Experienced builders know that the strength of the foundation under the walls of the house directly depends on the correctly chosen design of the reinforcing frame to create a strip foundation, and the correct installation. In this design, all the, so to speak, “responsibilities” of its constituent elements are clearly distributed. Thus, the reinforcement takes on deforming linear stresses that arise not only from the weight of the walls, but also from temperature changes, and the concrete part of the structure prevents its compression. Thus, together these materials create reliable support for the walls.
Knitting reinforcement for a strip foundation
Tying reinforcement under a strip foundation is the best option for fastening the metal “backbone” of a reinforced concrete structure. Such a connection, while maintaining the given linear and spatial forms of the frame, nevertheless leaves the opportunity to somewhat “balance” when the concrete hardens and gains its grade strength, taking the optimal position when exposed to emerging loads. If you make the skeleton of the foundation rigid, that is, fasten the reinforcement by welding, then even with slight shrinkage of the soil or under pressure from the walls of the house, the concrete part of the structure may begin to collapse, since when the solution hardened, the optimal shift of the frame parts did not occur and in a seemingly strong monolithic the slab retains significant internal stresses.
A few words about the features of strip foundations
The strip type of foundation can be safely called universal, the most common, making it possible to construct buildings from almost any building materials. The widespread use of this foundation design is explained, among other things, by significant cost savings, simplicity and accessibility of its independent arrangement, as well as the fact that the strip foundation has been comprehensively tested by the very wide practice of its many years of operation.
The strip foundation rightfully occupies a leading position as the most popular type of foundation for buildings among developers
Such a foundation itself is a reinforced concrete strip, which can have different widths, thicknesses and heights. These parameters depend on the design of the future building - the size of the walls and the material from which the walls are planned to be built, the overall massiveness of the structure, the condition of the soil at the construction site and a number of other important factors. But in any case, the strip foundation is installed along the perimeter of the future structure, has a closed contour, which is intended for the further construction of load-bearing walls. If necessary, this type of foundation is supplemented with internal lintels, which become the basis for the construction of intra-house capital partitions on them.
The depth of the tape base can vary significantly, depending on the specific circumstances. Thus, in case of unstable upper layers of soil at the construction site, the base of the strip base is completely buried below the freezing level or is performed in combination with a pile foundation. If the soil is dense, or when it is planned to build a building with a small overall mass, then it is quite possible to get by with a shallow strip foundation.
The foundation strip can be deep or shallow, sometimes additionally reinforced with monolithic piles
Be that as it may, the requirements for complete and high-quality reinforcement are equally important for any type of strip foundation. Only under this condition will the foundation optimize the load from the walls of the house on the ground along the entire perimeter of the building, which minimizes the risk of subsidence of the building, distortion and deformation of all its component building structures.
How to fill a strip foundation with your own hands?
In this publication we will not delve too deeply into the intricacies of the design of such a base. to the issues of calculation and sequence of work on independent construction of a strip foundation .
Knitting methods
Methods of fastening steel frame elements are carried out:
- Completely manual, which requires physical effort, but provides reliable fastening at low cost.
- Using semi-automatic methods that facilitate and speed up the fixation process, requiring additional acquisition costs.
If the rods are tied manually and fastening with loops is used, the elements will have to be connected separately
The manual fastening option is carried out using the following tool:
- wire cutters or pliers, the working surface of which is rounded;
- a self-made hook from a welding electrode or rod with a diameter of 3-4 millimeters;
- a manual reversible device, the rotation of which is carried out by reciprocating movement of the handle;
- special pliers, the operating principle of which is similar to a reversible tool;
- a purchased crochet hook, the use of which is one of the simplest options.
Semi-automatic methods of fixing frame rods are carried out using the following devices:
- An automatic knitting gun that ensures high efficiency and quality of work.
- A screwdriver or electric drill equipped with a special attachment that allows you to quickly tie steel bars. You can use a regular nail bent at a right angle.
Let's consider the features of the main types of manual and semi-automatic tools, with the help of which a bunch of reinforcement for the foundation is carried out.
What kind of reinforcement is used to knit the frame?
So, moving on to preparing everything necessary for arranging the foundation, it is necessary to obtain information about which reinforcement is best suited for forming the frame of a strip foundation. Nowadays, “classic” steel and composite reinforcement can be found on sale in construction markets. Which one is better for a strip foundation is worth figuring out.
Metal fittings.
Steel reinforcement used to create frames for pouring foundations must comply with the requirements of current GOSTs. In residential construction, material manufactured in accordance with GOST-5781-82 is most often used. This standard regulates the parameters of hot-rolled reinforcement intended for use in conventional and prestressed building structures.
To reinforce foundations, hot-rolled reinforcement is most often used, produced in accordance with GOST-5781-82.
In accordance with the provisions of GOST, this fittings are divided into six classes. If for the first class ordinary low-carbon steel is used, then as the class increases, the content of special and even alloying additives increases, sharply increasing the mechanical strength of the material.
Class I reinforcing bars have a smooth outer surface. All others (with rare exceptions) are given a corrugated shape, the so-called periodic profile of annular, crescent or mixed type. This relief structure of the surface is intended for maximum contact of the reinforcing elements of the structure with the concrete gaining strength.
For the main reinforcement of a strip foundation, the optimal choice, from the standpoint of a sufficient degree of strength and reasonable price, would be class A-III reinforcement, with a diameter of 12 to 18 mm, depending on the features of the structure being created. The indicators of classes from the fourth and above will simply remain unclaimed, but A-II may turn out to be rather weak.
It is worth paying attention to the presence of a letter index.
- So, the letter “C” indicates that this reinforcement can be connected by welding. With all other types, welding work is completely eliminated - the structure of the steel changes during high-temperature heating, and the frame will lose the necessary strength.
- The letter designation “K” is used for products made of steel with increased anti-corrosion properties. They are usually used in the construction of objects that have special requirements, and for a strip foundation for private construction, the purchase of such reinforcement (and it certainly costs much more) does not seem necessary.
Smooth hot-rolled bars of class AI are the best option for the manufacture of clamps that combine the main reinforcement into a single volumetric frame.
But for additional structural elements - lintels, racks, clamps that give the main frame the necessary volume, smooth reinforcing bars of class AI with a diameter of 6 mm (with tape height up to 800 mm) or 8 mm (at a higher height). They are easily bent into the required configuration, and their strength characteristics are quite sufficient for such an application. You can also use corrugated rods of class A-II, but this will be somewhat more expensive.
Prices for fittings
fittings
Fastening of reinforcement is most often done using a special binding wire, which is installed and looped at all intersection points of steel rods. The use of welding is not recommended for several reasons:
- Any weld, even a well-made one, is a place with increased vulnerability to corrosion.
- Lack of penetration at the joint, which may not be noticed when installing the frame, can result in a violation of the integrity of the structure at the stage of pouring heavy concrete mortar.
- Even slight overheating of the rod at the point of its intersection with another structural element reduces the reinforcing qualities inherent in it.
So even if the developer considers himself an experienced welder and has a machine at his disposal, it is still better to refrain from such an operation. By the way, only masters of the highest qualification category are allowed to work on welding reinforcement structures, where it is necessary in industrial construction conditions. And in this case, only fittings marked with the letter “C” should be used.
Composite reinforcement
Composite reinforcement is a relatively new building material. It can be produced on different bases - fiberglass, carbon fiber or basalt plastic.
Fiberglass reinforcement is a material that is gaining popularity, but its application is still not entirely clear.
The most common in this category is fiberglass reinforcement, as it has a more affordable price compared to the other two types, while having high strength qualities.
Composite rods are used to reinforce various types of foundations, including strip foundations. The advantage of this type of reinforcement is its low thermal conductivity compared to metal rods. Therefore, these products are well suited for reinforcing foundations and basement walls that are planned to be insulated, since there will be no unnecessary heat loss due to this material.
Polymer reinforcement is inert to external influences, therefore it is quite durable - it is not afraid of moisture and fairly high temperature changes. If high-quality concrete and fiberglass reinforcement are used when arranging the foundation, the foundation for the house should be strong and durable.
Installation of polymer rods is much simpler than installation and fastening of metal reinforcement, since they are light in weight, easily fastened with clamps or wire and do not leave traces of rust on hands and clothes.
A comparison can be made with steel reinforcement based on basic indicators:
- Tensile strength, with equal diameter, for a steel rod is 390 MPa, for a fiberglass rod - 1000 MPa.
- Fiberglass has a mass 3.5 times less than steel.
- Steel is susceptible to corrosion, polymer is resistant to acidic environments.
- Fiberglass does not conduct electricity, unlike metal.
- Steel has a high thermal conductivity, while polymer practically does not conduct heat.
- Metal is a non-flammable material, while fiberglass is a low-flammable, self-extinguishing material.
- The elasticity of steel is several times higher than that of fiberglass.
- Polymers have great tensile strength, however, when heated to very high temperatures, the plastic binding fiber becomes soft, losing elasticity.
- Composite reinforcement is fastened only with plastic clamps or wire; metal reinforcement can be welded or twisted with wire.
From a comparison of the characteristics of these two materials, the conclusion suggests itself that for heavy buildings it is best to use metal reinforcement, and for light structures a frame for a fiberglass strip foundation is also suitable. However, there are several important nuances to keep in mind.
- To date, clear technological recommendations for the use of composite reinforcement have not yet been developed - all calculations are so far based on the use of steel products. So the owner who decides to use a fiberglass frame takes a certain risk.
- The market is literally flooded with fiberglass reinforcement of very dubious quality. This is not surprising - if the production of rolled steel requires extremely specific production conditions, then lines for the production of composite rods are advertised and sold to everyone who wants to try their hand at this business. Naturally, in this case there is no need to talk about any compliance with GOST - at best, compliance with independently established technical conditions (TS) is declared, in which the criteria for assessing product quality are either deliberately underestimated or unclearly stated. And very often, consignments of goods do not have any accompanying technical documentation at all.
If we dare to use fiberglass reinforcement, then only with quality that complies with GOST.
Alas, the market is literally overflowing with low-grade material. Such rods may have longitudinal or transverse (noticeable on the cut) cracks, delaminations, protruding fibers, knots, resin drips, uneven curling pitch, differences in color, which, in turn, indicates obvious non-compliance temperature-time regime of processing.
It is difficult to say how such reinforcement will behave in a loaded state as part of a strip foundation frame, and hoping that it will “carry through” is not the most reasonable solution.
Types of reinforcement for tying
Before starting work, you need to decide on the fittings that are best suited. How to properly knit reinforcement for a strip foundation? Tying the strip foundation reinforcement is done with any pneumatic tool or hook. What if they are not around? An improvised tool is used. This is what is good about a strip foundation. Knitting of reinforcement can even be done using pliers.
Corrugated reinforcement is used in the main sections, because it has better adhesion to cement concrete, and smooth reinforcement is used for bonding in cross sections. It will cost a little less than the corrugated one.
Tying metal reinforcement
There are certain rules for mating. When choosing fittings, it is necessary to choose one that meets the requirements of GOST. During construction, a material that complies with GOST-5781-82 is often used. Has six strength classes.
It can be bent if necessary, and also welded using a welding machine. In the manufacture of the first class, low-carbon steel is used, and when the class is changed, the concentration of alloying additives increases, due to which the mechanical strength increases.
Bonding of composite reinforcement
Made from fiberglass, carbon fiber, basalt plastic. It contains fibers of carbon, basalt, as well as glass and aramid. The most common is fiberglass. It is lighter, cheaper, does not rust, does not bend, and cannot be welded with a welding machine. In the absence of welding capabilities, composite reinforcement has to be tied together. The advantage of this type is that it has low thermal conductivity.
Tying fiberglass reinforcement
Bound plastic reinforcement can be distinguished from metal reinforcement by the permissible distributed weight. When choosing fiberglass reinforcement as a reinforcing material, it is necessary to calculate the possible loads because the specific gravity it perceives is significantly different from the weight that metal reinforcement is capable of supporting. The binding process itself remains the same. The same tools and the same accompanying materials are used.
Schemes for distribution of reinforcement in the structure of a strip foundation frame
As mentioned above, the reinforcement in the foundation structure contributes to the uniform distribution of the main load from the weight of the building and external dynamic influences, maintains the integrity of the structure under the influence of emerging internal stresses. Therefore, how well the frame elements are fastened, so strong and durable will be the foundation, which means and the entire building as a whole.
When arranging the frame of a strip foundation, you need to take into account some nuances:
- The greatest loads fall on the longitudinal rods of the frame of the upper and lower (especially) reinforcement belt. Therefore, taking into account the characteristics of the soil and the features of the future building, periodic profile reinforcement with a diameter of 10 mm or more is selected for them, and if the length of the tape in any of the sections exceeds 3 meters (and this is what happens most often), then at least 12 mm.
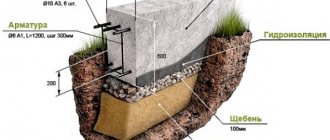
- Longitudinal reinforcement should be located at a distance from the bottom, side walls and the upper boundary of the cement mortar pouring at a distance of 30 to 50 mm. For example, if a foundation with a width of 400 mm is being built, the distance between the longitudinal rods in the horizontal plane should be 300 mm.
- The distance between two adjacent parallel bars of longitudinal reinforcement should not exceed 400 mm.
- For transverse and vertical elements of the frame, smooth rods with a diameter of 6÷8 mm are used (for a tape height of 800 mm or more - at least 8 mm). Such a section will be quite sufficient, since they bear less load.
One of the simplest schemes for reinforcing a shallow strip foundation
- The distance between clamps (transverse reinforcement sections and posts) can vary from 100 to 500 mm. The last value is the maximum, so you cannot exceed it. It is best to proceed from the calculation that the installation step of the clamps is 0.75 × h, where h is the total height of the foundation strip.
- The number of tiers of longitudinal reinforcement and the number of rods will depend on the height and width of the strip foundation. SNiP establishes minimum ratios of the cross-sectional area of the tape and the total cross-sectional area of the rods of the longitudinal main reinforcement.
- If the load on the foundation is not too great, then the frame design is extremely simplified and is a rectangle in cross-section without additional reinforcing rods. That is, in the lower and upper reinforcing belts, two longitudinal rods are used, which are linked to vertical and horizontal jumpers or ready-made clamps.
Areas that require additional reinforcement are of increased complexity - these are corners and areas where foundation strips adjoin. This is discussed in detail in the corresponding article.
Prices for fiberglass reinforcement
fiberglass reinforcement
How to correctly calculate and plan the reinforcing frame of a strip foundation?
When building a large country house, it would be wiser to entrust this issue to qualified specialists. But if a small structure is being erected, then you can do it yourself - a special publication on our portal contains drawings of strip foundation reinforcement and offers convenient calculation calculators.
Requirements for fittings
During the reinforcement of strip foundations, the type and controlled values of the quality of the reinforcement are established. The standards allow for the use of hot-rolled construction reinforcement of periodic profile, heat-treated reinforcement or mechanically strengthened reinforcement.
Construction fittings
The class of reinforcement is selected taking into account the guaranteed value of the yield strength at maximum loads. In addition to tensile characteristics, ductility, corrosion resistance, weldability, resistance to negative temperatures, relaxation resistance and permissible elongation before the onset of destructive processes are standardized.
Table of reinforcement classes and steel grades
| Profile type | Class | Diameter, mm | steel grade |
| Smooth profile | A1 (A240) | 6-40 | St3kp, St3ps, St3sp |
| Periodic profile | A2 (A300) | 10-40, 40-80 | St5sp, St5ps, 18G2S |
| Periodic profile | A3 (A400) | 6-40, 6-22 | 35GS, 35G2S, 32G2Rps |
| Periodic profile | A4 (A600) | 10-18 (6-8), 10-32 (36-40) | 80С, 20ХГ2Ц |
| Periodic profile | A5 (A800) | 10-32 (6-8), (36-40) | 23Х2Г2Т |
| Periodic profile | A6 (A1000) | 10-22 | 22Х2Г2АУ, 22Х2Г2Р |
The calculation of the strip foundation is carried out in accordance with the recommendations of GOST 27751, the indicators of limiting loaded states are calculated by group.
GOST 27751 (page 1)
GOST 27751 (page 2)
GOST 27751 (page 3)
GOST 27751 (page 4)
GOST 27751 (page 5)
GOST 27751 (page 6)
GOST 27751 (page 7)
The first group includes conditions that lead to complete unsuitability of the foundation, the second group includes conditions that lead to partial loss of stability, complicating the normal and safe operation of buildings. According to the maximum permissible states of the second group, the following are produced:
- calculations for the appearance of primary cracks on the surface of a strip foundation;
- calculations based on the time period of increase in cracks formed in concrete structures;
- calculations of linear deformations of strip foundations.
The main indicators for resistance to deformation and strength of building reinforcement include maximum tensile or compressive strength, determined in laboratory conditions on special test benches. The technology and test methods are prescribed in state standards. In some cases, the manufacturer may use regulatory and technical documentation developed by the enterprise. At the same time, regulatory and technical documentation must be approved by regulatory authorities.
For concrete structures, these values may be limited by the maximum rates of change in concrete linearity. Actual diagrams of the state of reinforcement under short-term one-sided exposure to design standard loads are taken as generalized indicators. The nature of the state diagrams of building reinforcement is established taking into account its specific type and brand. During the engineering calculation of a reinforced foundation, the state diagram is determined after replacing the standard indicators with actual ones.
Wire for tying reinforcement cage
The reinforcement is knitted when installing the foundation frame using wire, the technical characteristics of which are specified in the documents GOST 3282–74.
For tying reinforcement, annealed steel wire of the BP grade is most often used.
The wire is made from low-carbon steel and is divided into several types:
- According to the processing method. There is heat-treated (annealed) and untreated wire.
- In terms of manufacturing accuracy. So, the wire can be of high precision or regular.
- According to the temporary resistance to loads and rupture of a product that has not undergone heat treatment, there are first and second groups.
- The wire may have a special protective coating or be without it.
The wire can be steel or black. The cross-section diameter varies from 0.16 to 10 mm. In this case, deviations in the cross-section of the product are allowed by 0.02 mm.
In GOST documents you can find more detailed characteristics of this product. Some of them:
- The elongation of wire that has undergone heat treatment and has a protective coating is 12÷18%, and without protection 15÷20%.
- For products not treated at high temperatures, depending on their cross-section, a parameter such as tensile strength varies and is (N/mm²):
— 590÷1270 for diameter 1.0÷2.5 mm;
— 690÷1370 for diameter less than 1.0 mm.
The manufacturer of these products must ensure compliance with the following GOST standards:
— products without heat treatment with a diameter of 0.5 to 6.0 mm must maintain integrity after four or more folds;
— the zinc protective coating must maintain its integrity and fit tightly into the steel after winding the wire in the form of a spiral. In this case, the presence of small zinc deposits, plaque, white sparkles and color heterogeneity is allowed;
— wire should be sold in coils. These coils can have different weights, which depend on the diameter of the wire and the presence or absence of a protective coating. Thus, the mass of the coil varies from one kilogram with a cross-section of products of 0.16÷0.18 mm to 40 kg with 6.3÷10 mm.
Heat treatment of the wire (annealing it) makes the material more plastic, easier to use, without significant loss of strength properties. So it makes sense to immediately purchase this option. Annealing, of course, can be done independently - but is it worth spending effort on this when ready-made wire is already on sale, and at a more than affordable price?
Probably, for a strip foundation there is no particular need to purchase zinc-coated wire if concrete is poured immediately after installing the reinforcing frame. In such a short period of time, corrosion will not have time to “gobble up” the connections, and then, after the concrete has fully matured, it will not be terrible at all.
As a rule, when constructing strip foundations independently, wire with a diameter of 1.2 or 1.4 mm is used, less often - up to 1.8 mm. The millimeter one is still rather weak for such purposes - it can cause breaks when tightening the knots, and with a diameter of 2 mm or more it will be very difficult to work with, it will take a lot of effort for high-quality tying without any special benefits.
The construction market has been replenished with another extremely convenient material for knitting frames. These are coils of ready-made wire segments with a diameter, as a rule, of 1.2 mm and a length of 80 to 180 mm, already having ready-made loops at the ends. Usually there are 1 thousand of these products in a bay.
Coils of ready-made wire loops “Kazachka” or “Bison” are a very good purchase, greatly simplifying the knitting of the reinforcement cage.
The cost of such packages of wire loops is very affordable, and labor productivity, as practice shows, almost triples.
Below, the reader is offered a calculator that will help to quickly calculate approximately how many connection points will need to be connected to the reinforcement frame being created, and how much wire will be required for this. It is taken into account that some areas of reinforcement require additional reinforcement.
Calculator for calculating the amount of wire for tying the reinforcement cage of a strip foundation
Go to calculations
It should be correctly understood that this is the minimum required amount of material. During work, it is quite possible that the tightened knots will break, your work will be defective, and it’s easy to drop and lose cut pieces of wire at a construction site. Its cost is low, so it is quite possible to lay down a reserve of 50 or even more percent. Moreover, since the construction of the foundation is still underway, there are still many different construction operations ahead, and there will always be a use for excess wire.
Step-by-step instruction
Before knitting, you need to set up the formwork, concrete it, you need to purchase materials, deliver them and perform a number of other preparatory steps.
Start of reinforcement
List of actions for reinforcement and binding:
- Sorting;
- Cleaning from dirt;
- If necessary, align the rods;
- Cutting into pieces of the required size;
- Tying reinforcement blanks in the plane of the frame;
- Connecting planes to each other.
The diameter of the selected reinforcement and wire is selected based on the total load and the expected dimensions of the strip foundation.
Installation is carried out at the construction site. The four frame elements are tied together with an overlap. As a result, the belt will consist of pairs of twisted rods, which will be vertically and horizontally located.
Laying the finished reinforcement cage
Before installation, you need to prepare the base and place the formwork. Then comes the installation of two belts, which are then both concreted.
Action diagram:
- Driving in fixing rods;
- Sequential stacking of blocks;
- Checking elements.
Core mating
The best options are considered to be a rectangular or square strip foundation. For maximum stability, the reinforcement is made in a square, at 90 degrees. At the corners of the foundation, the production process becomes a little more complicated due to the use of bent rods. The workpieces are attached with bundles (clamps), and reinforcements are attached at the joints. To increase the strength of the house, the reinforcement is bent and overlapped using clamps.
Helpful Tips:
- Pay attention to the reinforced corners of the foundation;
- Use clamps so that the reinforcement cage does not come into contact with the soil and formwork;
- Use metal of the required quality without rust;
- Knit reinforcement with overlaps;
- If the wire is not flexible enough, place it in the fire for half an hour.
Using additional parts for spatial fixation of reinforcement
You should not assume that the use of fixing devices when constructing a strip foundation can be neglected. They form a “protective layer” that will help protect your foundation from corrosion and premature destruction. This seemingly trifle will save the building and a huge amount of money.
Clamps are used to fix the lower plane of the reinforcement frame, laying them on the base, and fixing the side planes to the walls of the formwork. Also for temporary fastening of elements during frame installation.
Another great tool is staples, which are used to tie together rebar intersections. They are very elastic and act in a springy manner. They have a diameter from 2 to 4 millimeters.
When building a strip foundation, it is necessary to take work with reinforcement very seriously. Be extremely careful! It is very important to choose high-quality materials that do not have rust, and when working, strictly follow the technological sequence so that your home lasts a long time. If in doubt, it is better to leave this work to professionals.
Tools for tying reinforcing bars
It is almost impossible to fasten reinforcement with wire manually, that is, simply with the efforts of your fingers, so special tools, both manual and mechanical, were created to carry out this process. These devices and devices will not only speed up the work, but will also significantly improve the quality of the reinforcement element bundles.
So, knitting rods into a reinforcing structure under the foundation can be done with the following tools:
- handmade crochet hooks, factory-made or homemade;
— inertial crochet hook of semi-automatic action;
- a special knitting gun;
In addition, for the knitting process they learned to use a regular electric drill (which switches to low speed) or a screwdriver with a special homemade hook attachment.
- Knitting gun
The highest quality binding is obtained when using a specialized knitting gun. But this is a fairly expensive tool, and in order to make only one foundation, rarely anyone buys it. Basically, professional builders have it in their set of tools, since, moving from object to object, they cannot waste much time on the already rather lengthy and labor-intensive operation of linking the frame.
Prices for a knitting gun
knitting gun
A convenient and quick way is to use a special knitting gun. Who knows, maybe there is a possibility of renting...
For the pistol, special replacement coils are produced with wire wound on them, with which the device is charged. Many of these tools can be powered by a battery, and since two batteries are usually included with the knitting gun, work can proceed almost uninterruptedly. Another advantage of such a device is that it is not connected by a cable to an outlet, so it can work in autonomous conditions - in the absence of nearby network connection points.
The knitting gun produces connections that are reliable and completely uniform in terms of wire tightening force.
The tying gun grabs the desired area of the metal rods, releases the wire and loops it around them, and then twists the edges of the wire together. The disadvantage, besides the high cost of the device itself, is the inability to work in some hard-to-reach places, where you still have to switch to “manual labor”.
- Crochet hooks
A universal device for tying reinforcement in the foundation frame can be called a crochet hook, since it can be used in the most inaccessible and narrow places. The hooks are small in size, so they are quite convenient for tying rods in a narrow trench under a strip foundation.
A universal tool for tying reinforcement – a hook on the handle
Hooks may vary slightly in appearance and configuration, so when purchasing this tool, you should ask to test it on site. The tool that fits comfortably in the hand, which means it will be more comfortable to work with, is worth choosing for further work. Keep in mind that an uncomfortable hook can quickly cause calluses on your fingers.
You can easily make a convenient hook for yourself
A homemade hook is made like a factory model, repeating its shape. To make it, you can use a sharpened piece of reinforcement, which is bent in a vice and then inserted into the handle. The handle can be made from molten plastic by screwing it onto the fittings, or by placing a thick-walled polymer tube on it, heating it and then cooling it. When cooled, the plastic will press tightly against the fittings, forming a handle convenient for working manipulations.
Another option for a crochet hook, the design of which will significantly speed up the work of installing the frame, is a semi-automatic tool that operates on the inertial principle.
The cost of such a semi-automatic hook is quite affordable, and the work will go much faster and require less effort
The hook itself is located on a kind of leg, which has grooves cut into it like a spiral. There is a return spring mechanism located inside the hook handle.
This tool works as follows: hook loops of wire and pull them up, applying force. At this time, the leg, when leaving the handle, when moving the spiral grooves along the guide protrusions, rotates, making several turns, twisting the two ends of the wire together until the knot stops against the fastened elements of the frame structure. If necessary, the operation is repeated until the required tightening of the unit is achieved. Thus, just one or two forward movements are required to link the point.
A hook made from a steel dowel can be inserted into a screwdriver or drill chuck
A hook attachment installed in a drill or screwdriver will speed up the work with less physical effort. These tools quickly twist the two ends of the wire until they stop, securely fixing the crossed reinforcement together. It is easy to experimentally set the optimal tightening torque on a screwdriver ratchet. It will be more convenient to work with a compact tool, since the trench space for a strip foundation is often very limited. In addition, if you plan to use a conventional electric drill to tie the reinforcement, you will need to stock up on a multi-meter extension cord.
Whatever knitting tool is chosen, the principle of twisting the wire is the same, so its choice depends on the financial capabilities and preferences of the master.
How to knit reinforcement mesh yourself
We have already said above that in this way you can knit reinforcement on the ground. Only straight sections of the mesh are made, the corners are tied after they are lowered into the trench.
Step 1. Prepare pieces of reinforcement. The standard length of the rods is six meters; if possible, there is no need to touch them. If you are afraid that such dina will be difficult to work with, cut them in half.
Rebar cutting
We advise you to start knitting reinforcement for the shortest section of the strip foundation; this will give you the opportunity to gain a little experience and be more confident in handling long rods. It is not recommended to cut them; this increases metal consumption and reduces the strength of the foundation. Let's consider the dimensions of the blanks using the example of a strip foundation 120 cm high and 40 cm wide.
The reinforcement must be filled with concrete on all sides with a thickness of at least 5 centimeters. These are the initial conditions. Taking into account such indicators, the net dimensions of the reinforcement frame should be no more than 110 cm in height (minus 5 cm on each side) and 30 cm in width (minus 5 cm on each side). To knit, you need to add two centimeters on each side for the overlap. This means that the blanks for horizontal jumpers should have a length of 34 cm, the blanks for vertical jumpers should have a length of 144 cm. But you shouldn’t make the frame so high, it’s enough to have a height of 80 cm.
How to knit reinforcement correctly
Step 2. Select a flat area, lay two long rods, and trim their ends.
Step 3. At a distance of ≈ 20 cm from the ends, tie horizontal spacers on both extreme sides. For knitting you need a wire approximately 20 centimeters long. Fold it in half, slide it under the tying point and tighten the wire with the usual twist of a crochet hook. Do not overdo it with force, the wire may not withstand it. The amount of twisting force is determined experimentally.
Step 3. At a distance of approximately 50 centimeters, tie all the remaining horizontal struts one by one. Everything is ready - set the structure aside in a free space and make another frame element in the same way. You have the top and bottom parts, now you need to fasten them together.
Step 4. Next, you should adjust the stops for the two parts of the mesh; you can rest them on any object. The main thing is that the connected elements occupy a stable lateral position; the distance between them should be equal to the height of the knitted reinforcement.
Knitting reinforced frame
Step 5. Attach two vertical spacers at the ends; you already know the dimensions. When the frame begins to more or less resemble the finished product, tie all the other pieces. Take your time and check all sizes. Even though your pieces are the same length, checking the dimensions won't hurt.
Step 6. Using the same algorithm, you need to connect all straight sections of the frame on the ground.
Step 7. Place pads at least five centimeters high at the bottom of the foundation trench; the lower mesh bars will lie on them. Place side supports and set the net in the correct position.
Reinforcement (frame installed in formwork)
Step 8. Take the dimensions of the unknitted corners and joints, prepare pieces of reinforcement to connect the frame into a single structure. Keep in mind that the overlap of the ends of the reinforcement must be at least fifty bar diameters.
Step 9. Tie the bottom turn, then the vertical posts and the top one to them. Check the reinforcement distance to all formwork surfaces.
Knitting reinforcement in corners
The reinforcement is ready, you can start pouring the foundation with concrete.
The need for reinforcement
Often the foundation experiences very uneven loads. This is caused either by heterogeneous soil or structural differences in individual parts of the structure erected on it. In this case, concrete prevents compression of the structure, and metal resists tension. It is in tension zones that cracks most often form, so it is very important to reinforce any foundation, especially a strip foundation. For high-quality reinforcement, in addition to accurate calculations, you only need reinforcement. When constructing private houses or country cottages and garden houses, reinforcement is most often used. Its diameter can vary from 6 to 14 mm. In order to assemble the reinforcement frame, that is, to connect all the rods into one whole structure, knitting wire is used.