foundation, freed from the formwork, is coated very carefully, without leaving any white spots. The work is carried out in several layers after the previous one has dried.
We must not allow the surface to be a frozen hill, otherwise the first crown will come with flaws. For smooth work, you can use a leveling spatula. The tree must also be coated. Or, using a blowtorch, it is wrapped in basalt fiber.
- The next method is glued. For it, roofing material is used, which is also heated and tightly applied to the surface of the foundation. You can't get by with just one layer. Two are mandatory, three depending on the condition of the soil.
- The third method, in which waterproofing the foundation for a log house will last almost forever, involves the use of progressive means of protection from the current industry.
We are talking about styrene. Foam derivatives are the best moisture protectors today. How to apply them:
Sheets of polystyrene foam, expanded polystyrene, or an extruded derivative material are placed in a compacted ditch along the perimeter of the walls of the entire foundation. You can attach them “to the core”; anyway, the filling and the reinforcement will press as it should. In this way, the entire base is processed.
There is a nuance: when digging, you need to take into account the thickness of the material and make the width appropriate. It also happens when careless owners do not think about waterproofing right away, then the work will be complicated by the fact that a place is being dug near the finished foundation for inserting slabs of material, which will also serve as insulation.
But before this, the surface must be dried from moisture and tarred, but while the bitumen is hot, it is convenient to glue the slabs. Needless to say, the first crown in this case is also coated.
This is how the foundation is waterproofed. You can combine insulation and protection from moisture using the third method - laying styrene, then the cost of additional materials will be reduced, which will reduce the cost of independent construction.
Waterproofing of residential log house and bathhouse
Protection from moisture is not only required for the foundation - the living space also needs it. For this purpose, a kind of pie is laid - in addition to insulation, layers of hydro- and vapor barrier are laid both inside and outside. However, this is intended for such residential log houses that do not require cladding.
If the waterproofing of a log house occurs in this way and covers the rounded log, there is no longer any point in buying decorative material. What to do in this case? On the outside, only impregnation and sealing will help. The inner side can be layered and decorated with wooden elements - block house, clapboard.
The bathhouse is the “wettest” room. Moreover, all its premises are in constant contact with steam. But it cannot be impregnated, with the exception of particularly advanced compounds or waste oil.
There is only one way out - the bathhouse must have good ventilation and water flow. To do this, the floor is constructed in such a way that it looks like a concrete pad at an angle.
Waterproofing the foundation slab
Slab foundations for bathhouses are not often installed, but sometimes - on unstable and heavily heaving soils - this is one of the best solutions. In addition to the labor-intensive work of preparing the pit and then tying the reinforcement, it is also necessary to carry out thorough waterproofing work. Moreover, they consist of several layers.
The first stage is laying waterproofing under the slab - on the bedding. Previously, roofing felt was used for this. But it is made on the basis of cardboard; the bitumen used has low elasticity. But there was no alternative; we worked with what we had. Today there is a wide selection of roll waterproofing. Outwardly, it is very similar to roofing felt (Stekloizol, Rubemast and the like). Their difference is that they are made on the basis of fiberglass (more durable) and fiberglass. They are impregnated with modified bitumen, which does not lose its plasticity at sub-zero temperatures. This material has better characteristics and a longer service life. It is advisable to use these materials for waterproofing slab foundations.
The entire slab foundation is covered with waterproofing
They are laid directly on top of the bedding (a rough screed was made under the roofing felt). The strips overlap each other by 10 cm, the joints are glued with mastic and pressed to ensure tightness. Along the perimeter, the waterproofing should be 20-25 cm larger, it is then placed on the slab.
After installing the reinforcing belt, pouring and curing the concrete, proceed to the second stage of laying the waterproofing of the slab foundation. Now we need to isolate the monolith itself. This can be done using the same roll materials. Only this time they are fused using a torch using standard roll roofing technology. This option is not the only one, there are others:
- Coating waterproofing - bitumen and bitumen-polymer mastics. Apply to a dry, even base using a brush or spatula. Creates a waterproof film on the surface. Therefore, it is advisable to apply it in two layers, and in different directions, so that the coating is continuous.
Penetrating impregnation. Here the mechanism of action is different. Chemically active components clog the pores that exist in concrete. This significantly reduces the water permeability of the base slab. Impregnation is applied with a brush, the number of treatments is also double. But be sure to read the instructions: some compounds need to be applied to a dry base, some to a wet base, and a certain amount of time must be maintained between applying layers. An example of such material is “Penetron”. It can be used to reduce the hygroscopicity of any concrete, brick and foam concrete surfaces.
The first waterproofing layer is laid on top of the concrete preparation layer
Which way is better? Probably coating and roll waterproofing. Why? They are also a vapor barrier at the same time. After all, water in the soil is present not only in liquid form, but also in the form of vapor. And impregnations make concrete impermeable to water, not to steam. To protect against it, another layer is required. At the same time, both mastics and Euro-roofing felts do not allow water to pass through in the gaseous state. So these materials are better in this case.
Please note that the side surface of the slab foundation is also coated with liquid waterproofing, and then the remaining edge of the rolled material (the one that lies on the bedding) is wrapped and glued to the mastic. When laying two layers of rolled material, roofing material, which goes from below, is first glued to the sides of the slab. Then the one laid on top is bent and also “sits” on the mastic.
Materials and technologies
To insulate the base, floor and foundation of a house, coating waterproofing made from polymer and bitumen mastics, as well as weld-on insulation, are most often used. Such materials are suitable for basements of houses made of profiled timber, stone, brick, concrete.
Disadvantages of coated and weld-on insulation are swelling and peeling at low water pressure due to hydrostatic pressure.
More effective modern methods of insulating the base are penetrating waterproofing, mineral-based coating compounds, membrane materials, liquid rubber and glass insulation. Such insulation is suitable even for the old foundation of a house made of timber.
Rolled materials for waterproofing
Insulation of the base with roll materials on a bitumen or polymer base is called lining. Roofing felt, roofing felt, glass roofing felt, foil isolon, hydroisol, brizol are used. They can be glued to cold or hot bitumen mastic and fused. The method is suitable for houses made of timber and logs.
The waterproofing is glued to the cleaned and dried walls of the basement from the inside. To do this, bitumen mastic is first applied. It is necessary to overlap the strips by 15 cm. The material is also wrapped by 15 cm at the joints between the walls and the floor.
Advantages:
- low price;
- the ability to carry out work independently.
Flaws:
- at low temperatures such insulation becomes brittle and breaks easily;
- rolled materials are susceptible to damage by fungi and mold;
- the effectiveness of insulation depends on the quality of the work performed.
Membrane insulation
Previously, this type of roll waterproofing was intended for external pressure insulation of the foundation. But now a membrane material has appeared for internal use. It is ideal for basement insulation in houses made of profiled timber and other wood materials. Cone-shaped spikes on the surface of the material perfectly remove accumulated moisture.
Before using membrane protection, the basement walls must be cleared of debris, cracks and crevices between structural elements must be sealed, and the surface must be primed. The membrane is attached to the walls with dowels. The open ends of the membrane must be secured with a horizontal insulating layer.
- long service life;
- Possibility of use on damp walls;
- Suitable for self-application.
Cons – cannot be used without horizontal waterproofing of the foundation.
Penetrating insulation
This insulation inside the house penetrates through microcapillaries and cracks in the basement envelope and crystallizes there. The process occurs due to the use of penetrates (alkali metal carbonates, silica, aluminum oxide) in the composition. As a result, the foundation walls become impenetrable. Insulation is suitable for houses made of timber, stone, brick and concrete with block and concrete monolithic foundations.
Advantages:
- high efficiency due to penetration deep into the material;
- the frost resistance of concrete basement structures increases;
- suitable for DIY application;
- thorough plugging of even small cracks;
- such insulation cannot be damaged;
- durability.
Application method:
- To open the pores of the concrete, the surface must be thoroughly degreased and cleaned. To do this, you can use a wire brush or a water jet.
- The solution is being prepared.
- The composition is applied to the damp inner surface of the foundation. In this case, first the joints between the walls and the floor and the corners are processed, and then the solution is applied to the walls.
- After two hours, you can apply the second layer of the composition.
- To ensure uniform hardening of the solution, the surface must be moistened for several more days after waterproofing.
It is important to know: in order for the solution to penetrate to a depth of half a meter in the foundation structure, several layers will need to be applied.
More details about the use of penetrating waterproofing can be seen in the following video:
Injection insulation
To install such waterproofing, a liquid gel-like composition must be introduced into special holes in the foundation. For these purposes, microcement, polyurethane, epoxy or acrylic gel are used.
An important aspect in wood construction is to prevent the wood from constantly coming into contact with water. Weather precipitation is excluded, because rain and snow are short-term phenomena and the absorption of a log or beam depends more on the care of the owner himself. It is he who will have to foresee everything and take measures in advance to process the wooden elements. However, there is one area of the house that will always have a risk of interaction with water - this is the foundation, and protecting it is the most important task of the owner.
Waterproofing strip foundation
The use of modern technologies in construction leads to the fact that vertical waterproofing of strip foundations is not always necessary. Horizontal is absolutely necessary (between the foundation and the wall).
Two layers of rolled waterproofing are laid on the strip foundation under the first row of masonry (can be coated twice with bitumen mastic)
When not to do it
If there is no basement in the bathhouse or house, in most cases additional measures to protect against water are not needed. If concrete grade B15 or higher was used when pouring, then its frost resistance and water-repellent properties are sufficient to resist the harmful effects of water for decades. For such staves, the number of defrosting/freezing cycles that they can withstand is 300.
The construction of a blind area around the house and thermal insulation of the foundation also add vitality to the foundation. The presence of these components cuts off most of the water. And the concrete will handle the rest itself. After all, for normal well-being, cement needs water, only then does it “live” for a long time.
When to do it is necessary
If the house has a residential basement, regardless of the brand and properties of concrete, a full range of waterproofing and vapor barrier work is required. The main task then is to make a “trough” from insulating materials through which neither water nor water vapor will penetrate inside.
You can use any material that provides hydro- and vapor insulation. Then it all starts with waterproofing, which is laid on the bedding. It is better to use materials such as Stekloizol, Aquastop, Rubemast, etc. Next, after casting and ripening of the base, a layer of protection against water penetration is placed on the mastic. Next, the reinforcement frame is knitted, the formwork is installed and everything is filled with concrete. After setting, begin vertical waterproofing. In this case, a combination will work best: a layer of mastic or impregnation, and on top - a fused roll of waterproofing or a sticker of a spike-shaped polymer membrane.
If the basement is planned to be heated, the foundation must be insulated. The best material for this is slab polystyrene foam. It has excellent heat-protective characteristics, does not rot, and is not damaged by insects and rodents. Plus, it has waterproofing properties. And only on top of the thermal insulation layer is a waterproofing layer applied. Although, with proper installation of polystyrene foam (in two layers, the seams are staggered and taped), there is no longer a need for it. But you can play it safe. Only rolled materials will have to be glued onto mastic again: fusing onto polystyrene foam will not work.
Expanded polystyrene boards provide both insulation and waterproofing
In any case (with or without insulation) on soils prone to heaving, it is better to use membranes. Due to the large number of rounded spikes, they still partially compensate for the forces of heaving. On the other hand, the presence of air between the membrane and the foundation wall serves as an additional heat-insulating layer. So polymer membranes solve the problem of protecting the foundation in a complex (water + steam + heaving + thermal insulation).
During further work it will be necessary to waterproof the floor in the basement. Moreover, it must be done in such a way that it and the waterproofing of the foundation form a single whole and the possibility of leakage at the joints is excluded.
If you have a residential basement, you need to properly waterproof it
Upon completion of the foundation work, it is advisable to make an insulated blind area around the bathhouse or house. Firstly, it will divert water from the walls to a safe distance, and secondly, it will protect the foundation from freezing.
Special design of the lower crown
If you imagine the volumetric structure of a log house, you can see that the classic lower crown, assembled “in a bowl,” cannot be placed on a single-level foundation without a gap. It should be remembered that the larger such cracks and gaps are, the higher the likelihood that they will become moisture accumulators and cause the logs to rot.
In this connection, sealing the lower crown begins not with treating the logs with mastic or impregnation, but with pairing its geometry with the geometry of the foundation.
There are two options for solving this problem:
The first option is used for the construction of small buildings (baths, barns, etc.).
The second method is more commonly used, as it avoids the need for “shaped casting” in the corners of the foundation and allows the use of a solid interlining board made of durable wood.
We will separately consider such a solution as the above-mentioned spacer board, which is the simplest way to extend the service life of a log house by a good ten years, and also greatly facilitates the repair of the lower crown, if the need arises.
The essence of this solution is that a wide board made of the most stable type of wood (oak or larch) is laid between the foundation and the lower crown of the log house.
Please note that a wide board is always made from the central sectors of a log, the maximum stability of which is observed only in larch.
At the same time, it is important to take into account one feature of this technology: additional processing of the padding boards with any chemical compounds is not carried out. The sealant is laid using the same method as for inter-crown gaps.
Features of waterproofing a pile or columnar foundation
It is very difficult to protect piles and pillars from moisture penetration. To increase waterproofing properties, concrete piles are made with special water-repellent additives. If wooden piles are used to construct the foundation, it is necessary to treat them with protective compounds.
Waterproofing of pile foundation
The actual layer of waterproofing materials in these cases is laid along the grillage (part of the foundation that combines piles/pillars into a single structure). When insulating a columnar or pile foundation, roofing felt is usually used, which is laid in several layers.
If you take into account all these features and nuances, you can make high-quality waterproofing of the bathhouse foundation with your own hands. If you know how and what to do, it won’t be difficult.
Types of waterproofing for baths
All types of waterproofing materials are classified according to several criteria: method of application, place and time of use. Depending on the place of use, it can be external or internal; it is quite obvious that some materials are used for finishing rooms and structures from the inside of buildings, and others from the outside.
External and internal waterproofing
In terms of time, waterproofing can be primary or secondary. The primary one is done at the stage of construction work. The secondary one is used in case of violation of the initial waterproofing characteristics of the primary one, as the planned operating conditions change or after detection of damaged areas.
Primary waterproofing of the foundation