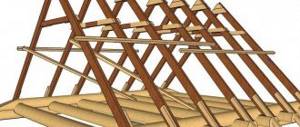
If you decide to install the log house yourself, you need to think about connecting the timber in the corners. You will also need to understand how, if necessary, to join two logs or beams in length and insert a partition.
[toc]
Regardless of what the frame is made of, there are two types of corner joints:
- with a remainder (or release) - this is when there is still some piece of log or timber behind the junction;
- or without any remainder.
When cutting with residue, there is a fairly large waste of material. Each remainder is at least 20-25 cm. These “tails” in one crown take 160-200 cm. The consumption is quite considerable. But on the other hand, such a cutting is called a “warm corner”, precisely because with normal caulking they do not dry out.
The corner in the log house can be with or without remainder
Cutting a log house without residue is more economical in terms of material consumption during the construction stage, but in this option the corner is the most freezing place. Also, with this method of connecting logs and beams in the corner, even small errors greatly affect the quality. Therefore, increased demands are placed on the quality of cutting bowls.
There is a big difference in the technology of constructing a log house from logs and timber. The logs have a round shape and without processing it is impossible to join them tightly. Therefore, a recess is made in the lower or upper crown - a groove, into/on which the next log is laid. This increases the surface of their contact. It is the width of the groove that is the actual thickness of the log wall. How warm the wall will be depends on the shape of the groove and the accuracy of its execution.
With timber everything is different. Since the planed one has almost the same dimensions, and the profiled and glued ones have no “almost”, and their edges are flat, no adjustment or groove is needed. Therefore, the entire assembly of a log house from timber consists of forming joints in the corners. Inter-crown insulation (jute, tow, moss) successfully copes with blocking small inconsistencies. As a result, a log house is built many times faster.
Beam connection - types and features
Houses, bridges, ramps are built from timber material, and decking for warehouses and piers is laid. The material is in demand among landscape designers and interior decorators. In construction, an important role is played by the methods of joining different types and types of materials, the types of their connection in wooden structures. There are different ways to connect timber in building structures:
- Splicing, production of molded structures;
- Construction of walls and partitions;
- Laying flooring;
- Cross stitch;
- Butt joints;
- Connection at any angle.
Price for drank cups
The price for sawing bowls in a profiled beam depends on the complexity of the structure, the cross-section and type of timber, and the complexity of the house structure. You can buy profiled timber with cups as a ready-made kit from any large construction company that produces the material. In large cities the price differs little; we calculated the average and present it in the form of a table:
| A company engaged in cutting cups on profiled bursa | Type of connection | Beam cross-section, mm | Price, rub./m3 |
| LLC "Russian Forest" | four-way | 150x150 | 2850 |
| 200x200 | 3250 | ||
| LLC "Lesmag" | four-way | 150x150 | 3100 |
| 200x200 | 3450 | ||
| LLC "UralLes" | T-shaped | 150x150 | 5300 |
| 200x200 | 6550 | ||
| Kirstroyservis LLC | T-shaped | 150x150 | 6000 |
| 200x200 | 6500 |
You should not expect that by ordering bowl cutting from a construction company you will get impeccable material. The human factor has not been canceled. The only thing worth paying extra for is the complex shape of the bowl for a warmer corner connection.
Length extension
The length of industrially produced timber is determined by GOST 24454-80; of the many sizes of timber, 3- and 6-meter blanks are most in demand. When splicing, the ends of the joined beams are secured in various ways:
- Half-tree connection;
- On the root thorn;
- Straight patch lock;
- Oblique patch lock;
- Oblique cut.
The choice of fastening for the connected beams depends on the tasks at hand. For decking, a straight lock is used; for vertical supports, a half-tree or tenon lock is used; for the construction of 3D structures, oblique locks are used. Locks are reinforced with building brackets, dowels and dowels; bolted fastenings are used for load-bearing supports. In order to maintain the uniformity of the surface texture of the laminated veneer lumber, the length is increased using the toothed connection method or butt joints with a key, and the joints are reinforced with waterproof glue.
The longitudinal installation of timber roof rafters has its own characteristics - it is necessary to take into account the impact of multidirectional loads. For the connection, an oblique cut is used, reinforced with bolted fastening with a diameter of 10-12 mm.
Altitude bonding
When constructing wooden walls and partitions, masonry made from solid timber of natural moisture is reinforced with dowels, staples or “coupling” fastening. The corrugated timber has increased adhesion; reliable adhesion of the crowns is ensured by the tongue-and-groove connection.
The most common construction operation for height bonding is the construction of walls. Dowels with a diameter of 25-30 mm are used as connecting elements; one dowel holds together several crowns. To fix masonry made of corrugated timber, dowels are required 2-3 times less. The dowel connection is reliable and retains its properties throughout the entire period of operation of the structure.
With the help of fastening “on the coupling” they prevent deformation and the formation of cracks when the lumber dries, the screw tie creates an adjustable vertical tension.
Requirements
What properties should the compound have?
- Durability. It is clear that the beam is supported by its own weight, the mass of the floors and roof; however, the connections will have to withstand the inevitable fluctuations in the linear dimensions of the timber with changes in atmospheric humidity and temperature.
Please note: a house built from so-called natural moisture timber is most susceptible to deformation and experiences maximum internal stress. On the contrary, material dried to 16-20% creates a minimum of problems for builders and the owner.
- Tightness. At a minimum, straight and corner joints of the timber should not be blown through: drafts are unlikely to please the residents of the house. The practical conclusion from this requirement is obvious: the more complex the form of the connection, the less likely it is for drafts to occur.
How to fasten beams together across widths
The lumber material is used to make bridge decks, lay floors in freight cars and industrial buildings, and make panels for laying on foundations and soil. Unlike floor laths, timber structures are joined together without the use of a tongue-and-groove lateral connection; this method of installation is called “smooth reveal”. The structures are fastened with construction staples, fixed with 30-40 mm edged boards laid around the perimeter and 100 mm nails, and a screw metal tie is used. This connection allows
disassemble and assemble structures, make temporary flooring.
Reinforced floors are used in warehouses, sports and entertainment complexes. To hold lumber together indoors, synthetic glue is used; when finishing the interior, the timber is fastened with a longitudinal dovetail key.
Cross Lap Knit
Lap knitting is a universal connection of lumber, used when laying walls made of logs and timber. The workpieces are placed at right angles into cut-out grooves; the size of this groove depends on the size of the material used. Such a lock is used in the construction of log houses and ceilings, the construction of bridges, and the construction of canopies. The main methods of cross fastening:
- Half-tree connection;
- Quarter and third wood joint;
- Notch in one row.
The most widespread cross-shaped connection in half a tree is when cutting corners into a bowl; it is used in the construction of utility structures, residential buildings and baths. The structure is reinforced with building brackets, dowels and dowels.
Connecting logs in corners with remainder
First, let's talk about log houses. Recently, they have become popular again, especially in suburban construction: they look attractive and are also natural. Moreover, even despite a significant overconsumption of material, the corners are made with a remainder. These methods of joining logs are traditional. They came to us from our great-grandfathers, this is how they built their houses.
Log house in a bowl
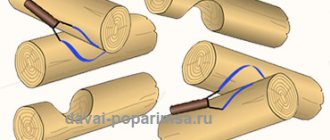
As has already been said, a longitudinal recess is made in each log - a groove. In the corners they are trimmed more, according to the shape of the log lying across. This notch is round in shape, which is why it is called a bowl, and the method of cutting a corner is called a bowl. The second name is “in the oblo”.
Marking the upper and lower bowl
Depending on the location of the bowl, there are upper and lower bowls. The upper bowl is so called because the log rests on top of the crown, clasping the lower one. This connection is also called “clap”. Remember: the bowl is upper, despite the fact that it is formed at the bottom of the log.
The work is carried out in several stages. The log is first placed in the log house and leveled. Then they outline the contours of the groove and the bowl, place it on a flat surface and process it there - cutting the bowls. When the excavation is ready, the log is raised again and placed in place, trying it on. If necessary, they are adjusted (removed again, trimmed where necessary) and only then laid on a compactor (tow, jute, moss). All these movements are compensated by the fact that with this method of cutting, sediment simply flows down the side surfaces of the wall, and they, as a rule, are well protected by several layers of impregnations and paints.
Types of bowls for joining logs in corners
The lower bowl can be molded directly in the log house: all manipulations can be done on the laid crown. When the walls are already raised high, it is very inconvenient to do this if you lack dexterity, so you still have to drag the logs up/down. Perhaps this is why this method is less popular.
It is easier to make a frame into a bowl: it allows you to correct almost all mistakes. In addition, despite all the apparent complexity, it is this type of joining of logs that is easier for beginners to do. All others require more carpentry skill.
How to make a joint from a log frame into the lower bowl is shown in the video below. The explanation is detailed, showing techniques for working with an ax and the full procedure. First you just need to talk about the tool that is used to draw the log. This is a carpenter's trait or scriber.
The device is very similar to a school compass. There is also a sharp stop on one side and a pencil on the other. Just like in a compass, the required distance is fixed with a screw. Having placed the ends at the required distance, the sharp part is guided along the log for which the bowl needs to be cut. Using a pencil, respectively, according to the one in which the groove and bowl will be cut. This produces markings, which are then drawn with a marker. It will become clearer when you see the process of marking the bowl in the video.
Actually, now a video about how to connect logs into the lower bowl. The first part deals with molding the longitudinal groove, the second directly deals with cutting the bowl.
Connection in okhryap
This type of connection consists of two semicircular bowls. In order for a corner folded using this method to be warm, considerable experience is required: even minor errors in the width of the groove or the thickness of the lintel will cause drafts.
Log in okhryap
Knitting log corners
A variation of the cross-shaped connection is the method of fastening the beams together without any residue; in this case, the two sides of the cross-shaped connection have no continuation. This connection is used when laying corners and is called “no residue in the paw.” Cutting a castle without leaving any residue does not require the use of special tools; the construction of a log house using this method is popular among individual developers.
A more complex method of corner mounting is dovetail installation; a dovetail lock is a reliable but complex fastening. Marking and complex cutting of such a connection requires professional skills; the technology is widely used in the construction of low-rise economy class housing.
Cutting logs with corners without residue
As we said earlier, the corners are colder without any residue, but they allow you to significantly save on building materials.
Angle "to the paw"
Among the joints of logs in the corners, the “paw” method is popular. It is easy to implement, and at the same time provides high strength and reliability of the connection. Also, the presence of inclined cuts makes it possible to achieve high tightness. The method has been tested for a long time, even GOST standards have been developed: size tables for each log diameter (see photo).
Table of foot joint sizes for different log diameters
All dimensions are plotted relative to the found middle of the log and a vertical line drawn from it (it is drawn using a plumb line).
Connecting logs without leaving any residue. Angle to paw
The order of work is as follows:
- Find the length of the cut part (called the block). It must be no less than the diameter of the largest log available (in the figure it is marked L). We set this value aside from the edge of the log (let it be 250 mm), draw vertical lines in these places. They will be the boundaries of the idiot.
- Let the diameter of the processed log be 200 mm. From the middle line, ½ of the value of A is set aside. D for a 200 mm log is 141 mm. We divide this value in half and put it on both sides of the center. We draw vertical lines.
- We trim (cut with a chain saw). As a result, you should get the same picture as in figure a).
- We take the appropriate dimensions from the table and mark them on the block.
- We trim off the excess (cut it off). The result should be a figure like in Figure b).
This is what the angle from the logs into the paw looks like (dovetail due to the fact that the connection is in the form of a trapezoid)
All logs are processed in this way one by one. As you can see, the dimensions depend on the diameters of the logs. In order not to have to worry about drawing every time, they make templates from thin plywood according to the diameters of the logs that are available (they label them). Then, having found the middle and made a block, they apply and trace a suitable template. With this order of work, there is less chance of making mistakes, and chopping bowls takes less time.
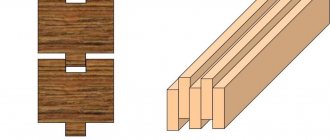
Butt joint of timber
Butt fastenings are the simplest type of connection; the workpieces are fastened at right angles using construction staples or standardized fasteners; the building material is not processed. The technology is used in the construction of temporary buildings, field storage facilities and sheds, and arrangement of work sites. The structures are easy to disassemble, and the lumber can be reused many times.
With the advent of new generation woodworking equipment and laminated lumber, the technology has received innovative development. To strengthen the fastening, a hidden tongue-and-groove lock and a trapezoidal key are used. The castle was called the root thorn; the shape and dimensions of the castle were standardized. The groove and tenon are made on modern milling machines, the reliability of fastening is ensured by high precision processing of workpieces. In such a lock, the tenon is securely fixed inside the workpiece.
Special requirements are imposed on the quality of the material; this method of installing timber is used when working with kiln-dried laminated wood. The corners of cottages and luxury housing are fastened to a secret tenon; the technology is used in the design of facades, interiors, furniture manufacturing, the main advantages of fastening:
- The structures are easy to assemble and disassemble; you can purchase an industrial house disassembled and assemble it yourself;
- The corners of buildings are durable and airtight; this method of assembling corners is called a “warm corner”;
- The front side is not processed, the uniformity of the wood texture and the absence of cuts make the façade of the building attractive;
- The fastening can be strengthened with construction adhesive.
The use of butt fastening on trapezoidal dowels ensures reliable fastening of structures while saving building material.
Working principle of cup cutting machine
[ads1]When cutting cups on profiled timber, use an electric milling cutter, for example, Makita 3612C, AEG 2050, Felisatti RF62/2200VE, Interskol FM-62/2200E or their equivalent.
The cutter contains durable, complex alloy plates that have two sharp edges. In order to reduce the load when working on a cutter, these plates are installed at an angle from the axis of rotation of the cutter. These plates are removable and are secured with screws. This cutter is mounted in a special frame, which can move and adjust the width or height of the lock along the entire cross-section of the beam. A special lifting device makes it possible to adjust the depth of the future cup on a profiled beam and make the depth of the groove lock planned according to the diagram.
The milling machine on the frame is attached to the cleats, on which the beam is already installed in the place where the cup cut is supposed to be placed. At the same time, the frame itself easily moves along the base of the device in the transverse direction. The combined movement of the cutter along and across makes it possible to make a groove of the desired depth and width.
How to count washed down
For each beam width with a different cross-section, it is not possible to make a cut in any form. Otherwise, you can damage the profiled timber or make it brittle at the junction of the corners of the log house.
The formula for calculating such cuts today sounds like this:
H=(M+a):4, where H is the thickness of the groove in the profiled beam, M is the total height of the beam, and is the size of the tenon or groove on the beam.
For example, let’s calculate the cut of a cup for a beam with a cross-section of 150x150 with a lock equal to 12 mm. The calculation will look like this: (150+12):4=40.25 mm.
Processing washed down cups
Processing the cut of the cup cutter should also be carried out using the following technology:
- It is processed to a depth of 15-25 mm of the border of future cutting.
The middle of the future groove is marked and the milling machine is lowered to a pre-calculated depth and the processing operations with the cutter are repeated.
Mounting at any angle
The developer is faced with the need to assemble at an arbitrary angle when constructing roof frames and arched structures. This type of fastening is used when assembling timber logs onto a ridge assembly and connecting them to the mauerlat - a supporting beam laid on the upper crown of the log house. Mounting at an angle also provides for the technology of installing support posts.
When assembling on a ridge run, the ends of the timber logs are placed in the corner as follows:
- Overlapping, the lock is reinforced with a through bolt;
- In half a tree or on a tenon, the fastening is reinforced with metal or wooden overlays. The covers are secured with nails and self-tapping screws.
To insert rafters into the mauerlat, a single notch is made at the desired angle, the fastening unit of each beam is reinforced with bolts and plates.
Vertical supports are cut into half-tree logs or mounted on special metal hinges. The hinged structure is attached to the joists using metal clamps and secured to the supports with self-tapping screws.
Mobile cup cutter
Judging by customer reviews, ready-made factory cups do not always fit in size when assembled and they still have to be modified. To simplify the work, you can buy a manual cup cutter. The price of the machine starts from 35,000 rubles, but by purchasing timber without cups you can save money. Use a manual cup cutter directly while assembling a house or bathhouse from profiled timber. The saw can be measured on the spot and adjusted to the desired shape.
In this case, the connection in the warm corner is more airtight. If the production of profiled timber is small, then purchasing such a hand tool will be more profitable. Moreover, the work can be performed to the same quality as on a powerful milling machine. Depending on the type of frieze chosen, you can make different cuts for the cup. The number of cutters depends on the brand of cup cutter and its power. The more fezes included in the package and the higher the power of the equipment, the higher the price of the cup cutter.